ASTM D4891-13
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Heating Value of Gases in Natural Gas and Flare Gases Range by Stoichiometric Combustion
Standard Test Method for Heating Value of Gases in Natural Gas and Flare Gases Range by Stoichiometric Combustion
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method provides an accurate and reliable procedure to measure the total heating value of a fuel gas, on a continuous basis, which is used for regulatory compliance, custody transfer, and process control.
5.2 Some instruments which conform to the requirements set forth in this test method can have response times on the order of 1 min or less and can be used for on-line measurement and control.
5.3 The method is sensitive to the presence of oxygen and nonparaffin fuels. For components not listed and composition ranges that fall outside those in Table 1 and Table 2, modifications in the method and changes to the calibration gas or gasses being used may be required to obtain correct results.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the heating value of natural gases and similar gaseous mixtures within the range of composition shown in Table 1, and Table 2 that covers flare components but is not intended to limit the components to be measured in flare gases.TABLE 1 Natural Gas Components and Range of Composition Covered
Compound
Concentration Range, mole, %
Helium
0.01 to 5
Nitrogen
0.01 to 20
Carbon dioxide
0.01 to 10
Methane
50 to 100
Ethane
0.01 to 20
Propane
0.01 to 20
n-butane
0.01 to 10
isobutane
0.01 to 10
n-pentane
0.01 to 2
Isopentane
0.01 to 2
Hexanes and heavier
0.01 to 2
TABLE 2 Natural Gas Components and Range of Composition CoveredA
Compound
CAS Number
Volatile Analytes
Acetone
67-64-1
Acetonitrile
75-05-8
Acrolein
107-05-8
Acrylonitrile
107-13-1
Benzene
71-43-2 2
1,3-Butadiene
106-99-0
Carbon disulfide
75-15-0
Chlorobenzene
108-90-7
Cumene (isopropylbenzene)
98-82-8
1,2-Dibromoethane
106-93-4
Ethylbenzene
100-41-4 2,2,4
Hexane
110-54-3
Methanol
67-56-1
Methyl isobutyl ketone
108-10-1
Methyl t-butyl ether
1634-04-4
Methylene chloride
75-09-2
Nitrobenzene
98-95-3
Nitropropane
79-46-9
Pentane2
109-66-0
Styrene
100-42-5
Tetrachloroethene
127-18-4
Toluene
108-88-3
Trichloroethene
79-01-6
Trimethylpentane
2 540-84-1
Xylenes (mixed isomers)
1330-20-7
Trimethylpentane
2 540-84-1
Xylenes (mixed isomers)
1330-20-7
Semi-volatile Analytes
Acenaphthene
83-32-9
Acenaphthylene
208-96-8
Aniline
62-53-3
Anthracene
120-12-7
Benzidine1
92-87-5
Benz[a]anthracene
56-55-3
Benzo[b]fluoranthene
205-99-2
Benzo[k]fluoranthene
207-08-9
Benzo[g,h,i]perylene
191-24-2
Benzo[a]pyrene
50-32-8
Benzo[e]pyrene2
192-97-2
Biphenyl2,
92-52-4
Cresol (mixed isomers)
1319-77-3
Chrysene
218-01-9
Dibenz[a,h]anthracene
53-70-3
Dibenzofuran
132-64-9
Dibenzo(a,e)pyrene
192-65-4
3,3’- Dimethoxybenzidine
119-90-4
Dimethylaminobenzene
60-11-7
7,12-Dimethylbenz(a)anthracene
57-97-6
3,3’- Dimethylbenzidine
119-93-7
á,á- Dimethylphenethylamine
122-09-8
2,4-Dimethylphenol
105-67-9
Fluoranthene
206-44-0
Fluorene
86-73-7
Indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene
193-39-5
Isophorone
78-59-1
3-Methylcholanthrene
56-49-5
2-Methylnaphthalene
91-57-6
Naphthalene
91-20-3
Perylene2
198-55-0
Phenanthrene
85-01-8
Phenol
108-95-2
1,4-Phenylenediamine
106-50-3
Pyrene
129-00-0
o-Toluidine
95-53-4
Aldehydes
Methanol
67-56-1
Formaldehyde
50-00-0
Acetaldehyde
75-07-0
Propanal
123-38-6
C1 to C5 Hydrocarbons
Description
Compound
CAS Number
C1 Alkanes
Methane
74-82-8
C2 Alkanes
Ethane
74-84-0
C3 Alkanes
Propane
74-...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4891 − 13
Standard Test Method for
Heating Value of Gases in Natural Gas and Flare Gases
1
Range by Stoichiometric Combustion
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4891; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
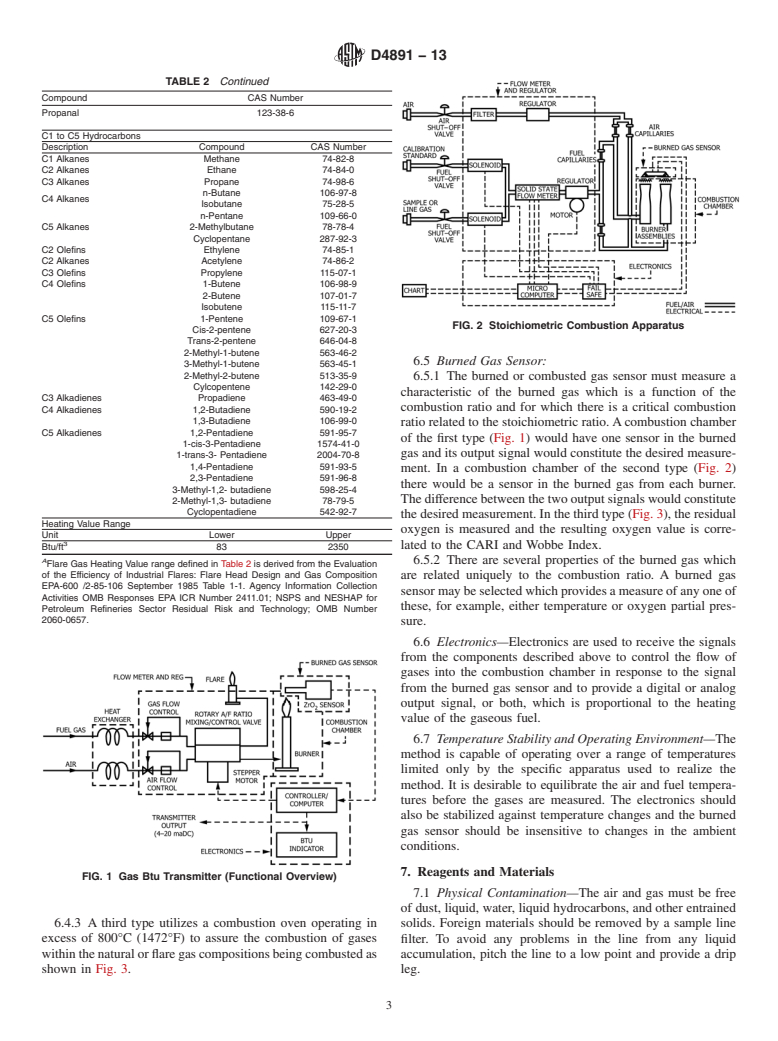
1. Scope 3.2.2 burned gas parameter, n—apropertyoftheburnedgas
after combustion which is a function of the combustion ratio.
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationoftheheating
3.2.3 critical combustion ratio, n— for a specific burned gas
value of natural gases and similar gaseous mixtures within the
parameter, the combustion ratio at which a plot of burned gas
rangeofcompositionshowninTable1,andTable2thatcovers
parameter versus combustion ratio has either maximum value
flarecomponentsbutisnotintendedtolimitthecomponentsto
or maximum slope.
be measured in flare gases.
3.2.4 combustion air requirement index (CARI), n—is the
1.2 This standard involves combustible gases. It is not the
amount of air required for complete combustion of the gas
purpose of this standard to address the safety concerns, if any,
being measured and can be used to index against other
associated with their use. It is the responsibility of the user of
measured values such as the Wobbe Index or Heating Value.
this standard to establish appropriate safety and health prac-
tices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations 3.2.5 stoichiometric ratio, n—thecombustionratiowhenthe
prior to use.
quantity of combustion air is just sufficient to convert all of the
combustibles in the fuel to water and carbon dioxide.
2. Referenced Documents
4. Summary of Test Method
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.1 Air is mixed with the gaseous fuel to be tested. The
D1826TestMethodforCalorific(Heating)ValueofGasesin
mixture is burned and the air-fuel ratio is adjusted so that
Natural Gas Range by Continuous Recording Calorimeter
essentially a stoichiometric proportion of air is present. More
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
exactly, the adjustment is made so that the air-fuel ratio is in a
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
constant proportion to the stoichiometric ratio that is a relative
3
2.2 EPA Standard:
measure of the heating value. To set this ratio, a characteristic
EPA-600/2-85-106EvaluationoftheEfficiencyofIndustrial
property of the burned gas is measured, such as temperature or
Flares: Flare Head Design and Gas Composition
oxygen concentration.
3. Terminology
5. Significance and Use
3.1 All of the terms defined in Test Method D1826 are
5.1 This test method provides an accurate and reliable
included by reference.
procedure to measure the total heating value of a fuel gas, on
a continuous basis, which is used for regulatory compliance,
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
custody transfer, and process control.
3.2.1 combustion ratio, n—the ratio of combustion air to
gaseous fuel.
5.2 Some instruments which conform to the requirements
set forth in this test method can have response times on the
orderof1minorlessandcanbeusedforon-linemeasurement
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD03onGaseous
and control.
Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.03 on Determination of
Heating Value and Relative Density of Gaseous Fuels. 5.3 The method is sensitive to the presence of oxygen and
Current edition approved May 1, 2013. Published May 2013. Originally
nonparaffin fuels. For components not listed and composition
approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D4891–89(2001).
ranges that fall outside those in Table 1 and Table 2, modifi-
DOI: 10.1520/D4891-89R06.
2
cations in the method and changes to the calibration gas or
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
gasses being used may be required to obtain correct results.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
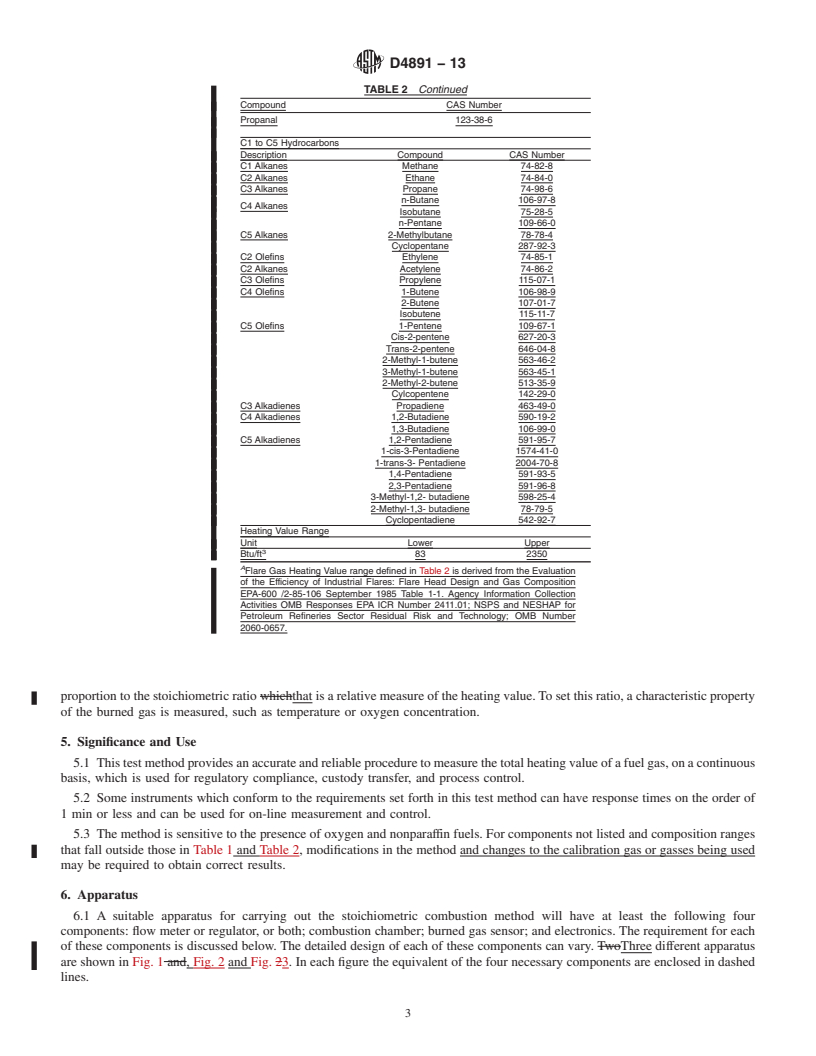
6. Apparatus
3
Available from United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Ariel
6.1 A suitable apparatus for carrying out the stoichiometric
Rios Bldg., 1200 Pennsylvania Ave., NW, Washington, DC 20004, http://
www.epa.gov. combustion method will have at least the following four
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4891 − 13
TABLE 1 Natural Gas Components and Range of Composition TABLE 2 Natural Gas Components and Range of Composition
A
Covered Covered
Compound C
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4891 − 89 (Reapproved 2006) D4891 − 13
Standard Test Method for
Heating Value of Gases in Natural Gas and Flare Gases
1
Range by Stoichiometric Combustion
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4891; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the heating value of natural gases and similar gaseous mixtures within the
range of composition shown in Table 1., and Table 2 that covers flare components but is not intended to limit the components to
be measured in flare gases.
1.2 This standard involves combustible gases. It is not the purpose of this standard to address the safety concerns, if any,
associated with their use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1826 Test Method for Calorific (Heating) Value of Gases in Natural Gas Range by Continuous Recording Calorimeter
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3
2.2 EPA Standard:
EPA-600 /2-85-106 Evaluation of the Efficiency of Industrial Flares: Flare Head Design and Gas Composition
3. Terminology
3.1 All of the terms defined in Test Method D1826 are included by reference.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 combustion ratio—ratio, n—the ratio of combustion air to gaseous fuel.
3.2.2 stoichiometric ratio—the combustion ratio when the quantity of combustion air is just sufficient to convert all of the
combustibles in the fuel to water and carbon dioxide.
3.2.2 burned gas parameter—parameter, n—a property of the burned gas after combustion which is a function of the
combustion ratio.
3.2.3 critical combustion ratio—ratio, n— for a specific burned gas parameter, the combustion ratio at which a plot of burned
gas parameter versus combustion ratio has either maximum value or maximum slope.
3.2.4 combustion air requirement index (CARI), n—is the amount of air required for complete combustion of the gas being
measured and can be used to index against other measured values such as the Wobbe Index or Heating Value.
3.2.5 stoichiometric ratio, n—the combustion ratio when the quantity of combustion air is just sufficient to convert all of the
combustibles in the fuel to water and carbon dioxide.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Air is mixed with the gaseous fuel to be tested. The mixture is burned and the air-fuel ratio is adjusted so that essentially
a stoichiometric proportion of air is present. More exactly, the adjustment is made so that the air-fuel ratio is in a constant
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.03 on Determination of
Heating Value and Relative Density of Gaseous Fuels.
Current edition approved June 1, 2006May 1, 2013. Published June 2006May 2013. Originally approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as
D4891–89 (2001). DOI: 10.1520/D4891-89R06.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Ariel Rios Bldg., 1200 Pennsylvania Ave., NW, Washington, DC 20004, http://www.epa.gov.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4891 − 13
TABLE 1 Natural Gas Components and Range of Composition TABLE 2 Natural Gas Components and Range of Composition
A
Covered Covered
Compound CAS Number
Compound Concentration Range, mole, %
Volatile Analytes
Helium 0.01 to 5
Acetone 67-64-1
Nitrogen 0.01 to 20
Acetonitrile 75-05-8
Carbon dioxide 0.01 to 10
Acrolein 107-05-8
Methane 50 to 100
Acrylonitrile 107-13-1
Ethane 0.01 to 20
Benzene 71-43-2 2
Propane 0.01 to 20
1,3-Butadiene 106-99-0
n-butane 0.01 to 10
Carbon disulfide 75-15-0
isobutane 0.01 to 10
Chlorobenzene 108-90-7
n-pentane 0.01 to 2
Cumene 98-82-8
Isopentane 0.01 to 2
(isopropylbenzen
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.