ASTM F1470-09
(Guide)Standard Practice for Fastener Sampling for Specified Mechanical Properties and Performance Inspection
Standard Practice for Fastener Sampling for Specified Mechanical Properties and Performance Inspection
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Sampling shall be selected in a random manner, ensuring that any unit in the lot has an equal chance of being chosen. Sampling should not be localized by selections being taken from the top of a container or from only one container of multicontainer lots.
The purchaser should be aware of the supplier's quality assurance system. This can be accomplished by auditing the supplier's quality system, if qualified auditors are available, or by third-party assessment certification, such as provided by ISO/TS 16949, or ISO 9001.
SCOPE
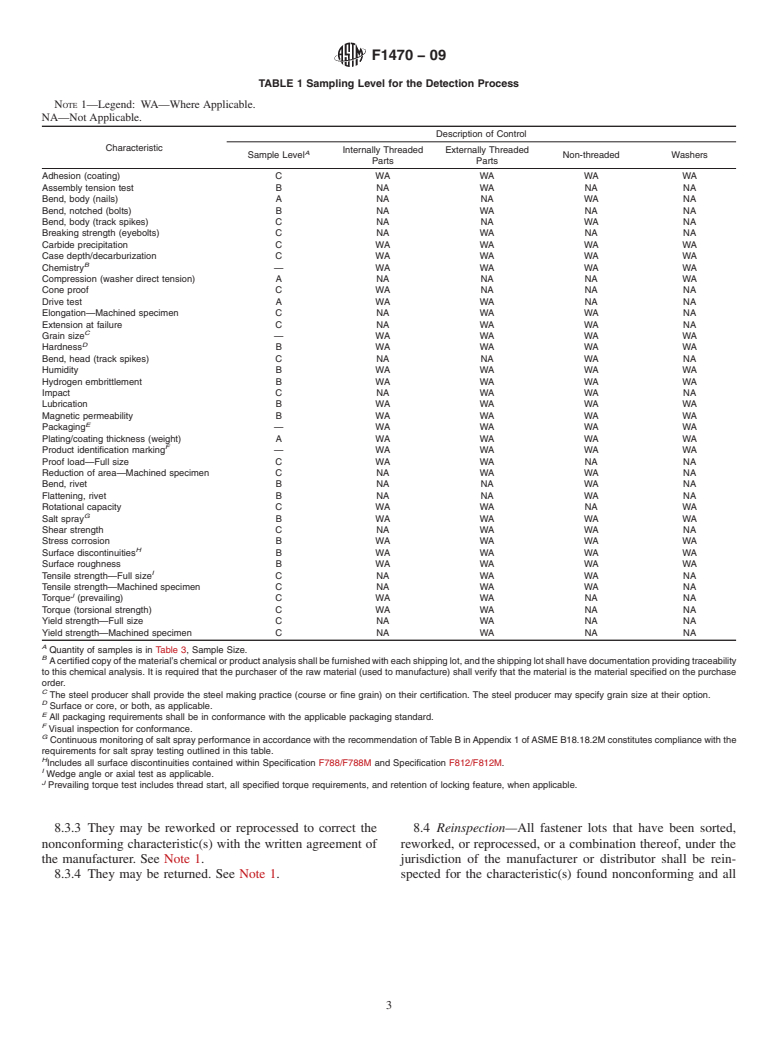
1.1 This practice provides sampling methods for determining how many fasteners to include in a random sample in order to determine the acceptability or disposition of a given lot of fasteners.
1.2 This practice is for mechanical properties, physical properties, performance properties, coating requirements, and other quality requirements specified in the standards of ASTM Committee F16. Dimensional and thread criteria sampling plans are the responsibility of ASME Committees B18.1 and B18.18.2M-B18.18.6M.
1.3 This practice provides for two sampling plans: one designated the “detection process,” as described in Terminology F 1789, and one designated the “prevention process,” as described in Terminology F 1789.
1.4 This practice is intended to be used as either a Final Inspection Plan for manufacturers, or as a Receiving Inspection Plan for purchasers/users. It is not valid for third-party qualification testing.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F1470 −09
StandardPractice for
Fastener Sampling for Specified Mechanical Properties and
1
Performance Inspection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1470; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Throughoutthispracticetheterms detectionand preventionapplytoqualitycontrolsystems.Abrief
description of both is provided to assist the purchaser in the application of this practice.
The detection system relies on inspection as the primary means of controlling the quality of
furnished material. Methods include in-process and final inspection. In-process inspection is typically
performed by the individual performing the process and generally includes a first-piece inspection by
someone other than the operator. Quality-control inspection may perform audit inspections on the
process output during the course of the production run. In addition, a final inspection is performed by
quality control inspectors according to a prescribed sample plan. The other sample plans utilize zero
defects as their acceptance criteria.
The prevention system uses advanced quality planning in addition to many of the techniques used
in the detection system. Quality planning incorporates a systems approach to quality control that
focuses on defect prevention and continual improvement. In addition, Statistical Process Control
(SPC) is usually applied to control the process, to achieve process stability and improve the capability
by reducing the variability.
2
ISO 9001, ISO/TS 16949, ASQ Q9001, and Guide F2688 quality system standards, or a
combination thereof, are models that may be used in establishing a prevention-based quality system.
1. Scope 1.4 This practice is intended to be used as either a Final
InspectionPlanformanufacturers,orasaReceivingInspection
1.1 This practice provides sampling methods for determin-
Plan for purchasers/users. It is not valid for third-party quali-
ing how many fasteners to include in a random sample in order
fication testing.
to determine the acceptability or disposition of a given lot of
fasteners.
2. Referenced Documents
1.2 This practice is for mechanical properties, physical 3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
properties, performance properties, coating requirements, and
F1789 Terminology for F16 Mechanical Fasteners
other quality requirements specified in the standards ofASTM
F788/F788M Specification for Surface Discontinuities of
Committee F16. Dimensional and thread criteria sampling
Bolts, Screws, and Studs, Inch and Metric Series
plans are the responsibility of ASME Committees B18.1 and
F812/F812M Specification for Surface Discontinuities of
B18.18.2M-B18.18.6M.
Nuts, Inch and Metric Series
1.3 This practice provides for two sampling plans: one
F2688 Guide for System-Based, Customer-Centered Quality
designated the “detection process,” as described in Terminol-
Plan for Manufacturers
ogy F1789, and one designated the “prevention process,” as
2.2 ASME Standards:
described in Terminology F1789.
ASME B18.18.1 Inspection and QualityAssurance for Gen-
eral Purpose Fasteners
ASME B18.18.2M Inspection and Quality Assurance for
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F16 on Fasteners
High-Volume Machine Assembly Fasteners
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F16.93 on Quality Assurance
Provisions for Fasteners.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2009. Published January 2009. Originally
3
approved in 1993. Last previous edition approved 2002 as F1470–02. DOI: For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
10.1520/F1470-09. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
2
A practice for developing a quality management system that does not require Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
third party certification. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1470−09
ASME B18.18.3M Inspection and Quality Assurance for 7. Acceptance Criteria
4
Special Purpose Fasteners
7.1 The acceptance criteria for Table 3 is to accept the lot if
ASME B18.18.5M Inspection and Quality Assurance Plan
zero nonconforming parts are detected in the random sample
4
Requiring In-Process Inspection and Controls
and reject the lot if at least one nonconforming part is detected
ASME B18.18.6M Quality Assurance Plan for Fasteners
in the random sample.
4
Produced in Third Party Accreditation System
2.3 ASQ Standards:
8. Disposition of Nonconf
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:F 1470–02
Standard Guide for Designation: F 1470 – 09
Standard Practice for
Fastener Sampling for Specified Mechanical Properties and
1
Performance Inspection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1470; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Throughout this guidepractice the terms detection and prevention apply to quality control systems.
Abrief description of both is provided to assist the purchaser in the application of this guide. practice.
The detection system relies on inspection as the primary means of controlling the quality of
furnished material. Methods include in-process and final inspection. In-process inspection is typically
performed by the individual performing the process and generally includes a first-piece inspection by
someone other than the operator. Quality-control inspection may perform audit inspections on the
process output during the course of the production run. In addition, a final inspection is performed by
quality control inspectors according to a prescribed sample plan. The other sample plans utilize zero
defects as their acceptance criteria.
The prevention system uses advanced quality planning in addition to many of the techniques used
in the detection system. Quality planning incorporates a systems approach to quality control that
focuses on defect prevention and continual improvement. In addition, Statistical Process Control
(SPC) is usually applied to control the process, thereby reducing to achieve process stability and
improve the variability of capability by reducing the output.variability.
2
The ISO 9000 ISO 9001, ISO/TS 16949, QS 9000ASQ Q9001, and theASQ Q9000Guide F 2688,
quality system standards, or a combination thereof, are models that may be used in establishing a
prevention-based quality system.
1. Scope
1.1This guide provides sampling methods for determining how many fasteners to include in a random sample in order to
determine the acceptability or disposition of a given lot of fasteners.
1.2This guide is for mechanical properties, physical properties, coating requirements, and other quality requirements specified
in the standards of ASTM Committee F16. Dimensional and thread criteria sampling plans are the responsibility of ASME
Committee B18.
1.3This guide provides for two sampling plans: one designated the “detection process,” as described inTerminology F1789, and
one designated the “prevention process,” as described in Terminology F1789.
1.1 This practice provides sampling methods for determining how many fasteners to include in a random sample in order to
determine the acceptability or disposition of a given lot of fasteners.
1.2 This practice is for mechanical properties, physical properties, performance properties, coating requirements, and other
quality requirements specified in the standards of ASTM Committee F16. Dimensional and thread criteria sampling plans are the
responsibility of ASME Committees B18.1 and B18.18.2M-B18.18.6M.
1.3 This practice provides for two sampling plans: one designated the “detection process,” as described inTerminology F 1789,
and one designated the “prevention process,” as described in Terminology F 1789.
1
This guidepractice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F16 on Fasteners and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F16.93 on Quality Assurance
Provisions for Fasteners.
Current edition approved April 10, 2002.Jan. 1, 2009. Published May 2002.January 2009. Originally published as F1470–93.approved in 1993. Last previous edition
approved 2002 as F 1470–012.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.08.
2
A practice for developing a quality management system that does not require third party certification.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F 1470 – 09
1.4 This practice is intended to be used as either a Final Inspection Plan for manufacturers, or as a Receiving Inspection Plan
for purchasers/users. It is not valid for third-party qualification testing.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
F1789 Terminology for F16 Mechanical Fasteners F 1789 Terminology for F16 Mechanical Fasteners
F 788/F 788M Specification for Surface Discontinuities of Bol
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:F 1470–02
Standard Guide for Designation: F 1470 – 09
Standard Practice for
Fastener Sampling for Specified Mechanical Properties and
1
Performance Inspection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1470; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Throughout this guidepractice the terms detection and prevention apply to quality control systems.
Abrief description of both is provided to assist the purchaser in the application of this guide. practice.
The detection system relies on inspection as the primary means of controlling the quality of
furnished material. Methods include in-process and final inspection. In-process inspection is typically
performed by the individual performing the process and generally includes a first-piece inspection by
someone other than the operator. Quality-control inspection may perform audit inspections on the
process output during the course of the production run. In addition, a final inspection is performed by
quality control inspectors according to a prescribed sample plan. The other sample plans utilize zero
defects as their acceptance criteria.
The prevention system uses advanced quality planning in addition to many of the techniques used
in the detection system. Quality planning incorporates a systems approach to quality control that
focuses on defect prevention and continual improvement. In addition, Statistical Process Control
(SPC) is usually applied to control the process, thereby reducing to achieve process stability and
improve the variability of capability by reducing the output.variability.
2
The ISO 9000 ISO 9001, ISO/TS 16949, QS 9000ASQ Q9001, and theASQ Q9000Guide F 2688,
quality system standards, or a combination thereof, are models that may be used in establishing a
prevention-based quality system.
1. Scope
1.1This guide provides sampling methods for determining how many fasteners to include in a random sample in order to
determine the acceptability or disposition of a given lot of fasteners.
1.2This guide is for mechanical properties, physical properties, coating requirements, and other quality requirements specified
in the standards of ASTM Committee F16. Dimensional and thread criteria sampling plans are the responsibility of ASME
Committee B18.
1.3This guide provides for two sampling plans: one designated the “detection process,” as described inTerminology F1789, and
one designated the “prevention process,” as described in Terminology F1789.
1.1 This practice provides sampling methods for determining how many fasteners to include in a random sample in order to
determine the acceptability or disposition of a given lot of fasteners.
1.2 This practice is for mechanical properties, physical properties, performance properties, coating requirements, and other
quality requirements specified in the standards of ASTM Committee F16. Dimensional and thread criteria sampling plans are the
responsibility of ASME Committees B18.1 and B18.18.2M-B18.18.6M.
1.3 This practice provides for two sampling plans: one designated the “detection process,” as described inTerminology F 1789,
and one designated the “prevention process,” as described in Terminology F 1789.
1
This guidepractice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F16 on Fasteners and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F16.93 on Quality Assurance
Provisions for Fasteners.
Current edition approved April 10, 2002.Jan. 1, 2009. Published May 2002.January 2009. Originally published as F1470–93.approved in 1993. Last previous edition
approved 2002 as F 1470–012.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.08.
2
A practice for developing a quality management system that does not require third party certification.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F 1470 – 09
1.4 This practice is intended to be used as either a Final Inspection Plan for manufacturers, or as a Receiving Inspection Plan
for purchasers/users. It is not valid for third-party qualification testing.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
F1789 Terminology for F16 Mechanical Fasteners F 1789 Terminology for F16 Mechanical Fasteners
F 788/F 788M Specification for Surface Discontinuities of Bol
...











Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.