ASTM C305-20
(Practice)Standard Practice for Mechanical Mixing of Hydraulic Cement Pastes and Mortars of Plastic Consistency
Standard Practice for Mechanical Mixing of Hydraulic Cement Pastes and Mortars of Plastic Consistency
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This practice is intended for use in the mechanical mixing of pastes and mortars for the testing of hydraulic cements.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the mechanical mixing of hydraulic cement pastes and mortars of plastic consistency.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C305 − 20 American Association State
Highway and Transportation Officials Standard
AASHTO No.: T162
Standard Practice for
Mechanical Mixing of Hydraulic Cement Pastes and Mortars
1
of Plastic Consistency
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C305; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3.1.1 The terms in this practice are defined in Terminology
C125 and Terminology C219.
1.1 This practice covers the mechanical mixing of hydraulic
cement pastes and mortars of plastic consistency.
4. Significance and Use
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
4.1 This practice is intended for use in the mechanical
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
mixing of pastes and mortars for the testing of hydraulic
standard.
cements.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5. Apparatus
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5.1 Mixer—The mixer shall be an electrically driven me-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
chanical mixer of the epicyclic type, which imparts both a
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
planetary and a revolving motion to the mixer paddle. The
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
mixer shall have a minimum of two controlled speeds. (Rheo-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
stat adjustment of speed is not acceptable.) The first, or slow
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
speed shall revolve the paddle at a rate of 140 6 5 r/min, with
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
a planetary motion of approximately 62 r/min. The second
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
speed shall revolve the paddle at a rate of 285 6 10 r/min, with
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
a planetary motion of approximately 125 r/min. The electric
1
motor shall be at least 124 W ( ⁄6 hp). The mixer shall be
2. Referenced Documents
equipped with either an adjustment screw which is an integral
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
part of the mixer or a clearance adjustment bracket such as the
C125 Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Ag-
one shown in Fig. 1 (Note 1) to provide clearance between the
gregates
lower end of the paddle and the bottom of the bowl that is not
C219 Terminology Relating to Hydraulic and Other Inor-
greater than 2.5 mm but not less than 0.8 mm (Note 2) when
ganic Cements
the bowl is in the mixing position.
C511 Specification for Mixing Rooms, Moist Cabinets,
NOTE 1—When the bracket is in the proper position beneath the motor
Moist Rooms, and Water Storage Tanks Used in the
housing, the lugs are to the front and facing upward and the heads of the
Testing of Hydraulic Cements and Concretes
adjustment screws are to the rear and facing downward in the path of the
C778 Specification for Standard Sand
sliding frame that holds the bowl. It is intended that the bracket be
fastened at the front housing connection by inserting replacement screws
3. Terminology
onanappropriatesizeupwardthroughtheopeningineachlugandintothe
existing threaded holes in the bottom of the motor housing. The original
3.1 Definitions:
stops for the sliding frame are to be filed down if they prevent the frame
from coming in contact with the adjustment screws.
NOTE 2—This is the approximate diameter of a grain of 20 to 30 sand
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C01 on Cement and as described in Specification C778.
is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C01.22 on Workability.
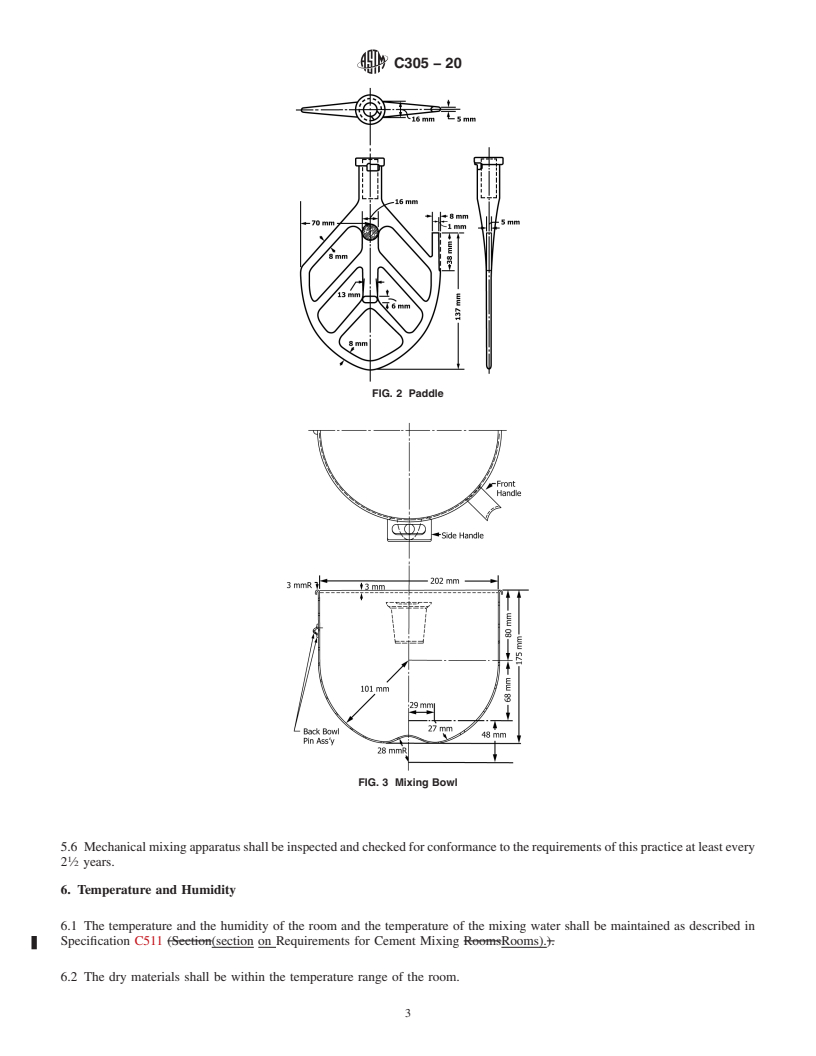
5.2 Paddle—The paddle shall be readily removable, made
Current edition approved July 15, 2020. Published August 2020. Originally
of stainless steel, and shall conform to the basic design shown
approved in 1953. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as C305 – 14. DOI:
10.1520/C0305-20.
in Fig. 2.The dimensions of the paddle shall be such that when
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
in the mixing position the paddle outline conforms to the
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
contour of the bowl used with the mixer, and the clearance
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. betweencorrespondingpointsontheedgeofthepaddleandthe
*A Su
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C305 − 14 C305 − 20 American Association State
Highway and Transportation Officials Standard
AASHTO No.: T162
Standard Practice for
Mechanical Mixing of Hydraulic Cement Pastes and Mortars
1
of Plastic Consistency
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C305; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This practice covers the mechanical mixing of hydraulic cement pastes and mortars of plastic consistency.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C125 Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Aggregates
C219 Terminology Relating to Hydraulic and Other Inorganic Cements
C511 Specification for Mixing Rooms, Moist Cabinets, Moist Rooms, and Water Storage Tanks Used in the Testing of Hydraulic
Cements and Concretes
C778 Specification for Standard Sand
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 The terms in this practice are defined in Terminology C125 and Terminology C219.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This practice is intended for use in the mechanical mixing of pastes and mortars for the testing of hydraulic cements.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C01 on Cement and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C01.22 on Workability.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2014July 15, 2020. Published September 2014August 2020. Originally approved in 1953. Last previous edition approved in 20132014
as C305 – 13.14. DOI: 10.1520/C0305-14.10.1520/C0305-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C305 − 20
5. Apparatus
5.1 Mixer—The mixer shall be an electrically driven mechanical mixer of the epicyclic type, which imparts both a planetary and
a revolving motion to the mixer paddle. The mixer shall have a minimum of two controlled speeds. (Rheostat adjustment of speed
is not acceptable.) The first, or slow speed shall revolve the paddle at a rate of 140 6 5 r/min, with a planetary motion of
approximately 62 r/min. The second speed shall revolve the paddle at a rate of 285 6 10 r/min, with a planetary motion of
1
approximately 125 r/min. The electric motor shall be at least 124 W ( ⁄6 hp). The mixer shall be equipped with either an adjustment
screw which is an integral part of the mixer or a clearance adjustment bracket such as the one shown in Fig. 1 (Note 1) to provide
clearance between the lower end of the paddle and the bottom of the bowl that is not greater than 2.5 mm but not less than 0.8
mm (Note 2) when the bowl is in the mixing position.
NOTE 1—When the bracket is in the proper position beneath the motor housing, the lugs are to the front and facing upward and the heads of the adjustment
screws are to the rear and facing downward in the path of the sliding frame that holds the bowl. It is intended that the bracket be fastened at the front
housing connection by inserting replacement screws on an appropriate size upward through the opening in each lug and into the existing threaded holes
in the bottom of the motor housing. The original stops for the sliding frame are to be filed down if they prevent the frame from coming in contact with
the adjustment screws.
NOTE 2—This is th
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.