ASTM A937/A937M-12
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Interlaminar Resistance of Insulating Coatings Using Two Adjacent Test Surfaces
Standard Test Method for Determining Interlaminar Resistance of Insulating Coatings Using Two Adjacent Test Surfaces
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is particularly suitable for quality control in the application of insulating coatings. This test method measures the interlaminar resistance of insulating coatings, as defined in 3.1.4. Interlaminar resistance is the measure of the insulating quality of the coating. Interlaminar resistance is reported in units of kΩ.
5.2 The interlaminar resistance determined in accordance with this test method is not the same quantity determined by Test Method A717/A717M.
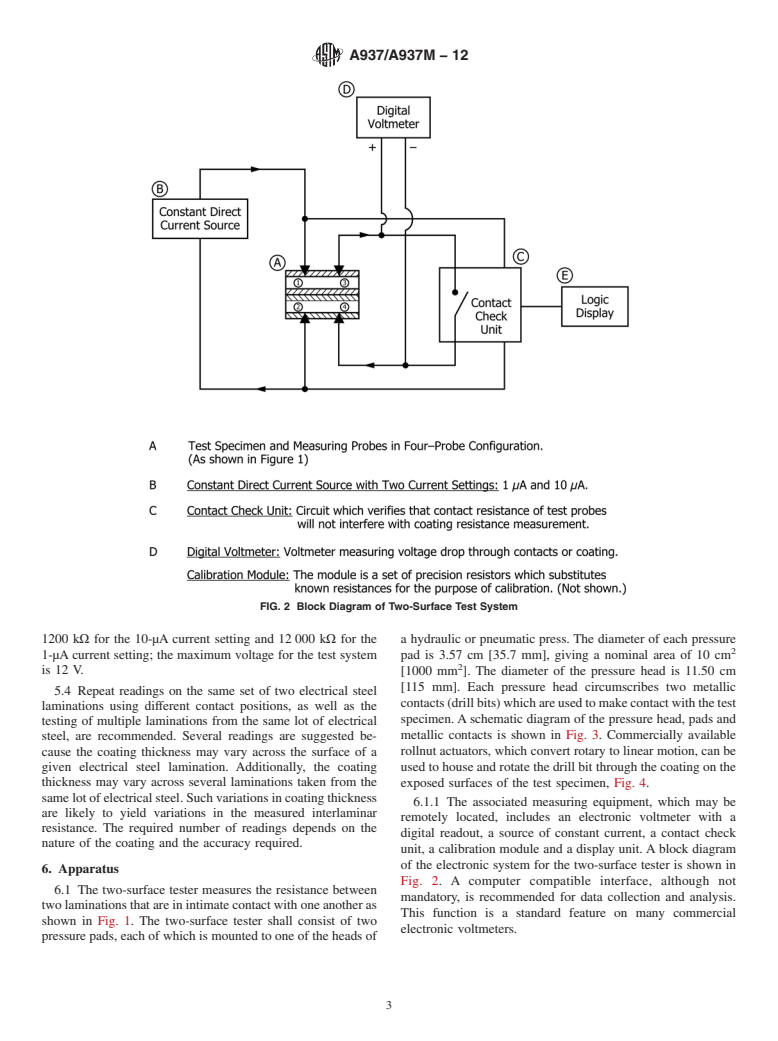
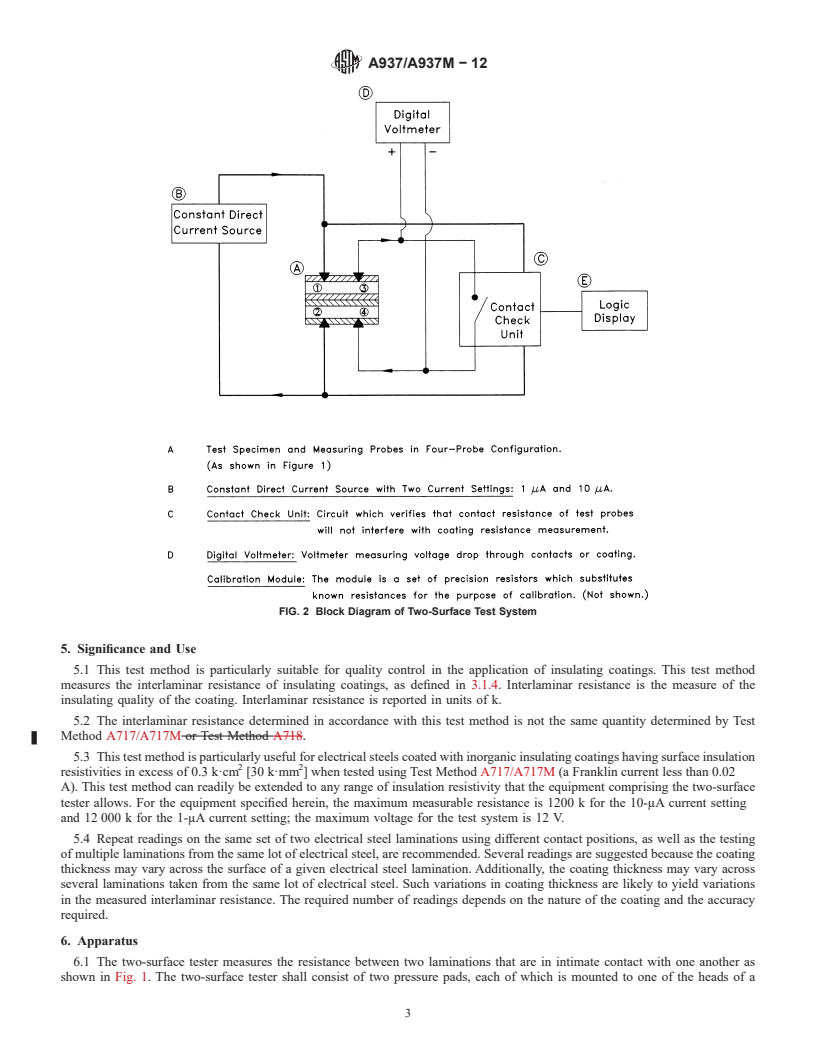
5.3 This test method is particularly useful for electrical steels coated with inorganic insulating coatings having surface insulation resistivities in excess of 0.3 kΩ·cm2 [30 kΩ·mm2] when tested using Test Method A717/A717M (a Franklin current less than 0.02 A). This test method can readily be extended to any range of insulation resistivity that the equipment comprising the two-surface tester allows. For the equipment specified herein, the maximum measurable resistance is 1200 kΩ for the 10-μA current setting and 12 000 kΩ for the 1-μA current setting; the maximum voltage for the test system is 12 V.
5.4 Repeat readings on the same set of two electrical steel laminations using different contact positions, as well as the testing of multiple laminations from the same lot of electrical steel, are recommended. Several readings are suggested because the coating thickness may vary across the surface of a given electrical steel lamination. Additionally, the coating thickness may vary across several laminations taken from the same lot of electrical steel. Such variations in coating thickness are likely to yield variations in the measured interlaminar resistance. The required number of readings depends on the nature of the coating and the accuracy required.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a means of testing the interlaminar resistance of electrically insulating coatings as applied to adjacent laminations of flat-rolled electrical steel, under predetermined conditions of voltage, pressure and temperature. It indicates the effectiveness of surface coatings on electrical sheet steels for limiting interlaminar losses in electrical machinery. The interlaminar resistance is measured directly in units of resistance (kΩ).
1.2 This test method is particularly useful for, but not limited to, electrical steels coated with inorganic insulating coatings.
1.3 The values and equations stated in customary (cgs-emu and inch-pound) or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within this standard, SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A937/A937M −12
Standard Test Method for
Determining Interlaminar Resistance of Insulating Coatings
1
Using Two Adjacent Test Surfaces
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA937/A937M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers a means of testing the inter- 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
laminar resistance of electrically insulating coatings as applied 3.1.1 bad contact—acontactwhichresultsinavoltagedrop
to adjacent laminations of flat-rolled electrical steel, under in excess of 0.6 V as described in 6.1.3.
predeterminedconditionsofvoltage,pressureandtemperature.
3.1.2 exposed test surface—the insulating top surface of the
It indicates the effectiveness of surface coatings on electrical
top lamination or the insulating bottom surface of the bottom
sheet steels for limiting interlaminar losses in electrical ma-
lamination of the test specimen.
chinery. The interlaminar resistance is measured directly in
3.1.3 four-terminal measuring technique, often referred to
units of resistance (kΩ).
as four-probe measuring technique—a common method to
1.2 This test method is particularly useful for, but not
measure resistance when a high degree of accuracy is re-
3
limited to, electrical steels coated with inorganic insulating
quired. In this standard, the circuit configuration for this
coatings.
technique is referred to as a four-probe configuration.Inthe
two-surface tester, this configuration features two probes con-
1.3 The values and equations stated in customary (cgs-emu
nected to the top lamination test surface and two probes
and inch-pound) or SI units are to be regarded separately as
connected to the bottom lamination test surface. One of the
standard. Within this standard, SI units are shown in brackets.
probesineachpaircarriesthemeasuringcurrent,andtheother
Thevaluesstatedineachsystemmaynotbeexactequivalents;
providesacontactforthevoltagemeasurement.Becauseofthe
therefore,eachsystemshallbeusedindependentlyoftheother.
extremely high impedance of the measuring circuit, very little
Combining values from the two systems may result in noncon-
current flows through the voltage contacts, and thus very little
formance with this standard.
voltage is produced across the contacts to influence the true
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
reading,thatis,anyeffectfromcontactresistanceisavoidedor
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
reduced to a negligible amount. The two-surface tester has
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
provision to check the integrity of the contacts made between
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
the probes and the test surfaces.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1.4 interlaminar resistance—theaverageresistanceoftwo
adjacent insulating surfaces in contact with each other, under
2. Referenced Documents
conditions specified in this standard.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.5 surface insulation resistivity—the effective resistivity
A34/A34MPractice for Sampling and Procurement Testing
of a single insulating layer tested between applied bare metal
of Magnetic Materials
contacts and the base metal of the insulated test specimen, as
A717/A717MTestMethodforSurfaceInsulationResistivity
per Test Method A717/A717M.
of Single-Strip Specimens
3.1.6 test specimen—two electrical steel laminations, each
having a minimum size of 25×25 cm [250×250 mm] and
1 each having an electrically insulating coating on both sides.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A06 on
MagneticPropertiesandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeA06.01onTest The two electrical steel laminations are placed one on top of
Methods.
the other for the interlaminar resistance measurement, Fig. 1.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2012. Published December 2012. Originally
3.1.7 two-surface tester—the apparatus used in this test
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as A937/A937M–06.
DOI: 10.1520/A0937_A0937M-12.
method.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Harris,F.K., Electrical Measurements,RobertE.KriegerPublishingCompany,
the ASTM website. Huntington, New York, 1975, pp. 220–224.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
--------------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A937/A937M − 06 A937/A937M − 12
Standard Test Method for
Determining Interlaminar Resistance of Insulating Coatings
1
Using Two Adjacent Test Surfaces
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A937/A937M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers a means of testing the interlaminar resistance of electrically insulating coatings as applied to
adjacent laminations of flat-rolled electrical steel, under predetermined conditions of voltage, pressure and temperature. It indicates
the effectiveness of surface coatings on electrical sheet steels for limiting interlaminar losses in electrical machinery. The
interlaminar resistance is measured directly in units of resistance (kΩ).
1.2 This test method is particularly useful for, but not limited to, electrical steels coated with inorganic insulating coatings.
1.3 The values and equations stated in customary (cgs-emu and inch-pound) or SI units are to be regarded separately as
standard. Within this standard, SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents;
therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in
nonconformance with this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A34/A34M Practice for Sampling and Procurement Testing of Magnetic Materials
A717/A717M Test Method for Surface Insulation Resistivity of Single-Strip Specimens
3
A718 Test Method for Surface Insulation Resistivity of Multi-Strip Specimens
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 bad contact—a contact which results in a voltage drop in excess of 0.6 V as described in 6.1.3.
3.1.2 exposed test surface—the insulating top surface of the top lamination or the insulating bottom surface of the bottom
lamination of the test specimen.
3.1.3 four-terminal measuring technique, often referred to as four-probe measuring technique—a common method to measure
3
resistance when a high degree of accuracy is required. In this standard, the circuit configuration for this technique is referred to
as a four-probe configuration. In the two-surface tester, this configuration features two probes connected to the top lamination test
surface and two probes connected to the bottom lamination test surface. One of the probes in each pair carries the measuring
current, and the other provides a contact for the voltage measurement. Because of the extremely high impedance of the measuring
circuit, very little current flows through the voltage contacts, and thus very little voltage is produced across the contacts to influence
the true reading, that is, any effect from contact resistance is avoided or reduced to a negligible amount. The two-surface tester
has provision to check the integrity of the contacts made between the probes and the test surfaces.
3.1.4 interlaminar resistance—the average resistance of two adjacent insulating surfaces in contact with each other, under
conditions specified in this standard.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A06 on Magnetic Properties and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A06.01 on Test Methods.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2006Nov. 1, 2012. Published November 2006 December 2012. Originally approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 20012006
as A937/A937M – 01.A937/A937M–06. DOI: 10.1520/A0937_A0937M-06. 10.1520/A0937_A0937M-12.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Harris, F. K., Electrical Measurements, Robert E. Krieger Publishing Company, Huntington, New York, 1975, pp. 220–224.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A937/A937M
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.