ASTM F2015-00(2013)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Lap Joint Flange Pipe End Applications
Standard Specification for Lap Joint Flange Pipe End Applications
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the material and dimensional requirements applicable to lap joint flange pipe ends that are manufactured by a mechanical forming process, and are widely used for low-pressure systems in the marine, process piping, and similar industries. Materials having acceptable forming qualities to produce lap joint ends are copper, copper-nickel, titanium, carbon steel, and stainless steel. The lap joint flange pipe connections shall be produced in accordance with accepted shop practices, and shall be free from burrs and cracks that would affect their suitability for intended service.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the pipe material and wall thickness applicable to lap joint flange pipe ends, manufactured by a mechanical forming process.
1.2 The lap joint flange connection has been widely used for low-pressure systems in the marine, process piping, and similar industries.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F2015 −00 (Reapproved 2013) An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
Lap Joint Flange Pipe End Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2015; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope A200 Specification for Seamless Intermediate Alloy-Steel
Still Tubes for Refinery Service (Withdrawn 1999)
1.1 This specification covers the pipe material and wall
A209/A209M Specification for Seamless Carbon-
thicknessapplicabletolapjointflangepipeends,manufactured
Molybdenum Alloy-Steel Boiler and Superheater Tubes
by a mechanical forming process.
A210/A210M Specification for Seamless Medium-Carbon
1.2 Thelapjointflangeconnectionhasbeenwidelyusedfor
Steel Boiler and Superheater Tubes
low-pressuresystemsinthemarine,processpiping,andsimilar
A250/A250M Specification for Electric-Resistance-Welded
industries.
Ferritic Alloy-Steel Boiler and Superheater Tubes
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the A252 Specification for Welded and Seamless Steel Pipe
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information Piles
only. A312/A312M Specification for Seamless, Welded, and
Heavily Cold Worked Austenitic Stainless Steel Pipes
2. Referenced Documents
A333/A333M Specification for Seamless and Welded Steel
2.1 ASTM Standards: PipeforLow-TemperatureServiceandOtherApplications
with Required Notch Toughness
A53/A53M Specification for Pipe, Steel, Black and Hot-
Dipped, Zinc-Coated, Welded and Seamless A334/A334M Specification for Seamless and Welded Car-
bon and Alloy-Steel Tubes for Low-Temperature Service
A106/A106M Specification for Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe
for High-Temperature Service A500 Specification for Cold-Formed Welded and Seamless
Carbon Steel Structural Tubing in Rounds and Shapes
A135 Specification for Electric-Resistance-Welded Steel
Pipe A512 Specification for Cold-Drawn Buttweld Carbon Steel
A139/A139M Specification for Electric-Fusion (Arc)- Mechanical Tubing
A519 Specification for Seamless Carbon and Alloy Steel
Welded Steel Pipe (NPS 4 and Over)
A161 Specification for Seamless Low-Carbon and Carbon- Mechanical Tubing
A587 Specification for Electric-Resistance-Welded Low-
Molybdenum Steel Still Tubes for Refinery (Withdrawn
1999) Carbon Steel Pipe for the Chemical Industry
A589 Specification for Seamless and Welded Carbon Steel
A178/A178M Specification for Electric-Resistance-Welded
Carbon Steel and Carbon-Manganese Steel Boiler and Water-Well Pipe
A672 Specification for Electric-Fusion-Welded Steel Pipe
Superheater Tubes
A199/A199M Specification for Seamless Cold-Drawn Inter- for High-Pressure Service at Moderate Temperatures
B42 Specification for Seamless Copper Pipe, Standard Sizes
mediate Alloy-Steel Heat-Exchanger and Condenser
Tubes (Withdrawn 1995) B88 Specification for Seamless Copper Water Tube
B88M Specification for Seamless Copper Water Tube (Met-
ric)
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships
B280 Specification for Seamless Copper Tube for Air Con-
and Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.11 on
Machinery and Piping Systems.
ditioning and Refrigeration Field Service
Current edition approved May 1, 2013. Published May 2013. Originally
B337 Specification for Seamless and Welded Titanium and
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as F2015 – 00 (2006).
Titanium Alloy Pipe (Withdrawn 1997)
DOI: 10.1520/F2015-00R13.
B338 Specification for Seamless and Welded Titanium and
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Titanium Alloy Tubes for Condensers and Heat Exchang-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
ers
the ASTM website.
3 B466/B466M Specification for Seamless Copper-Nickel
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. Pipe and Tube
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F2015−00 (2013)
B467 Specification for Welded Copper-Nickel Pipe 5. Fabrication
2.2 ANSI Standards:
5.1 The formed lap joint end may have a smooth or serrated
B31.1 Power Piping
face.
B31.3 Chemical Plant and Petroleum Refining Piping
4 5.2 The back-up flange may be a different material from the
B16.5 Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings
4 lap joint end pipe as long as it conforms to the applicable
B16.9 Factory-Made Wrought Steel Butt-Welding Fittings
piping system codes or standards.
B16.24 Cast Copper Alloy Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fit-
tings: Class 150, 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500 and 2500 5.3 Convoluted back-up flanges may be used if they comply
B16.42 Ductile Iron Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings, with the applicable piping system codes or standards.
Classes 150 and 300
6. Pipe Materials and Limitations
2.3 ISO Standard:
ISO-7005-1 Metallic Flanges Part 1: Steel Flanges
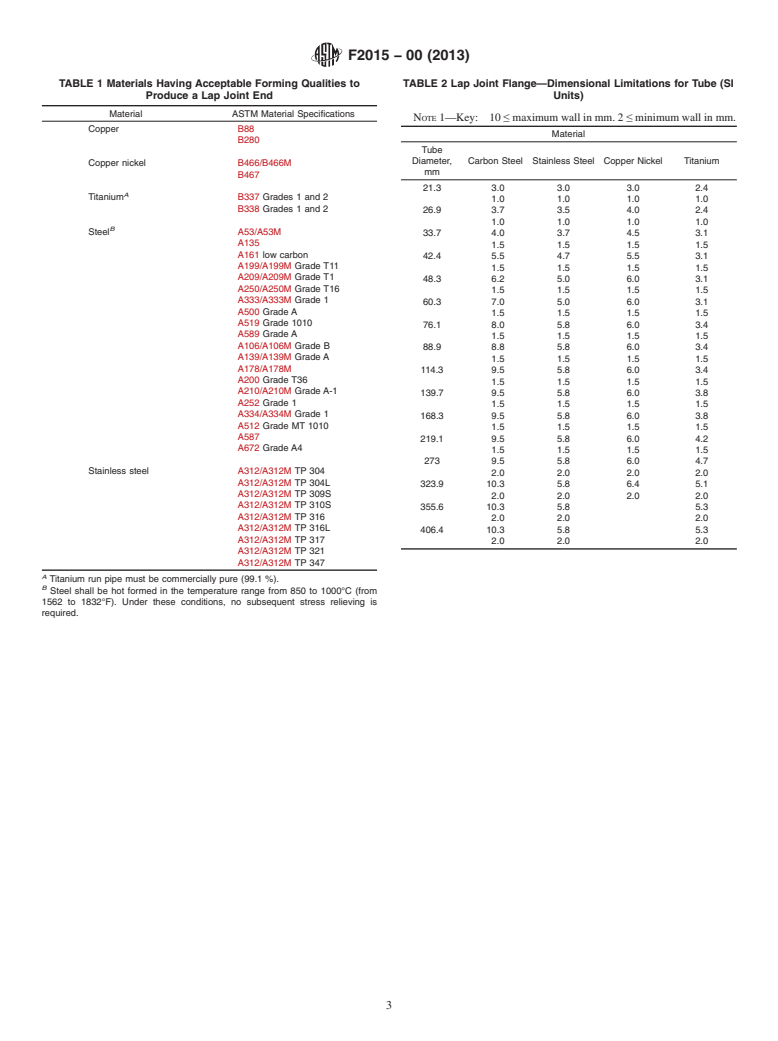
6.1 Table 1 contains a list of materials that have been found
ISO-7005-2 Metallic Flanges Part 2: Cast Iron Flanges
to have acceptable forming qualities to produce a lap joint end.
ISO-7005-3 Metallic Flanges Part 3: Copper Alloy and
Composite Flanges
7. Finish, Appearance and Repairs
7.1 Thelapjointflangepipeconnectionshallbeproducedin
3. Terminology
accordance with accepted shop practices and shall be free from
3.1 back-up flange—the flange used to back up the lap joint
burrs and cracks, which would affect the suitability for the
to facilitate the pipe connection, also known in industry as
intended service.
loose, slip, plate, or spin flange.
7.2 Pipe/tube repairs are permitted in accordance with the
3.2 convoluted flange—a back-up flange designed with a
applicable ASTM specification.
variable cross section to provide the material in the stress-
related zones.
8. Dimensional Limitations (see Tables 2-4)
3.3 lap joint end—the formed pipe end to accommodate the
8.1 Interpolation is allowable for sizes not covered.
back-up flange, commonly referred to as a Van Stone flange
(see Fig. 1).
8.2 The limitations are based on current technology subject
to amendment to equipment or process developments, or both.
4. Dimensions and Tolerances
4.1 Thelapjointendoutsidediametershallbeformedtothe 9. Allowable Pressure and Temperature
raised face flange diameter as covered under ISO Standard
9.1 The allowable pres
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.