ASTM D1743-13
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Corrosion Preventive Properties of Lubricating Greases
Standard Test Method for Determining Corrosion Preventive Properties of Lubricating Greases
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method differentiates the relative corrosion-preventive capabilities of lubricating greases under the conditions of the test.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the corrosion preventive properties of greases using grease-lubricated tapered roller bearings stored under wet conditions. This test method is based on CRC Technique L 412 that shows correlations between laboratory results and service for grease lubricated aircraft wheel bearings.
1.2 Apparatus Dimensions—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 All Other Values—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D1743 − 13
Standard Test Method for
Determining Corrosion Preventive Properties of Lubricating
1
Greases
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1743; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 3.1.1 corrosion, n—the chemical or electrochemical reac-
tion between a material, usually a metal, and its environment
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the corro-
that produces a deterioration of the material and its properties.
sion preventive properties of greases using grease-lubricated
3.1.1.1 Discussion—In this test method, corrosion is mani-
tapered roller bearings stored under wet conditions. This test
2 fested by red rust or black stains on the bearing race. Stains,
method is based on CRC Technique L 41 that shows correla-
through which the underlying metal surface is still visible, are
tions between laboratory results and service for grease lubri-
not considered corrosion in Test Method D1743 and shall be
cated aircraft wheel bearings.
ignored.
1.2 Apparatus Dimensions—The values stated in SI units
are to be regarded as standard.The values given in parentheses 4. Summary of Test Method
are for information only.
4.1 New, cleaned, and lubricated bearings are run under a
1.3 All Other Values—The values stated in SI units are to be light thrust load for 60 6 3 s to distribute the lubricant in a
regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are
pattern that might be found in service. The bearings are
included in this standard. exposed to water, then stored for 48 60.5hat52 6 1°C (125
6 2°F) and 100 % relative humidity. After cleaning, the
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
bearing cups are examined for evidence of corrosion.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5. Significance and Use
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.1 This test method differentiates the relative corrosion-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
preventive capabilities of lubricating greases under the condi-
2. Referenced Documents tions of the test.
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
6. Apparatus
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
6.1 Bearings—Timken bearing cone and roller assembly
D5969 Test Method for Corrosion-Preventive Properties of
4,5
LM11949, and cup LM11910.
Lubricating Greases in Presence of Dilute Synthetic Sea
1
Water Environments
6.2 Motor, 1750 6 50-rpm speed, ⁄15 hp (min).
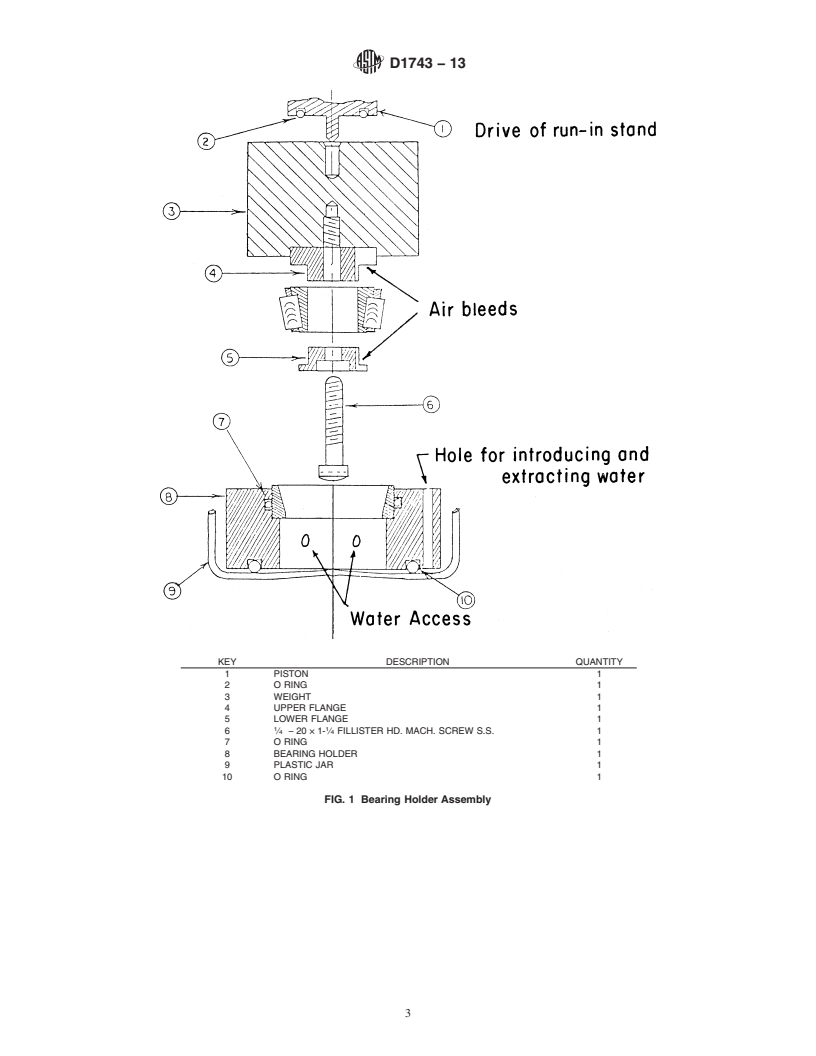
6.3 Bearing Holder, consists of a 1 6 0.10 kg weight, upper
3. Terminology
and lower plastic collars for the bearing cone (Parts A and B),
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
ametalscrew,andaplasticcollarforthecup(PartC).(SeeFig.
1.)
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
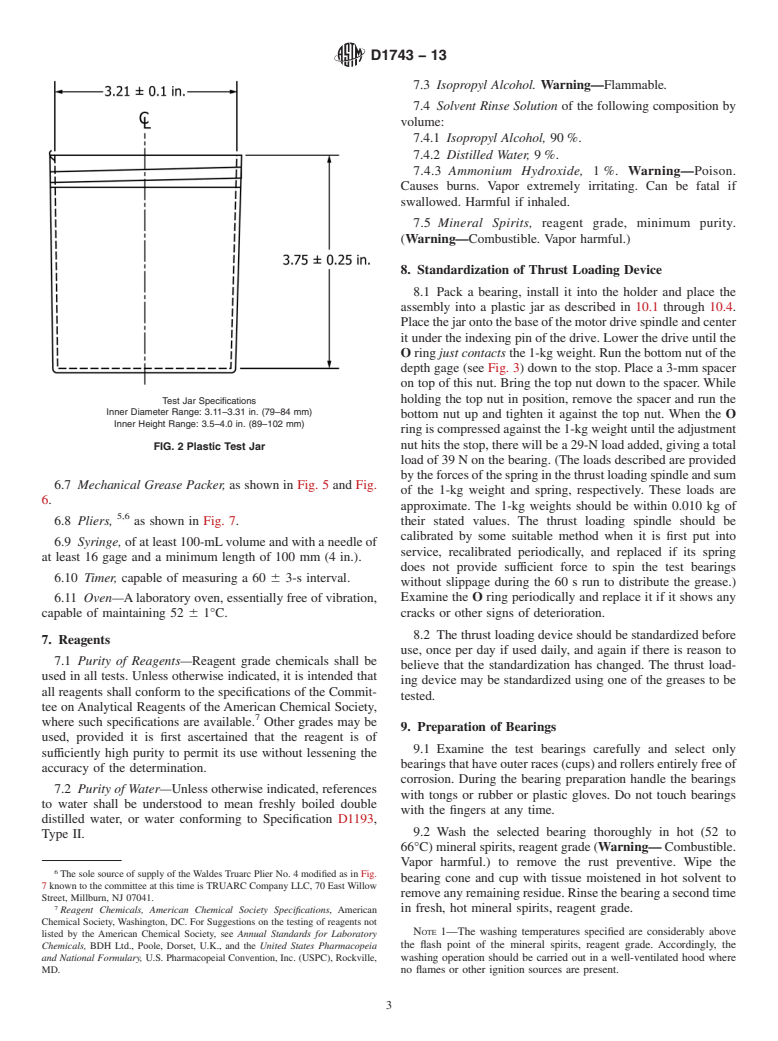
6.4 Plastic Test Jar, as shown in Fig. 2.
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
6.5 Run-in Stand, as shown in Fig. 3.
Subcommittee D02.G0.06 on Functional Tests - Contamination.
Current edition approved May 1, 2013. Published May 2013. Originally
6.6 Spindle/Thrust Loading Device, as shown in Fig. 4. (See
approved in 1960. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as D1743 – 10. DOI:
Table 1 for metric equivalents.)
10.1520/D1743-13.
2
“Research Technique for Determining Rust-Preventive Properties of Lubricat-
ing Greases in the Presence of Free Water,” L-41-957, undated, Coordinating
4
Research Council, Inc., 219 Perimeter Center Parkway, Atlanta, GA 30346. The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or is The Timken Co., Canton, OH 44706.
5
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM If you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consider-
1
the ASTM website. ation at a meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1743 − 13
KEY DESCRIPTION QUANTITY
1PISTON 1
2 O RING 1
3 WEIGHT 1
4 UPPER FLANGE 1
5 LOWER FLANGE 1
1 1
6 ⁄4−20×1- ⁄4 FILLISTER HD
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D1743 − 10 D1743 − 13
Standard Test Method for
Determining Corrosion Preventive Properties of Lubricating
1
Greases
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1743; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the corrosion preventive properties of greases using grease-lubricated tapered
2
roller bearings stored under wet conditions. This test method is based on CRC Technique L 41 that shows correlations between
laboratory results and service for grease lubricated aircraft wheel bearings.
1.2 Apparatus Dimensions—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
for information only.
1.3 All Other Values—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included
in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D5969 Test Method for Corrosion-Preventive Properties of Lubricating Greases in Presence of Dilute Synthetic Sea Water
Environments
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 corrosion, n—the chemical or electrochemical reaction between a material, usually a metal, and its environment that
produces a deterioration of the material and its properties.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.G0.06
on Functional Tests - Contamination.
Current edition approved May 1, 2010May 1, 2013. Published June 2010May 2013. Originally approved in 1960. Last previous edition approved in 20052010 as
ε1
D1743D1743 – 10.–05a . DOI: 10.1520/D1743-10.10.1520/D1743-13.
2
“Research Technique for Determining Rust-Preventive Properties of Lubricating Greases in the Presence of Free Water,” L-41-957, undated, Coordinating Research
Council, Inc., 219 Perimeter Center Parkway, Atlanta, GA 30346.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—
In this test method, corrosion is manifested by red rust or black stains on the bearing race. Stains, through which the underlying
metal surface is still visible, are not considered corrosion in Test Method D1743 and shall be ignored.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 New, cleaned, and lubricated bearings are run under a light thrust load for 60 6 3 s to distribute the lubricant in a pattern
that might be found in service. The bearings are exposed to water, then stored for 48 6 0.5 h at 52 6 1°C (125 6 2°F) and 100 %
relative humidity. After cleaning, the bearing cups are examined for evidence of corrosion.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1743 − 13
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method differentiates the relative corrosion-preventive capabilities of lubricating greases under the conditions of
the test.
6. Apparatus
4 ,5
6.1 Bearings—Timken bearing cone and roller assembly LM11949, and cup LM11910.
1
6.2 Motor, 1750 6 50-rpm speed, ⁄15 hp (min).
6.3 Bearing Holder, consists of a 1 6 0.10 kg weight, upper and lower plastic collars for the bearing cone (Parts A and B), a
metal screw, and a plastic collar for the cup (Part C). (See Fig. 1.)
6.4 Plastic Test Jar, as shown in Fig. 2.
6.5 Run-in Stand, as shown in Fig. 3.
6.6 Spindle/Thrust Loading Device, as shown in Fig. 4. (See Table 1 for metric equivalents.)
6.7 Mechanical Grease Packer, as shown in Fig. 5 and Fig. 6.
5,6
6.8 Pliers, as shown in Fig. 7.
6.9 Syringe, of at least 100-mL volume and with a needle
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.