ASTM D6361/D6361M-98(2015)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Selecting Cleaning Agents and Processes
Standard Guide for Selecting Cleaning Agents and Processes
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
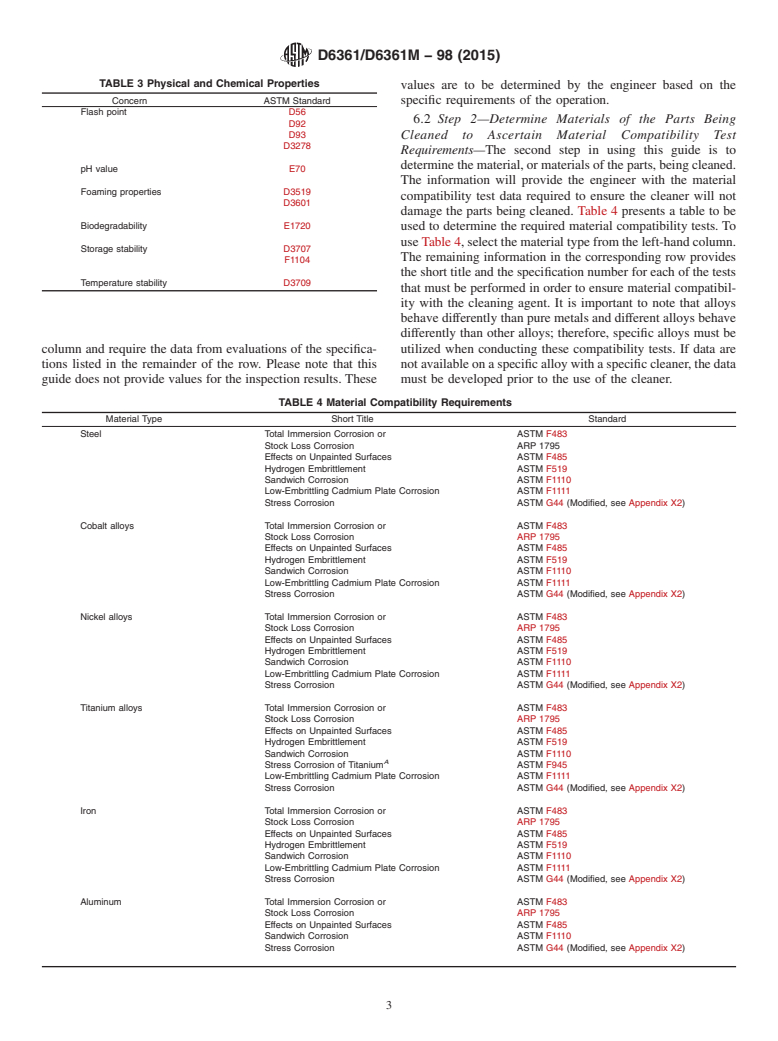
5.1 This guide is to be used by anyone developing cleaning requirements for specifications for manufacturing, maintenance, or overhaul. This guide has been designed to be application specific for each cleaning task and to assure the design engineer that the process selected by the industrial or manufacturing engineer will be compatible with both the part material and the subsequent process(es). This guide allows the industrial or manufacturing engineer to customize the selection of the cleaning product based on the materials of the part being cleaned; the cleanliness required for the subsequent process(es); and the environmental, cost, and health and safety concerns.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide is intended to assist design engineers, manufacturing/industrial engineers, and production managers in selecting the best fit cleaning agent and process. This guide takes into account environmental pollution prevention factors in a selection process.
1.2 This guide is not to be considered as a database of acceptable materials. It will guide the engineers and managers through the cleaning material selection process, calling for engineers to customize their selection based on the cleaning requirements for the cleaning tasks at hand. If a part can be cleaned, and kept clean, it can be cycled through several process steps that have cleaning requirements. This eliminates extra cleaning process steps during the total process. A total life cycle cost analysis or performance/cost of ownership study is recommended to compare the methods available.
1.3 This guide is for general industry manufacturing, equipment maintenance and remanufacturing operations, and to some extent precision cleaning of mechanical parts and assemblies. It is not intended to be used for optical, medical, or electronics applications, nor is it intended for dry-cleaning or super-critical fluid cleaning.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6361/D6361M − 98 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Guide for
1
Selecting Cleaning Agents and Processes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6361/D6361M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This guide is intended to assist design engineers,
D56 Test Method for Flash Point by Tag Closed Cup Tester
manufacturing/industrial engineers, and production managers
D92 Test Method for Flash and Fire Points by Cleveland
in selecting the best fit cleaning agent and process. This guide
Open Cup Tester
takes into account environmental pollution prevention factors
D93 Test Methods for Flash Point by Pensky-Martens
in a selection process.
Closed Cup Tester
1.2 This guide is not to be considered as a database of D2240 Test Method for Rubber Property—Durometer Hard-
acceptable materials. It will guide the engineers and managers ness
D3167 Test Method for Floating Roller Peel Resistance of
through the cleaning material selection process, calling for
Adhesives
engineers to customize their selection based on the cleaning
D3278 Test Methods for Flash Point of Liquids by Small
requirements for the cleaning tasks at hand. If a part can be
Scale Closed-Cup Apparatus
cleaned, and kept clean, it can be cycled through several
D3519 Test Method for Foam in Aqueous Media (Blender
process steps that have cleaning requirements. This eliminates
3
Test) (Withdrawn 2013)
extracleaningprocessstepsduringthetotalprocess.Atotallife
D3601 Test Method for Foam In Aqueous Media (Bottle
cycle cost analysis or performance/cost of ownership study is
3
Test) (Withdrawn 2013)
recommended to compare the methods available.
D3707 Test Method for Storage Stability of Water-in-Oil
1.3 This guide is for general industry manufacturing, equip- Emulsions by the Oven Test Method
D3709 Test Method for Stability of Water-in-Oil Emulsions
ment maintenance and remanufacturing operations, and to
Under Low to Ambient Temperature Cycling Conditions
some extent precision cleaning of mechanical parts and assem-
D3762 Test Method for Adhesive-Bonded Surface Durabil-
blies. It is not intended to be used for optical, medical, or
ity of Aluminum (Wedge Test)
electronics applications, nor is it intended for dry-cleaning or
E70 Test Method for pH of Aqueous Solutions With the
super-critical fluid cleaning.
Glass Electrode
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
E1720 Test Method for Determining Ready, Ultimate, Bio-
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
degradability of Organic Chemicals in a Sealed Vessel
3
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
CO Production Test (Withdrawn 2013)
2
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining F483 Practice for Total Immersion Corrosion Test for Air-
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance craft Maintenance Chemicals
F484 Test Method for Stress Crazing of Acrylic Plastics in
with the standard.
Contact with Liquid or Semi-Liquid Compounds
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
F485 Practice for Effects of Cleaners on Unpainted Aircraft
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Surfaces
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
F502 Test Method for Effects of Cleaning and Chemical
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
Maintenance Materials on Painted Aircraft Surfaces
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
F519 Test Method for Mechanical Hydrogen Embrittlement
1 2
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D26 on Halogenated For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Organic Solvents and Fire Extinguishing Agents and is the direct responsibility of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Subcommittee D26.03 on Cold Cleaning. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved June 1, 2015. Published June 2015. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as D6361/D6361M- The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
98(2010). DOI: 10.1520/D6361_D6361M-98R15. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6361/D6361M − 98 (2015)
TABLE 1 Summary of Guide
Evaluation of Plating/Coating Processes and Service En-
vironments Step Defined
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D6361/D6361M − 98 (Reapproved 2010) D6361/D6361M − 98 (Reapproved
2015)
Standard Guide for
1
Selecting Cleaning Agents and Processes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6361/D6361M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Units information and the designation were revised editorially in July 2010.
1. Scope
1.1 This guide is intended to assist design engineers, manufacturing/industrial engineers, and production managers in selecting
the best fit cleaning agent and process. This guide takes into account environmental pollution prevention factors in a selection
process.
1.2 This guide is not to be considered as a database of acceptable materials. It will guide the engineers and managers through
the cleaning material selection process, calling for engineers to customize their selection based on the cleaning requirements for
the cleaning tasks at hand. If a part can be cleaned, and kept clean, it can be cycled through several process steps that have cleaning
requirements. This eliminates extra cleaning process steps during the total process. A total life cycle cost analysis or
performance/cost of ownership study is recommended to compare the methods available.
1.3 This guide is for general industry manufacturing, equipment maintenance and remanufacturing operations, and to some
extent precision cleaning of mechanical parts and assemblies. It is not intended to be used for optical, medical, or electronics
applications, nor is it intended for dry-cleaning or super-critical fluid cleaning.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D56 Test Method for Flash Point by Tag Closed Cup Tester
D92 Test Method for Flash and Fire Points by Cleveland Open Cup Tester
D93 Test Methods for Flash Point by Pensky-Martens Closed Cup Tester
D2240 Test Method for Rubber Property—Durometer Hardness
D3167 Test Method for Floating Roller Peel Resistance of Adhesives
D3278 Test Methods for Flash Point of Liquids by Small Scale Closed-Cup Apparatus
3
D3519 Test Method for Foam in Aqueous Media (Blender Test) (Withdrawn 2013)
3
D3601 Test Method for Foam In Aqueous Media (Bottle Test) (Withdrawn 2013)
D3707 Test Method for Storage Stability of Water-in-Oil Emulsions by the Oven Test Method
D3709 Test Method for Stability of Water-in-Oil Emulsions Under Low to Ambient Temperature Cycling Conditions
D3762 Test Method for Adhesive-Bonded Surface Durability of Aluminum (Wedge Test)
E70 Test Method for pH of Aqueous Solutions With the Glass Electrode
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D26 on Halogenated Organic Solvents and Fire Extinguishing Agents and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D26.03 on Cold Cleaning.
Current edition approved June 1, 2010June 1, 2015. Published July 2010June 2015. Originally approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 20042010 as
D6361-98(2004).D6361/D6361M-98(2010). DOI: 10.1520/D6361_D6361M-98R10E01. 10.1520/D6361_D6361M-98R15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6361/D6361M − 98 (2015)
E1720 Test Method for Determining Ready, Ultimate, Biodegradability of Organic Chemicals in a Sealed Vessel CO Production
2
3
Test (Withdrawn 2013)
F483 Practice for Total Immersion Corrosion Test for
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.