ASTM E768-99(2018)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Preparing and Evaluating Specimens for Automatic Inclusion Assessment of Steel
Standard Guide for Preparing and Evaluating Specimens for Automatic Inclusion Assessment of Steel
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Inclusion ratings done either manually using Test Methods E45 or automatically using Practice E1122 or E1245 are influenced by the quality of specimen preparation. This guide provides examples of proven specimen preparation methods that retain inclusions in polished steel specimens.
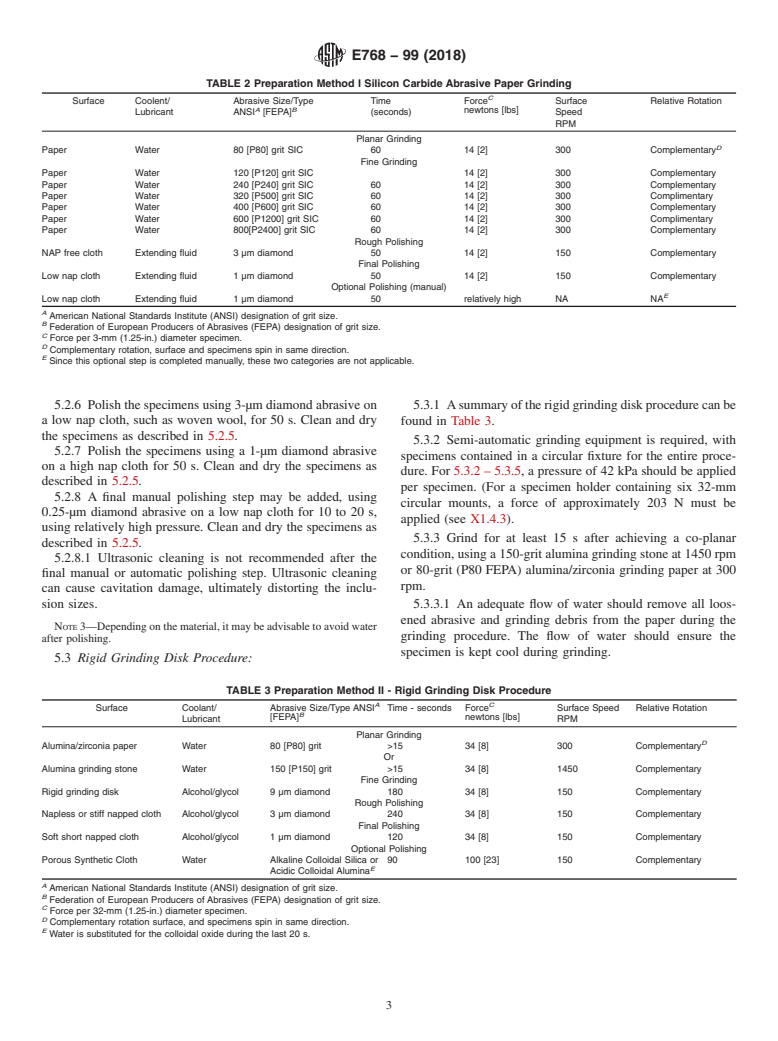
4.2 This guide provides a procedure to determine if the prepared specimens are of suitable quality for subsequent rating of inclusions. None of these methods should be construed as defining or establishing specific procedures or limits of acceptability for any steel grade.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide2 covers two preparation methods for steel metallographic specimens that will be analyzed for nonmetallic inclusions with automatic image analysis (AIA) equipment. The two methods of preparation are offered as accepted methods used to retain nonmetallic inclusions in steel. This guide does not limit the user to these methods.
1.2 A procedure to test the suitability of the prepared specimen for AIA inclusion work, using differential interference contrast (DIC), is presented.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E768 − 99 (Reapproved 2018)
Standard Guide for
Preparing and Evaluating Specimens for Automatic
1
Inclusion Assessment of Steel
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E768; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E1245Practice for Determining the Inclusion or Second-
2 Phase Constituent Content of Metals byAutomatic Image
1.1 This guide covers two preparation methods for steel
Analysis
metallographicspecimensthatwillbeanalyzedfornonmetallic
5
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
inclusions with automatic image analysis (AIA) equipment.
ADJE0768 Differential Interference Contrast Magnification
The two methods of preparation are offered as accepted
100× and 500× (6 micrographs)
methods used to retain nonmetallic inclusions in steel. This
guide does not limit the user to these methods.
3. Terminology
1.2 A procedure to test the suitability of the prepared
3.1 Definitions:
specimen for AIA inclusion work, using differential interfer-
3.1.1 For definitions used in this practice, refer to Termi-
ence contrast (DIC), is presented.
nology E7.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as 3.1.2 differential interference contrast microscopy—a com-
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
prehensive definition appears in Guide E883, section 11.8.
standard.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.2.1 rigid grinding disk—a non-fabric support surface,
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
such as a composite of metal/ceramic or metal/polymer,
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
charged with an abrasive (usually 6 to 15-µm diamond
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
particles), and used as the fine grinding operation in a metal-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
lographic preparation procedure.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4. Significance and Use
2. Referenced Documents
4.1 Inclusion ratings done either manually usingTest Meth-
3
ods E45 or automatically using Practice E1122 or E1245 are
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E3Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens influenced by the quality of specimen preparation. This guide
provides examples of proven specimen preparation methods
E7Terminology Relating to Metallography
E45Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of that retain inclusions in polished steel specimens.
Steel
4.2 This guide provides a procedure to determine if the
E883Guide for Reflected–Light Photomicrography
prepared specimens are of suitable quality for subsequent
E1122Practice for Obtaining JK Inclusion Ratings Using
rating of inclusions. None of these methods should be con-
4
Automatic Image Analysis (Withdrawn 2006)
strued as defining or establishing specific procedures or limits
of acceptability for any steel grade.
1
ThisguideisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeE04onMetallography
5. Preparation Methods
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E04.01 on Specimen Preparation.
5.1 Background:
Current edition approved May 1, 2018. Published June 2018. Originally
ɛ1
approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as E768–99(2010) .
5.1.1 The inclusions in the plane of polish must be fully
DOI: 10.1520/E0768-99R18.
preserved and clearly visible. Preparation should not produce
2
Supporting data have been filed atASTM International Headquarters and may
excessive relief around the perimeter of the inclusions that
be obtained by requesting Research Report RR:E04-1002.
3
would exaggerate the size and number of inclusions on the
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
5
the ASTM website. Acolored plate, consisting of six micrographs that illustrate the use of DIC in
4
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on determining a properly prepared sample (at 100x and 500x), is available from
www.astm.org. ASTM Headquarters. Order Adjuct: ADJE0768.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E768 − 99 (2018)
TABLE 1 Comparison of ANSI (CAMI) versus FEPA versus
plane of polish. In many cases
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.