ASTM D892-23
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Foaming Characteristics of Lubricating Oils
Standard Test Method for Foaming Characteristics of Lubricating Oils
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The tendency of oils to foam can be a serious problem in systems such as high-speed gearing, high-volume pumping, and splash lubrication. Inadequate lubrication, cavitation, and overflow loss of lubricant can lead to mechanical failure. This test method is used in the evaluation of oils for such operating conditions.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the foaming characteristics of lubricating oils at 24 °C and 93.5 °C. Means of empirically rating the foaming tendency and the stability of the foam are described.
1.2 WARNING—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous substance that can cause serious medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been demonstrated to be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Use caution when handling mercury and mercury-containing products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for additional information. The potential exists that selling mercury or mercury-containing products, or both, is prohibited by local or national law. Users must determine legality of sales in their location.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see Sections 7, 8, and 9.1.1.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D892 − 23 British Standard 5092
Standard Test Method for
1
Foaming Characteristics of Lubricating Oils
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D892; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the foam- 2.1 ASTM Standards:
ing characteristics of lubricating oils at 24 °C and 93.5 °C. D445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent
Means of empirically rating the foaming tendency and the and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscos-
stability of the foam are described. ity)
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid
1.2 WARNING—Mercury has been designated by many
Fuels, and Lubricants
regulatory agencies as a hazardous substance that can cause
D6082 Test Method for High Temperature Foaming Charac-
serious medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been dem-
teristics of Lubricating Oils
onstrated to be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials.
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
Use caution when handling mercury and mercury-containing
E128 Test Method for Maximum Pore Diameter and Perme-
products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
ability of Rigid Porous Filters for Laboratory Use
for additional information. The potential exists that selling
E1272 Specification for Laboratory Glass Graduated Cylin-
mercury or mercury-containing products, or both, is prohibited
ders
by local or national law. Users must determine legality of sales
in their location.
3. Terminology
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1 Definitions:
standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer
provided for information only and are not considered standard.
to Terminology D4175.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
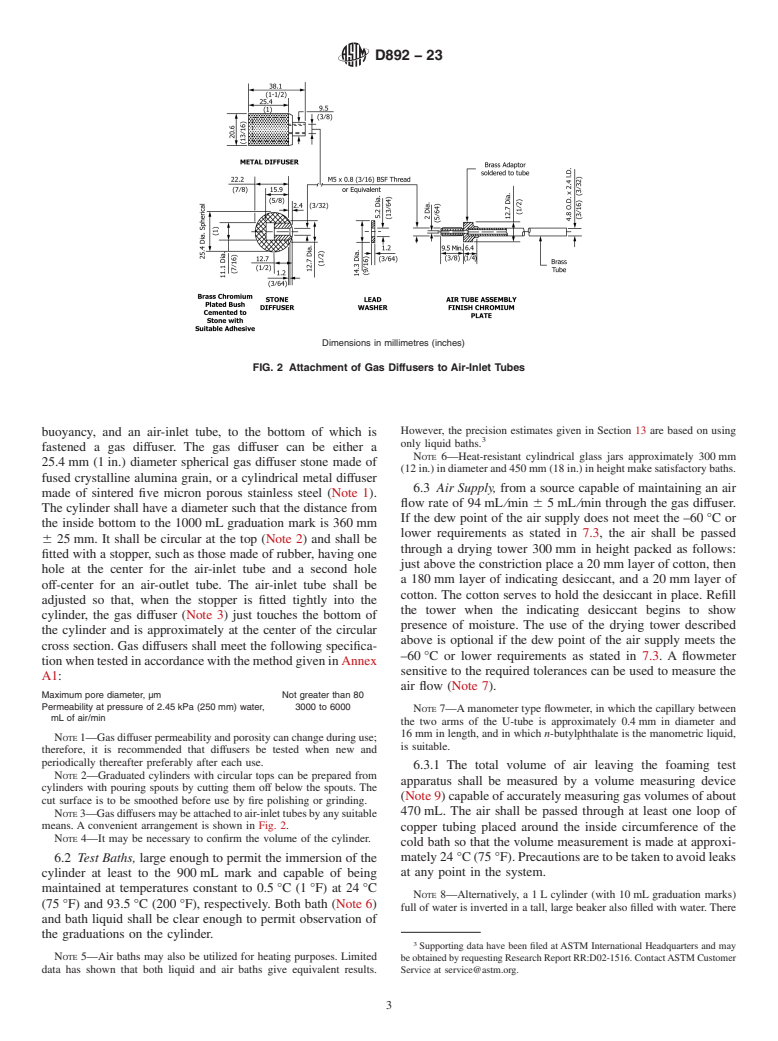
3.1.2 diffuser, n—for gas, a device for dispersing gas into a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
fluid.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.2.1 Discussion—In this test method the diffuser may be
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
made of either metallic or non-metallic materials.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1.3 entrained air (or gas), n—in liquids, a two-phase
For specific warning statements, see Sections 7, 8, and 9.1.1.
mixture of air (or gas) dispersed in a liquid in which the liquid
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
is the major component on a volumetric basis.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1.3.1 Discussion—Entrained air (or gas) may form micro
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
size bubbles in liquids that are not uniformly dispersed and that
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
may coalesce to form larger bubbles below or at the surface
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
which break or form foam.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3.1.4 foam, n—in liquids, a collection of bubbles formed in
or on the surface of a liquid in which the air or gas is the major
component on a volumetric basis.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of Committee D02 on Petroleum
Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
2
mittee D02.06 on Analysis of Liquid Fuels and Lubricants. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2023. Published October 2023. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
ɛ1
approved in 1946. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as D892 – 18 . Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI:10.1520/D0892-23. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D892 − 23
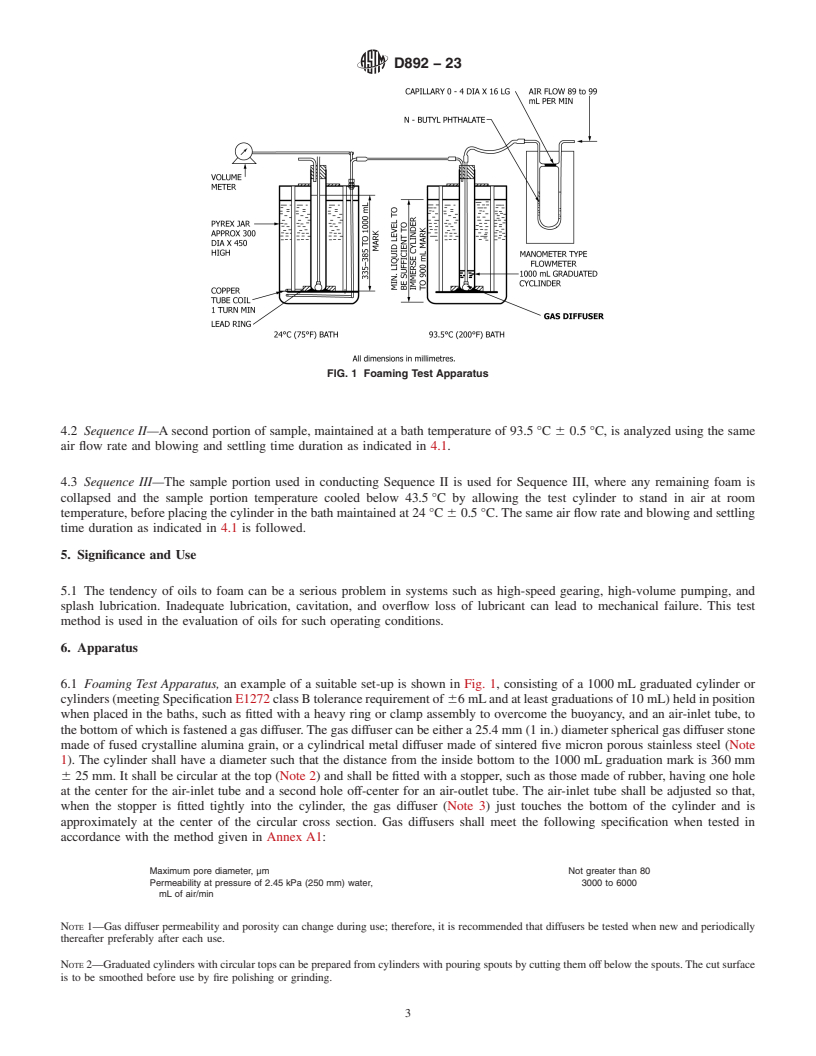
FIG. 1 Foaming Test Apparatus
3.1.5 lubricant, n—any material interposed between two 4. Summary of Test Method
surfaces that reduces friction or wear between them. D6082
4.1 Sequence I—A portio
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D892 − 18 D892 − 23 British Standard 5092
Standard Test Method for
1
Foaming Characteristics of Lubricating Oils
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D892; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1
ε NOTE—Editorially removed joint designation in February 2023.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the foaming characteristics of lubricating oils at 24 °C and 93.5 °C. Means of
empirically rating the foaming tendency and the stability of the foam are described.
1.2 WARNING—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous materialsubstance that can cause
central nervous system, kidney and liver damage. serious medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, may has been demonstrated to be
hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should be taken Use caution when handling mercury and mercury
containing mercury-containing products. See the applicable product Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for details and EPA’s
website—http://www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htm—for additional information. Users should be aware (SDS) for additional informa-
tion. The potential exists that selling mercury and/or mercury containing products into your state or country may be prohibited by
law.or mercury-containing products, or both, is prohibited by local or national law. Users must determine legality of sales in their
location.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are provided for
information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see Sections 7, 8, and 9.1.1.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity)
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants
D6082 Test Method for High Temperature Foaming Characteristics of Lubricating Oils
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.06
on Analysis of Liquid Fuels and Lubricants.
Current edition approved April 15, 2018Oct. 1, 2023. Published May 2018October 2023. Originally approved in 1946. Last previous edition approved in 20132018 as
ɛ1
D892 – 13D892 – 18 . DOI:10.1520/D0892-18E01.DOI:10.1520/D0892-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D892 − 23
E128 Test Method for Maximum Pore Diameter and Permeability of Rigid Porous Filters for Laboratory Use
E1272 Specification for Laboratory Glass Graduated Cylinders
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D4175.
3.1.2 diffuser, n—for gas, a device for dispersing gas into a fluid.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—
In this test method the diffuser may be made of either metallic or non-metallic materials.
3.1.3 entrained air (or gas), n—in liquids, a two-phase mixture of air (or gas) dispersed in a liquid in which the liquid is the major
component on a volumetric basis.
3.
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.