ASTM B660-96
(Practice)Standard Practices for Packaging/Packing of Aluminum and Magnesium Products
Standard Practices for Packaging/Packing of Aluminum and Magnesium Products
SCOPE
1.1 These practices describe methods of packaging/packing aluminum and magnesium products, in preparation for storage or shipment, both foreign and domestic. Assuming proper and normal handling in transit, these practices are designed to deliver the products to their destination in good condition. For DoD redistribution, see Supplementary Requirements.
1.2 Aluminum and magnesium products must be preserved and packed so as to be adequately protected from possible damage during shipment and storage. Major damage types are:
1.2.1 Mechanical, including bending, crushing, denting, scratching, or gouging during handling and storage; and abrasions resulting from vibration during transport of the material.
1.2.2 Corrosion, or water stain, resulting from exposure of packed material to water, either externally applied, or as condensate caused by temperature variations in a humid atmosphere.
Note 1—A complete metric companion to Practices B 660 is being developed-Practices B 660M; therefore, no metric equivalents are presented in these practices.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: B 660 – 96
Standard Practices for
Packaging/Packing of Aluminum and Magnesium Products
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 660; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope * D 3951 Practice for Commercial Packaging
D 3953 Specification for Strapping, Flat Steel and Seals
1.1 These practices describe methods of packaging/ packing
2.2 ANSI Standard:
aluminum and magnesium products, in preparation for storage
ANSI/AHA A135.4 Basic Hardboard
or shipment, both foreign and domestic. Assuming proper and
2.3 Federal Specifications:
normal handling in transit, these practices are designed to
FF-N-105 Nail, Brads, Staples and Spikes, Wire, Cut and
deliver the products to their destination in good condition. For
Wrought
DoD redistribution see Supplementary Requirements.
NN-P-530 Plywood, Flat Panel
1.2 Aluminum and magnesium products must be preserved
UU-P-553 Paper, Wrapping, Tissue
and packed so as to be adequately protected from possible
VV-L-800 Lubricating Oil, General Purpose Preservative
damage during shipment and storage. Major damage types are:
PPP-B-566 Box, Folding, Paperboard
1.2.1 Mechanical, including bending, crushing, denting,
PPP-B-636 Box, Shipping, Fiberboard
scratching, or gouging during handling and storage; and
PPP-B-640 Box, Fiberboard, Corrugated, Triple Wall
abrasions resulting from vibration during transport of the
PPP-C-96 Can, Metal, 28 Gage and Lighter
material.
PPP-D-705 Drum, Shipping and Storage: Steel 16 and 30
1.2.2 Corrosion, or water stain, resulting from exposure of
Gallon Capacity
packed material to water, either externally applied, or as
PPP-D-723 Drum, Fiber
condensate caused by temperature variations in a humid
PPP-D-729 Drum, Shipping and Storage: Steel, 55 Gallon
atmosphere.
PPP-F-320 Fiberboard, Corrugated and Solid, Sheet Stock
NOTE 1—A complete metric companion to Practices B 660 is being
(Container Grade) and Cut Shapes
developed—Practices B 660M; therefore, no metric equivalents are pre-
PPP-P-704 Pails, Metal: (Shipping, Steel, 1 through 12,
sented in these practices.
Gallons)
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
PPP-T-45 Tape, Gummed Paper, Reinforced and Plain, For
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Sealing and Securing
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
PPP-T-60 Tape, Packaging, Waterproof
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
PPP-T-76 Tape, Pressure-sensitive Adhesive Paper (For
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Carton Sealing)
PPP-T-495 Tubes, Mailing, and Filing
2. Referenced Documents
PPP-V-205 Veneer, Paper Overlaid, Container Grade
2.1 ASTM Standards: 5
2.4 Federal Standards:
D 779 Test Method for Water Resistance of Paper, Paper-
Fed. Std. No. 101 Preservation, Packaging and Packing
board, and Other Sheet Materials by the Dry-Indicator
Materials: Test Procedure
Method
PS 1-74 U.S. Product Standard (For Construction and In-
D 1732 Practices for Preparation of Magnesium Alloy
dustrial Plywood)
Surfaces for Painting 5
2.5 Military Specifications:
D 3950 Specification for Strapping, Nonmetallic (and Join-
MIL-L-7870 Lubricating Oil, General Purpose, Low Tem-
ing Methods)
perature
MIL-C-11796 Corrosion Preventive Compound, Petrola-
tum, Hot Application
These practices are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B-7 on Light
MIL-C-16173 Corrosion Preventive Compound, Solvent
Metals and Alloys and are the direct responsibilities of Subcommittee B07.03 on
Aluminum Alloy Wrought Products.
Current edition approved April 10, 1996. Published June 1996. Originally Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
published as B 660 – 79. Last previous edition B 660 – 95. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
2 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.09. Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.05. Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
B 660
Cutback, Cold Application 5.1.1 Materials not covered by applicable specifications or
MIL-P-17667 Paper, Wrapping, Chemically Neutral (Non- not specifically described herein shall be of high quality and
Corrosive) shall be compatible with and protect the contents.
2.6 Military Standard: 5.1.2 Splicing Requirement—When container members
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage must be spliced to obtain the required length or width, the
2.7 Other Standards: adjacent edges of the two pieces being spliced shall be
Aluminum Standards and Data-Protective Oil for Alumi- butt-jointed as specified in 5.1.2.1 and each piece fastened to
num the splice board. The fastening shall conform to the require-
ments specified for construction of the panels being spliced.
3. Classification
Nails must be clinched.
3.1 Levels of Protection—The following levels of protection
5.1.2.1 Splice boards shall be applied to extend on each side
apply equally to preservation and packing.
of the joint at least two times the width of and the same
3.1.1 Level A—The degree required for protection against
thickness as the box boards.
the most severe conditions known or anticipated to be encoun-
5.1.3 The inside dimensions of boxes shall be commensu-
tered during shipment, multiple rough handling, and intransit
rate with the size of the item.
storage.
5.2 Internal Packaging Materials:
3.1.2 Commercial Packaging—The degree required for pro-
5.2.1 Material Compatibility—Internal packaging materials
tection of material during shipment from supplier to user for
shall not adversely affect the contents.
immediate use or limited storage in a dry, heated storage
5.2.2 Blocking and Bracing—Articles not completely filling
facility. The methods and materials employed by the supplier to
the shipping container shall be blocked, braced, fastened, or
satisfy the requirements of the commercial distribution system otherwise secured. Articles having projecting parts that may be
to provide protection against corrosion, deterioration, and
broken or may puncture the container shall be rigidly sup-
damage during shipment to a user may be used. ported, suspended, or otherwise protected. Clearance of at least
1 in. shall be provided between projecting parts and the
4. Terminology
adjacent inside face of the container. Blocking and bracing
4.1 Definitions:
shall be prevented from coming in direct contact with any
4.1.1 corner protector—protective material placed under
unprotected surface of the item by use of suitable cushioning
ties to protect edges of a package.
material.
4.1.2 deckboard—piece of lumber at right angles to string-
5.3 Handling:
ers or skids of a pallet to form a bearing surface.
5.3.1 General—Containers and pallets in their shipping
4.1.3 filler—piece of material placed in a package to fill
configuration shall be provided with lifting and hoisting
void space for the purpose of squaring out the contents.
provisions commensurate with their weight, size, and intended
4.1.4 framing member—parts forming the main structure of
mode of transportation to ensure safe and efficient movement.
a crate.
5.3.2 Hoisting—Convenient means shall be provided on all
4.1.5 gross weight—bare item weight and the weight of all
shipping containers (except Fig. 1, Fig. 2, Fig. 3, and Fig. 4)
packaging and packing materials.
and pallets weighing more than 200 lb gross which will permit
4.1.6 header—member of skid-type base used to join the
hoisting by attaching suitable slings at the bottom of the
ends of two or more skids and provide added strength to the
containers and pallets.
base.
5.3.3 Forklift Truck Compatibility—Unless otherwise speci-
4.1.7 interleaving—placement of a sheet of protective ma-
fied herein and except Fig. 1, Fig. 2, Fig. 3, and Fig. 4, boxes,
terial between two adjacent pieces of metal.
containers, and pallets grossing over 200 lb must be capable of
4.1.8 net weight—bare item weight.
being handled from at least two sides by forklift trucks. For
4.1.9 nominal—referring to lumber size, rough sawn com-
DoD use, standard 40 by 48 in. pallets must have four-way
mercial size of soft wood lumber common to the industry.
forklift entry. Openings shall be a minimum of 3 in. high and
4.1.10 splice—to unite or join the ends of material such as
at least 20 in. apart inside-to-inside, symmetrically about the
lumber, plywood, or paper overlaid veneer.
center of balance. Containers may have a single opening 40 in.
4.1.11 tension tied—securement applied with mechanical
wide or more to provide forklift access.
tools.
6. Detailed Requirements
5. General Requirements
6.1 Packaging Preservation—Packaging shall be Level A,
5.1 Materials, Methods, and Containers—Materials, meth-
or commercial preservation as follows:
ods, and containers shall conform to the requirements of this
6.1.1 Level A—Detailed requirements for packaging (pres-
standard. Those exceeding the requirements may be substituted
ervation) of aluminum and magnesium products are listed
as negotiated by purchaser and producer or supplier.
alphabetically by product in Table 1. When Level A is
specified, items shall be preserved in accordance with the
detailed requirements outlined herein.
Available from The Aluminum Association, 818 Connecticut Ave., NW,
Washington, DC 20006.
B 660
K
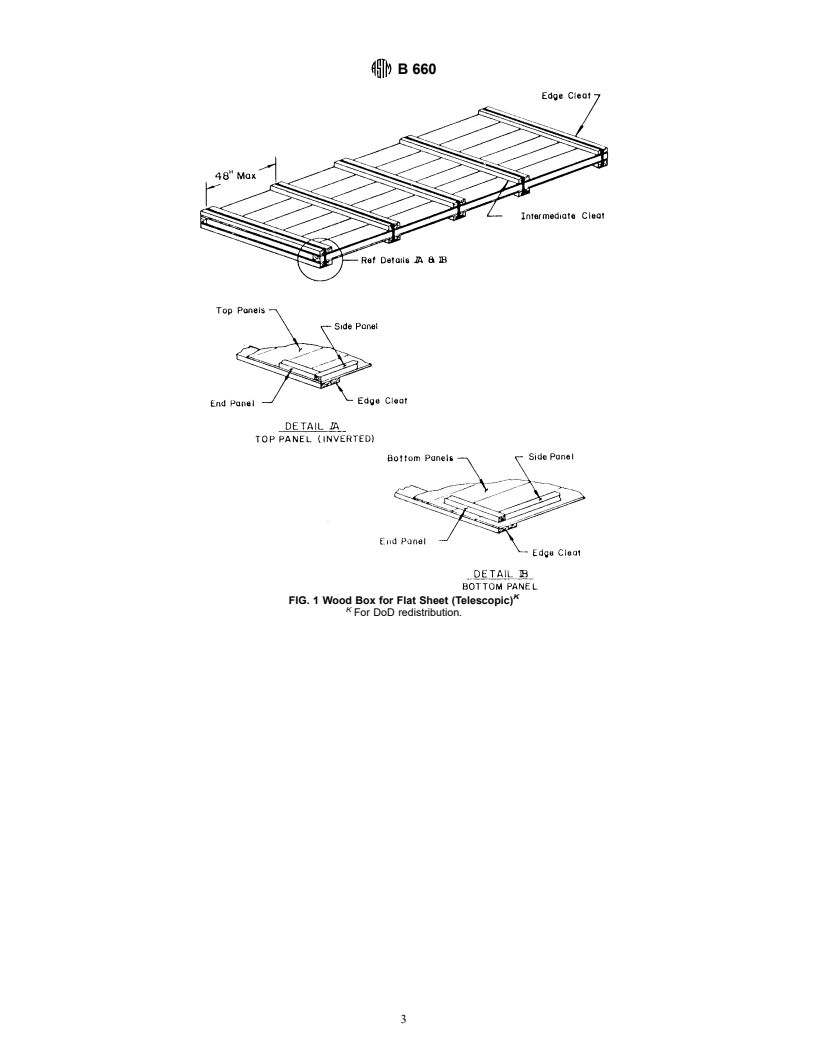
FIG. 1 Wood Box for Flat Sheet (Telescopic)
K
For DoD redistribution.
B 660
K
FIG. 2 Plywood or Paper Overlaid Veneer Box (Telescopic) for Flat Sheet
B 660
K
FIG. 3 Solid Fiberboard Panel Box (Telescopic) for Flat Sheet
B 660
K
FIG. 4 Solid Fiberboard Panel Box, With Spacer (Telescopic) for Flat Sheet
TABLE 1 Packaging (Preservation) and Packing for Level A (Note—For Commercial Packaging, See Section 8)
A
Maximum
Packing (Section 7) for Net Weight
Product Preservation (6.1.1)
Barrier, see Table 2 Per Con-
tainer (7.17)
Bar, rod and wire (cold-finished, drawn,
extruded, rolled, and forged):
Coiled, bare AL-oiled, Mg-Chrome pickled Wrapped coils (Fig. 5). Wrap with one layer of 120
(6.1.1.1-6.1.1.3) Type IIB barrier.
Coiled, covered none required Wrapped coils (Fig. 5). Wrap with one layer of 120
Type IIB barrier.
Spooled for military requirements: 5, 10, none required Wooden boxes (Figs. 6-9). Boxes shall be case- 300
15, 20, 30, lb per spool (other: lined with one layer of Type IIA barrier or two
standard commercial weights) layers of Type III barrier.
B
Straight lengths AL-oiled, Mg-Chrome pickled Wooden boxes (Figs. 10-12). Boxes shall be 1000
(6.1.1.1-6.1.1.3) case-lined with one layer of Type IIA barrier or
two layers of Type III barrier.
or
Corrugated fiberboard boxes, Class weather- 300
resistant (S6.1)
or
Fiber-drums (7.14) 200
Blooms and billets See ingot .
Bus conductors (cold-finished, drawn, See bar, straight lengths .
extruded and rolled)
Cable (bare and covered):
Size 1/0 and smaller none required Wrapped coils (Fig. 5). Wrap with one layer of (bare) 250
Type IIB barrier. (covered) 200
or
B 660
A
Maximum
Packing (Section 7) for Net Weight
Product Preservation (6.1.1)
Barrier, see Table 2 Per Con-
tainer (7.17)
Reels (Fig. 13). (bare) 1250
(covered) 1000
Size larger than 1/0 none required Reel (Fig. 13). (bare) 1600
(covered) 1300
Casting and forgings, finished. none required Wooden boxes (Figs. 6-9) or Style Fig. 14). 2000
Boxes and crates shall be case lined with one
layer of Type IIA barrier or two layers of Type
III barrier.
Castings and forgings, rough none required Bare bundles (Fig. 15). 1000
Conduit See ANSI schedule pipe. .
Extruded profiles (metal less than 1 lb per AL-oiled, Mg-Chrome-pickled Wooden boxes (Figs. 10-12). Boxes shall be 2000
C
linear foot) (6.1.1.1-6.1.1.3) case lined with one layer of Type IIA barrier
or
Fittings (pipe and conduit) AL-oiled, Mg-Chrome-pickled Corrugated fiberboard boxes, Class weather- 300
(6.1.1.1-6.1.1.3) resistant (56.1)
or
External threads shall be covered with Wooden boxes (Figs. 6-9) or Style 1 crate 100
suitable thread protectors. (Fig. 14) dependent upon size of fittings.
Boxes and crates shall be case lined with one
layer Type IIA barrier.
D,E
Foil
Coiled Foil shall be wound on aluminum fiber or Wooden boxes (Figs. 6-9). Coils shall be 500
steel cores. End of coil shall be secured suspended by extended cores or wood
with pressure sensitive tape. Sheared dowels through the core. Core extension or
edges shall be protected from flanges dowel shall be inserted in wood flanges so
and adjacent coils with suitable edge that periphery of coil does not contact inner
protectors. Each coil, or coils (see 7.10) surface of box (Fig. 16). Minimum flange
shall be wrapped with aluminum 0.001 thickness shall be as specified in 7.10.
in. thick aluminum foil.
Foil wrap shall be a conformable wrap Corrugated fiberboard boxes, Class weather- 300
completely enclosing the coil or coils resistant (S6.1) suspended as above.
and edge protectors on each core or
dowel (Fig. 16).
Flat none required Wooden boxes (Figs. 6-9). Contents shall be 500
wrapped with one separate layer of Type IIA
barrier.
or
Corrugated fiberboard boxes, Class weather- 300
resistant (S6.1)
Forgings See castings .
Forging stock See bar .
Impact extrusions none required Wooden boxes (Figs. 6-9). Boxes shall be lined 700
with one layer of Type IIA barrier.
or
Corrugated fiberboard boxes, Class weather- 300
resistant (S6.1)
Ingots:
500 lb per piece and over none required Loose .
30–500 lb per piece none required Bare bundles (Fig. 17). Size of bundle straps 3500
shall be as shown in Table 3. A minimum of
two straps shall be used per bundle.
Less than 30 lb per piece none required Pallets (Fig. 18). Size pallet straps shall be as 2500
shown in Table 3.
or
Self-palletized bundle. Interlocking ingots that 1500
are self-palletized may be shipped in strapped
bundles not over 42 in. high. Bundle shall be
strapped with a minimum of one ⁄4-in. steel
strap.
Grained and granulated ingot and shot Product to be packed in wood boxes Wooden boxes (Figs. 6-9) 500
(Figs. 6-9), shall be packaged in or
Federal Spe
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.