ASTM D2923-06
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Rigidity of Polyolefin Film and Sheeting
Standard Test Method for Rigidity of Polyolefin Film and Sheeting
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The rigidity of a polyolefin web can affect its machinability, particularly on those packaging machines where a cut portion of a web is required to remain flat momentarily without being supported on all sides.
Rigidity is not a simple property since it depends on two other properties of the sample: the thickness (gauge), and the stiffness which is an inherent property of the material of which the film or sheet is made. The combined effect of these two factors is the rigidity that influences performance on converting machines.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes two procedures for measuring the rigidity of polyolefin film and sheeting.
1.2 Procedure A prescribes a procedure using high-voltage static eliminators and the use of TFE-fluorocarbon-coated plates to overcome the spurious effects of static electricity and friction.
1.3 Procedure B prescribes the use of a fine powder on uncoated plates to achieve a similar effect. Note 1
Although the two procedures are designed to achieve similar effect, they may not achieve the same results.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in brackets are for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Note 2
There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 2923 – 06
Standard Test Method for
1
Rigidity of Polyolefin Film and Sheeting
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2923; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
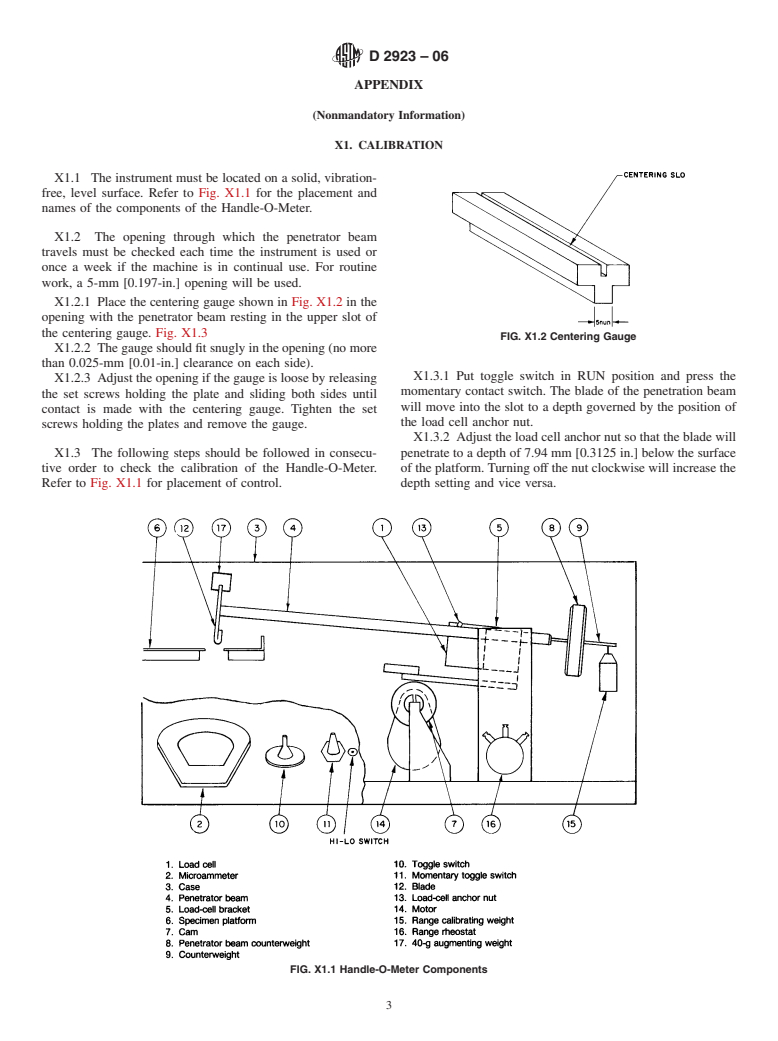
1. Scope* which flexes the sample by forcing it into a groove or slot in a
horizontal platform upon which the sample rests.An indicating
1.1 This test method describes two procedures for measur-
microammeter, wired to the strain gauge, is calibrated in grams
ing the rigidity of polyolefin film and sheeting.
of load sensed by the strain gauge. The rigidity is read directly
1.2 Procedure A prescribes a procedure using high-voltage
2
from the meter and expressed as grams per centimetre of
static eliminators and the use of TFE-fluorocarbon -coated
sample width.
plates to overcome the spurious effects of static electricity and
friction.
5. Significance and Use
1.3 Procedure B prescribes the use of a fine powder on
5.1 The rigidity of a polyolefin web can affect its machin-
uncoated plates to achieve a similar effect.
ability, particularly on those packaging machines where a cut
NOTE 1—Although the two procedures are designed to achieve similar
portion of a web is required to remain flat momentarily without
effect, they may not achieve the same results.
being supported on all sides.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
5.2 Rigidity is not a simple property since it depends on two
standard.Thevaluesgiveninbracketsareforinformationonly.
other properties of the sample: the thickness (gauge), and the
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
stiffness which is an inherent property of the material of which
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
the film or sheet is made. The combined effect of these two
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
factorsistherigiditythatinfluencesperformanceonconverting
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
machines.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
6. Interferences
NOTE 2—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
6.1 Static electricity has considerable influence on the
measured rigidity. It contributes to poor precision and accu-
2. Referenced Documents
3
racy, frequently giving results biased toward the high side.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
6.2 To a lesser extent, precision and accuracy are adversely
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
4 affected by the frictional properties of the sample, particularly
D 1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
when the coefficient of friction is close to 1.
3. Terminology 6.3 The interference caused by the level of static electricity
and friction of the specimen is overcome in Procedure A by
3.1 Definitions:
electrically destaticizing the sample and using TFE-
3.1.1 rigidity—that combination of thickness and inherent
fluorocarbon-coated plates and in Procedure B by dusting the
stiffness of a polyolefin film or sheet which resists flexure.
platform with a fine powder at the start of the test.
4. Summary of Test Method
7. Apparatus
4.1 The resistance to flexure of the sample is measured by a
7.1 Procedure A:
strain gauge affixed to the end of a beam, the opposite end of
7.1.1 Handle-O-Meter, or equivalent, with TFE-
fluorocarbon-coated plates complete with calibrating and aug-
5
1
menting weights.
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.19 on Film and Sheeting. 7.1.2 Cutting Board or Template suitable for preparing 203
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2006. Published November 2006. Originally
by 203-mm [8.0 by 8.0-in.] specimens.
approved in 1970. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D 2923 - 01.
6
7.1.3 High-Voltage Static Eliminator— and Generator.
2
This test method is based on the use of Teflon, a registered trademark of E. I.
duPont de Nemours & Co.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
5
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The Handle-O-Meter and auxiliary equipment are available from Thwing-
the ASTM website. Albert Instrument Co., Philadelphia, PA.
4 6
Withdrawn. Simco Shockless Bars are suitable for this test method.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2923–06
the slot) until an o
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.