ASTM E92-82(1997)e3
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Vickers Hardness of Metallic Materials
Standard Test Method for Vickers Hardness of Metallic Materials
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the Vickers hardness of metallic materials, using applied loads of 1 kgf to 120 kgf, the verification of Vickers hardness testing machines (Part B), and the calibration of standardized hardness test blocks (Part C). Two general classes of standard tests are recognized:
1.1.1 Verification, Laboratory, or Referee Tests , where a high degree of accuracy is required.
1.1.2 Routine Tests , where a somewhat lower degree of accuracy is permissible.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
e3
Designation: E 92 – 82 (Reapproved 1997)
Standard Test Method for
Vickers Hardness of Metallic Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 92; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
e NOTE—Section 27 was added editorially in October 1997.
e NOTE—The term load was changed to force editorially throughout in May 1999.
e NOTE— Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6 were editorially revised in April 2000.
1. Scope E 140 Hardness Conversion Tables for Metals (Relationship
Between Brinell Hardness, Vickers Hardness, Rockwell
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the Vickers
Hardness, Rockwell Superficial Hardness, Knoop Hard-
hardness of metallic materials, using applied forces of 1 kgf to
ness, and Seleroscope Hardness)
120 kgf, the verification of Vickers hardness testing machines
E 384 Test Method for Microhardness of Materials
(Part B), and the calibration of standardized hardness test
blocks (Part C). Two general classes of standard tests are
3. Terminology
recognized:
3.1 Vickers hardness number, HV—a number related to the
1.1.1 Verification, Laboratory, or Referee Tests, where a
applied force and the surface area of the permanent impression
high degree of accuracy is required.
made by a square-based pyramidal diamond indenter having
1.1.2 Routine Tests, where a somewhat lower degree of
included face angles of 136° (see Fig. 1 and Table 1), computed
accuracy is permissible.
from the equation:
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
2 2
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
HV 5 2P sin ~a/2!/d 5 1.8544P/d (1)
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
where:
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
P = force, kgf,
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
d = mean diagonal of impression, mm, and
a = face angle of diamond = 136°.
2. Referenced Documents
3.2 Vickers hardness test—an indentation hardness test
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3 using calibrated machines to force a square-based pyramidal
E 4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
diamond indenter having specified face angles, under a prede-
termined force, into the surface of the material under test and
to measure the diagonals of the resulting impression after
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E28 on
Mechanical Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E28.06 on
removal of the force.
Indentation Hardness Testing.
3.2.1 Vickers hardness tests are made at test forces of 1 kgf
Current edition approved July 30, 1982. Published December 1982. Originally
to 120 kgf.
published as E 92 – 52 T. Last previous edition E 92 – 72 (1977).
A procedure covering Vickers tests using applied forces of 1 gf to 1000 gf (1 3.2.2 For practical purposes the Vickers hardness number is
kgf) may be found in Test Method E 384, Test Method for Microhardness of
constant when a square-based diamond pyramid with a face
Materials, appearing in the Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
angle of 136° is used with applied forces of 5 kgf and higher.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
E92
FIG. 1 Vickers Hardness Test (see Table 1)
TABLE 1 Symbols and Designations Associated with Fig. 1
Number Symbol Designation
1 . Angle at the vertex of the pyramidal in-
denter (136°)
2 P Test force in kilograms-force
3 d Arithmetic mean of the two diagonals d
and d
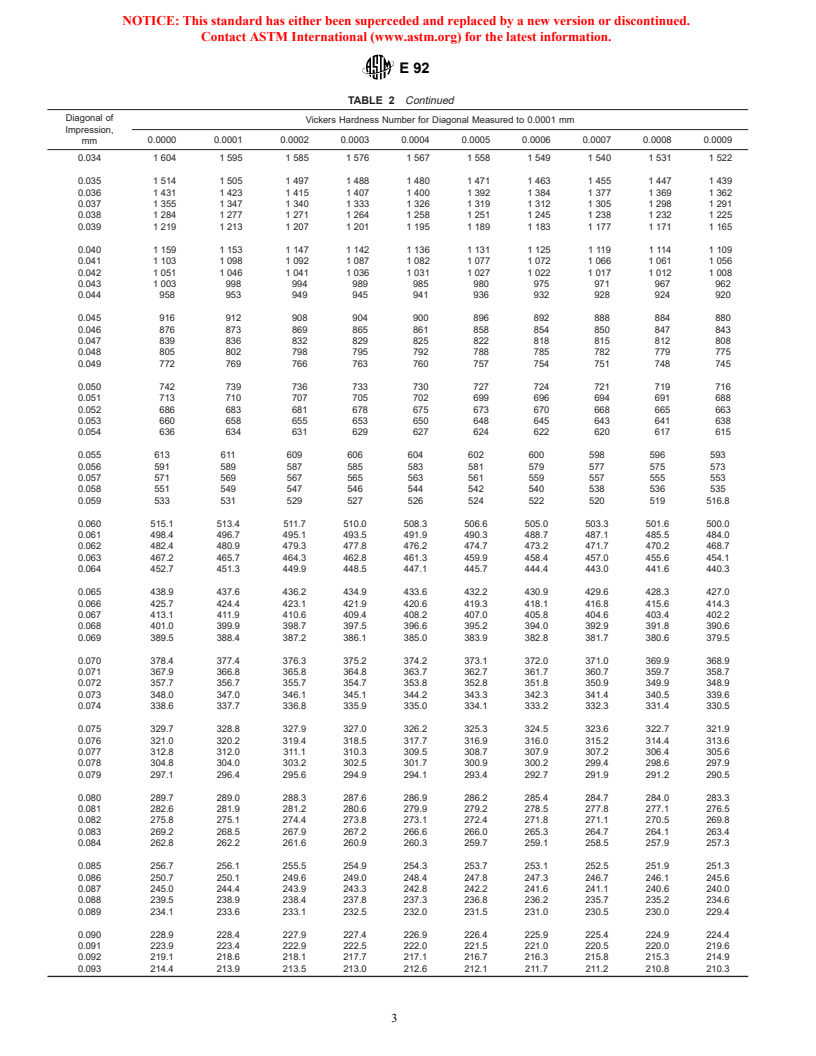
TABLE 2 Vickers Hardness Numbers
(Diamond, 136° Face Angle, force of 1 kgf)
Diagonal of
Vickers Hardness Number for Diagonal Measured to 0.0001 mm
Impression,
0.0000 0.0001 0.0002 0.0003 0.0004 0.0005 0.0006 0.0007 0.0008 0.0009
mm
0.005 74 170 71 290 68 580 66 020 63 590 61 300 59 130 57 080 55 120 53 270
0.006 51 510 49 840 48 240 46 720 45 270 43 890 42 570 41 310 40 100 38 950
0.007 37 840 36 790 35 770 34 800 33 860 32 970 32 100 31 280 30 480 29 710
0.008 28 970 28 260 27 580 26 920 26 280 25 670 25 070 24 500 23 950 23 410
0.009 22 890 22 390 21 910 21 440 20 990 20 550 20 120 19 710 19 310 18 920
0.010 18 540 18 180 17 820 17 480 17 140 16 820 16 500 16 200 15 900 15 610
0.011 15 330 15 050 14 780 14 520 14 270 14 020 13 780 13 550 13 320 13 090
0.012 12 880 12 670 12 460 12 260 12 060 11 870 11 680 11 500 11 320 11 140
0.013 10 970 10 810 10 640 10 480 10 330 10 170 10 030 9 880 9 737 9 598
0.014 9 461 9 327 9 196 9 068 8 943 8 820 8 699 8 581 8 466 8 353
0.015 8 242 8 133 8 026 7 922 7 819 7 718 7 620 7 523 7 428 7 335
0.016 7 244 7 154 7 066 6 979 6 895 6 811 6 729 6 649 6 570 6 493
0.017 6 416 6 342 6 268 6 196 6 125 6 055 5 986 5 919 5 853 5 787
0.018 5 723 5 660 5 598 5 537 5 477 5 418 5 360 5 303 5 247 5 191
0.019 5 137 5 083 5 030 4 978 4 927 4 877 4 827 4 778 4 730 4 683
0.020 4 636 4 590 4 545 4 500 4 456 4 413 4 370 4 328 4 286 4 245
0.021 4 205 4 165 4 126 4 087 4 049 4 012 3 975 3 938 3 902 3 866
0.022 3 831 3 797 3 763 3 729 3 696 3 663 3 631 3 599 3 567 3 536
0.023 3 505 3 475 3 445 3 416 3 387 3 358 3 329 3 301 3 274 3 246
0.024 3 219 3 193 3 166 3 140 3 115 3 089 3 064 3 039 3 015 2 991
0.025 2 967 2 943 2 920 2 897 2 874 2 852 2 830 2 808 2 786 2 764
0.026 2 743 2 722 2 701 2 681 2 661 2 641 2 621 2 601 2 582 2 563
0.027 2 544 2 525 2 506 2 488 2 470 2 452 2 434 2 417 2 399 2 382
0.028 2 365 2 348 2 332 2 315 2 299 2 283 2 267 2 251 2 236 2 220
0.029 2 205 2 190 2 175 2 160 2 145 2 131 2 116 2 102 2 088 2 074
0.030 2 060 2 047 2 033 2 020 2 007 1 993 1 980 1 968 1 955 1 942
0.031 1 930 1 917 1 905 1 893 1 881 1 869 1 857 1 845 1 834 1 822
0.032 1 811 1 800 1 788 1 777 1 766 1 756 1 745 1 734 1 724 1 713
0.033 1 703 1 693 1 682 1 672 1 662 1 652 1 643 1 633 1 623 1 614
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
E92
TABLE 2 Continued
Diagonal of Vickers Hardness Number for Diagonal Measured to 0.0001 mm
Impression,
mm 0.0000 0.0001 0.0002 0.0003 0.0004 0.0005 0.0006 0.0007 0.0008 0.0009
0.034 1 604 1 595 1 585 1 576 1 567 1 558 1 549 1 540 1 531 1 522
0.035 1 514 1 505 1 497 1 488 1 480 1 471 1 463 1 455 1 447 1 439
0.036 1 431 1 423 1 415 1 407 1 400 1 392 1 384 1 377 1 369 1 362
0.037 1 355 1 347 1 340 1 333 1 326 1 319 1 312 1 305 1 298 1 291
0.038 1 284 1 277 1 271 1 264 1 258 1 251 1 245 1 238 1 232 1 225
0.039 1 219 1 213 1 207 1 201 1 195 1 189 1 183 1 177 1 171 1 165
0.040 1 159 1 153 1 147 1 142 1 136 1 131 1 125 1 119 1 114 1 109
0.041 1 103 1 098 1 092 1 087 1 082 1 077 1 072 1 066 1 061 1 056
0.042 1 051 1 046 1 041 1 036 1 031 1 027 1 022 1 017 1 012 1 008
0.043 1 003 998 994 989 985 980 975 971 967 962
0.044 958 953 949 945 941 936 932 928 924 920
0.045 916 912 908 904 900 896 892 888 884 880
0.046 876 873 869 865 861 858 854 850 847 843
0.047 839 836 832 829 825 822 818 815 812 808
0.048 805 802 798 795 792 788 785 782 779 775
0.049 772 769 766 763 760 757 754 751 748 745
0.050 742 739 736 733 730 727 724 721 719 716
0.051 713 710 707 705 702 699 696 694 691 688
0.052 686 683 681 678 675 673 670 668 665 663
0.053 660 658 655 653 650 648 645 643 641 638
0.054 636 634 631 629 627 624 622 620 617 615
0.055 613 611 609 606 604 602 600 598 596 593
0.056 591 589 587 585 583 581 579 577 575 573
0.057 571 569 567 565 563 561 559 557 555 553
0.058 551 549 547 546 544 542 540 538 536 535
0.059 533 531 529 527 526 524 522 520 519 516.8
0.060 515.1 513.4 511.7 510.0 508.3 506.6 505.0 503.3 501.6 500.0
0.061 498.4 496.7 495.1 493.5 491.9 490.3 488.7 487.1 485.5 484.0
0.062 482.4 480.9 479.3 477.8 476.2 474.7 473.2 471.7 470.2 468.7
0.063 467.2 465.7 464.3 462.8 461.3 459.9 458.4 457.0 455.6 454.1
0.064 452.7 451.3 449.9 448.5 447.1 445.7 444.4 443.0 441.6 440.3
0.065 438.9 437.6 436.2 434.9 433.6 432.2 430.9 429.6 428.3 427.0
0.066 425.7 424.4 423.1 421.9 420.6 419.3 418.1 416.8 415.6 414.3
0.067 413.1 411.9 410.6 409.4 408.2 407.0 405.8 404.6 403.4 402.2
0.068 401.0 399.9 398.7 397.5 396.6 395.2 394.0 392.9 391.8 390.6
0.069 389.5 388.4 387.2 386.1 385.0 383.9 382.8 381.7 380.6 379.5
0.070 378.4 377.4 376.3 375.2 374.2 373.1 372.0 371.0 369.9 368.9
0.071 367.9 366.8 365.8 364.8 363.7 362.7 361.7 360.7 359.7 358.7
0.072 357.7 356.7 355.7 354.7 353.8 352.8 351.8 350.9 349.9 348.9
0.073 348.0 347.0 346.1 345.1 344.2 343.3 342.3 341.4 340.5 339.6
0.074 338.6 337.7 336.8 335.9 335.0 334.1 333.2 332.3 331.4 330.5
0.075 329.7 328.8 327.9 327.0 326.2 325.3 324.5 323.6 322.7 321.9
0.076 321.0 320.2 319.4 318.5 317.7 316.9 316.0 315.2 314.4 313.6
0.077 312.8 312.0 311.1 310.3 309.5 308.7 307.9 307.2 306.4 305.6
0.078 304.8 304.0 303.2 302.5 301.7 300.9 300.2 299.4 298.6 297.9
0.079 297.1 296.4 295.6 294.9 294.1 293.4 292.7 291.9 291.2 290.5
0.080 289.7 289.0 288.3 287.6 286.9 286.2 285.4 284.7 284.0 283.3
0.081 282.6 281.9 281.2 280.6 279.9 279.2 278.5 277.8 277.1 276.5
0.082 275.8 275.1 274.4 273.8 273.1 272.4 271.8 271.1 270.5 269.8
0.083 269.2 268.5 267.9 267.2 266.6 266.0 265.3 264.7 264.1 263.4
0.084 262.8 262.2 261.6 260.9 260.3 259.7 259.1 258.5 257.9 257.3
0.085 256.7 256.1 255.5 254.9 254.3 253.7 253.1 252.5 251.9 251.3
0.086 250.7 250.1 249.6 249.0 248.4 247.8 247.3 246.7 246.1 245.6
0.087 245.0 244.4 243.9 243.3 242.8 242.2 241.6 241.1 240.6 240.0
0.088 239.5 238.9 238.4 237.8 237.3 236.8 236.2 235.7 235.2 234.6
0.089 234.1 233.6 233.1 232.5 232.0 231.5 231.0 230.5 230.0 229.4
0.090 228.9 228.4 227.9 227.4 226.9 226.4 225.9 225.4 224.9 224.4
0.091 223.9 223.4 222.9 222.5 222.0 221.5 221.0 220.5 220.0 219.6
0.092 219.1 218.6 218.1 217.7 217.1 216.7 216.3 215.8 215.3 214.9
0.093 214.4 213.9 213.5 213.0 212.6 212.1 211.7 211.2 210.8 210.3
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
E92
TABLE 2 Continued
Diagonal of Vickers Hardness Number for Diagonal Measured to 0.0001 mm
Impression,
mm 0.0000 0.0001 0.0002 0.0003 0.0004 0.0005 0.0006 0.0007 0.0008 0.0009
0.094 209.9 209.4 209.0 208.5 208.1 207.6 207.2 206.8 206.3 205.9
0.095 205.5 205.0 204.6 204.2 203.8 203.3 202.9 202.5 202.1 201.6
0.096 201.2 200.8 200.4 200.0 199.5 199.1 198.7 198.3 197.9 197.5
0.097 197.1 196.7 196.3 195.9 195.5 195.1 194.7 194.3 193.9 193.5
0.098 193.1 192.7 192.3 191.9 191.5 191.1 190.7 190.4 190.0 189.6
0.099 189.2 188.8 188.4 188.1 187.7 187.3 186.9 186.6 186.2 185.5
indicating the duration of forceing when the latter differs from 10 to 15 s,
At lower test forces the Vickers hardness may be force-
which is the normal force time. Example:
dependent. In Table 2 are given the Vickers hardness numbers
440 HV 30 = Vickers hardness of 440 measured under a force of 30 kgf
for a test force of 1 kgf. For obtaining hardness numbers when
applied for 10 to 15 s.
other test forces are used, the Vickers hardness number
440 HV 30/20 = Vickers hardness of 440 measured under a force of 30
obtained from Table 2 is multiplied by the test force in
kgf applied for 20 s.
kilograms-force (Table 3).
3.3 verification—checking or testing to assure conformance
NOTE 1—The Vickers hardness number is followed by the symbol HV
with the specification.
with a suffix number denoting the force and second suffix number
3.4 calibration—determination of the values of the signifi-
cant parameters by comparison with values indicated by a
TABLE 3 Decimal Point Finder for Use with Table 2
reference instrument or by a set of reference standards.
An example of determination of hardness numbers follows the table.
Diagonal Length, Vickers Hardness (HV),
A. GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND TEST
mm 1-kgf Force
PROCEDURE FOR VICKERS HARDNESS TESTS
0.005 74 200
0.006 51 500
4. Apparatus
0.007 37 800
4.1 Testing Machine—Equipment for Vickers hardness test-
0.008 29 000
0.009 22 900
ing usually consists of a testing machine which supports the
0.010 18 540
specimen and permits the indenter and the specimen to be
0.020 4 640
0.030 2 060 brought into contact gradually and smoothly under a predeter-
0.040 1 159
mined force, which is applied for a fixed period of time. The
0.050 742
design of the machine should be such that no rocking or lateral
0.060 515
0.070 378 movement of the indenter or specimen is permitted while the
0.080 290
force is being applied or removed. A measuring microscope is
0.090 229
usually mounted on the machine in such a manner that the
0.100 185.4
0.200 46.4 impression in the specimen may be readily located in the
0.300 20.6
optical field.
0.400 11.6
4.2 Indenter:
0.500 7.42
0.600 5.15 4.2.1 The indenter shall be a highly polished, pointed,
0.700 3.78
square-based pyramidal diamond with face angles of 136° 6
0.800 2.90
30 min.
0.900 2.29
1.000 1.85 4.2.2 All four faces of the indenter shall be equally inclined
1.100 1.53
to the axis of the indenter (within 630 min) and meet at a sharp
1.200 1.29
point, that is, the line of junction between opposite faces shall
1.300 0.10
1.400 0.946
not be more than 0.001 mm in length as shown in Fig. 2.
1.500 0.824
4.2.3 The diamond should be examined periodically and if it
1.600 0.724
is loose in the mounting material, chipped, or cracked, it should
1.700 0.642
1.800 0.572
be discarded or reconditioned.
1.900 0.514
2.000 0.464
NOTE 2—The condition of the point of the indenter is of considerable
importance where the test force is light and the impression is small. It is
Example—Using a 50-kgf test force, the average measured diagonal length
recommended that the point be periodically checked by examining an
= 0.644 mm.
impression made in a polished steel block. Under a magnification of 6003
In Table 2 read:
or more, using a vertical illuminator, any chipping or rounding of the point
HV = 447 at 0.0644-mm diagonal length at 1-kgf force.
can be detected and the extent of the defect measured with a filar
micrometer. It is recommended that a diamond pyramid indenter should
Using Table 3 determine:
not be used for tests in which the maximum length of such a defect
exceeds 5% of the length of the impression diagonal.
HV = 4.47 at 0.644-mm diagonal length at 1-kgf force.
4.3
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.