ASTM D4625-03
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Distillate Fuel Storage Stability at 43°C (110°F)
Standard Test Method for Distillate Fuel Storage Stability at 43°C (110°F)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a method for evaluating the inherent storage stability of distillate fuels having flash points above 38°C (100°F) and 90 % distilled points below 340°C (644°F).
Note 1—ASTM specification fuels falling within the scope of this test method are Specification D 396, Grade Nos. 1 and 2; Specification D 975, Grades 1-D and 2-D; and Specification D 2880, Grades 1-GT and 2-GT.
1.2 This test method is not suitable for quality control testing but, rather it is intended for research use to shorten storage time relative to that required at ambient storage temperatures.
1.3 Appendix X1 presents additional information about storage stability and the correlation of Test Method D 4625 results with sediment formation in actual field storage.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: D 4625 – 03
Designation: 378/87
Standard Test Method for
1
Middle Distillate Fuel Storage Stability at 43°C (110°F)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4625; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope D 975 Specification for Diesel Fuel Oils
D 2880 Specification for Gas Turbine Fuel Oils
1.1 This test method covers a method for evaluating the
D 4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
inherent storage stability of distillate fuels having flash points
Petroleum Products
above 38°C (100°F) and 90 % distilled points below 340°C
(644°F).
3. Terminology
NOTE 1—ASTM specification fuels falling within the scope of this test
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
method are Specification D 396, Grade Nos. 1 and 2; Specification D 975,
3.1.1 adherent insolubles, n—gums formed during storage
Grades 1-D and 2-D; and Specification D 2880, Grades 1-GT and 2-GT.
which remain tightly attached to the walls of the vessel.
1.2 This test method is not suitable for quality control
3.1.2 filterable insolubles, n—solids formed during storage
testing but, rather it is intended for research use to shorten
which can be removed from the fuel by filtration.
storage time relative to that required at ambient storage
3.1.3 inherent storage stability, n—of middle distillate
temperatures.
fuel—the resistance to change in storage in contact with air, but
1.3 Appendix X1 presents additional information about
in the absence of other environmental factors such as water, or
storage stability and the correlation of Test Method D 4625
reactive metallic surfaces and dirt.
results with sediment formation in actual field storage.
3.1.4 total insolubles, n—sum of the filterable insolubles
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
plus the adherent insolubles.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.1 Four-hundred millilitre volumes of filtered fuel are aged
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
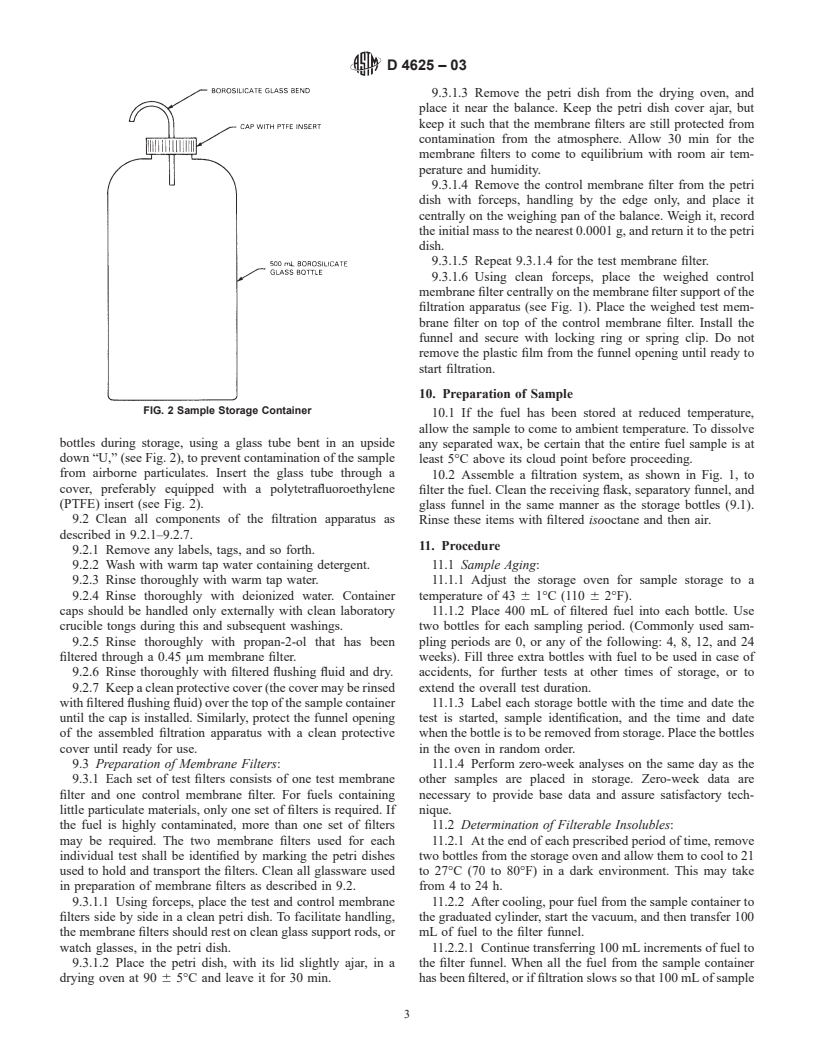
by storage in borosilicate glass containers at 43°C (110°F) for
periods of 0, 4, 8, 12, 18, and 24 weeks. After aging for a
2. Referenced Documents
selected time period, a sample is removed from storage, cooled
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
to room temperature, and analyzed for filterable insolubles and
D 381 Test Method for Existent Gum in Fuels by Jet
for adherent insolubles.
Evaporation
5. Significance and Use
D 396 Specification for Fuel Oils
5.1 Fuel oxidation and other degradative reactions leading
to formation of sediment (and color) are mildly accelerated by
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on the test conditions, compared to typical storage conditions. Test
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
results have been shown to predict storage stability more
D02.14 on Stability and Cleanliness of Liquid Fuels.
reliably than other more accelerated tests. See Appendix X1 for
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2003. Published December 2003. Originally
information on the correlation of test results with actual field
approved in 1986. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as D 4625–92(1998).
This test method was adopted as a joint ASTM/IP standard in 1986.
storage.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
5.2 Because the storage periods are long (4 to 24 weeks), the
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
test method is not suitable for quality control testing, but does
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. provide a tool for research on storage properties of fuels.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4625–03
FIG. 1 Schematic of Filtration System
5.3 Because environmental effects and the materials and Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society where
3
nature of tank construction affect storage stability, the results such specifications are available. Other grades may be used,
obtained by this test are not necessarily the same as those provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently
obtained during storage in a specific field storage situatio
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.