ASTM C1220-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Static Leaching of Monolithic Waste Forms for Disposal of Radioactive Waste
Standard Test Method for Static Leaching of Monolithic Waste Forms for Disposal of Radioactive Waste
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method can be used to provide a measure of the reactivity of a material in a dilute solution in which the test response is dominated by the dissolution or leaching of the test specimen. It can be used to compare the dissolution or leaching behaviors of candidate radioactive waste forms and to study the reactions during static exposure to dilute solutions in which solution feed-back effects can be maintained negligible, depending on the test conditions.
5.2 The test is suitable for application to natural minerals, simulated waste form materials, and radioactive waste form material specimens.
5.3 Data from this test may form part of the larger body of data that is necessary in the logical approach to long-term prediction of waste form behavior, as described in Practice C1174. In particular, measured solution concentrations and characterizations of altered surfaces may be used in the validation of geochemical modeling codes.
5.4 This test method excludes the use of crushed or powdered specimens and organic materials.
5.5 Several reference test parameter values and reference leachant solutions are specified to facilitate the comparison of results of tests conducted with different materials and at different laboratories. However, other test parameter values and leachant solution compositions can be used to characterize the specimen reactivity.
5.5.1 Tests can be conducted with different leachant compositions to simulate groundwaters, buffer the leachate pH as the specimen dissolves, or measure the common ion effect of particular solutes.
5.5.2 Tests can be conducted to measure the effects of various test parameter values on the specimen response, including time, temperature, and S/V ratio. Tests conducted for different durations and at various temperatures provide insight into the reaction kinetics. Tests conducted at different S/V ratio provide insight into chemical affinity (solution feed-back effects) and the approach to saturation.
...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides a measure of the chemical durability of a simulated or radioactive monolithic waste form, such as a glass, ceramic, cement (grout), or cermet, in a test solution at temperatures
1.2 This test method can be used to characterize the dissolution or leaching behaviors of various simulated or radioactive waste forms in various leachants under the specific conditions of the test based on analysis of the test solution. Data from this test are used to calculate normalized elemental mass loss values from specimens exposed to aqueous solutions at temperatures
1.3 The test is conducted under static conditions in a constant solution volume and at a constant temperature. The reactivity of the test specimen is determined from the amounts of components released and accumulated in the solution over the test duration. A wide range of test conditions can be used to study material behavior, including various leachant composition, specimen surface area-to-leachant volume ratios, temperatures, and test durations.
1.4 Three leachant compositions and four reference test matrices of test conditions are recommended to characterize materials behavior and facilitate interlaboratory comparisons of tests results.
1.5 Specimen surfaces may become altered during this test. Although not part of the test method, it is recommended that these altered surface regions be examined to characterize chemical and physical changes due to the reaction of waste forms during static exposure to solutions.
1.6 This test method is not recommended for evaluating metallic materials, the degradation of which includes oxidation reactions that are not controlled by this test method.
1.7 This test method must be performed in accordance with all applicable quality assurance requirements for acceptance of the data.
1.8 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. Other units of measurement are included for r...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C1220 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Static Leaching of Monolithic Waste Forms for Disposal of
1
Radioactive Waste
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1220; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.7 This test method must be performed in accordance with
all applicable quality assurance requirements for acceptance of
1.1 This test method provides a measure of the chemical
the data.
durability of a simulated or radioactive monolithic waste form,
1.8 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
such as a glass, ceramic, cement (grout), or cermet, in a test
standard. Other units of measurement are included for refer-
solution at temperatures <100 °C under low specimen surface-
ence only, with the following exceptions:
area-to-leachant volume (S/V) ratio conditions.
1.8.1 Grit size used in this standard can be converted to the
1.2 This test method can be used to characterize the disso-
corresponding µm values using the current revision of Guide
lutionorleachingbehaviorsofvarioussimulatedorradioactive
E3.
waste forms in various leachants under the specific conditions
1.8.2 Appendix X2 describes the usage of a model of saw
ofthetestbasedonanalysisofthetestsolution.Datafromthis
forwhichcomponentsandinstrumentsareimperialunitbased;
test are used to calculate normalized elemental mass loss
imperial units are used in this section.
values from specimens exposed to aqueous solutions at tem-
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the
peratures <100 °C.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
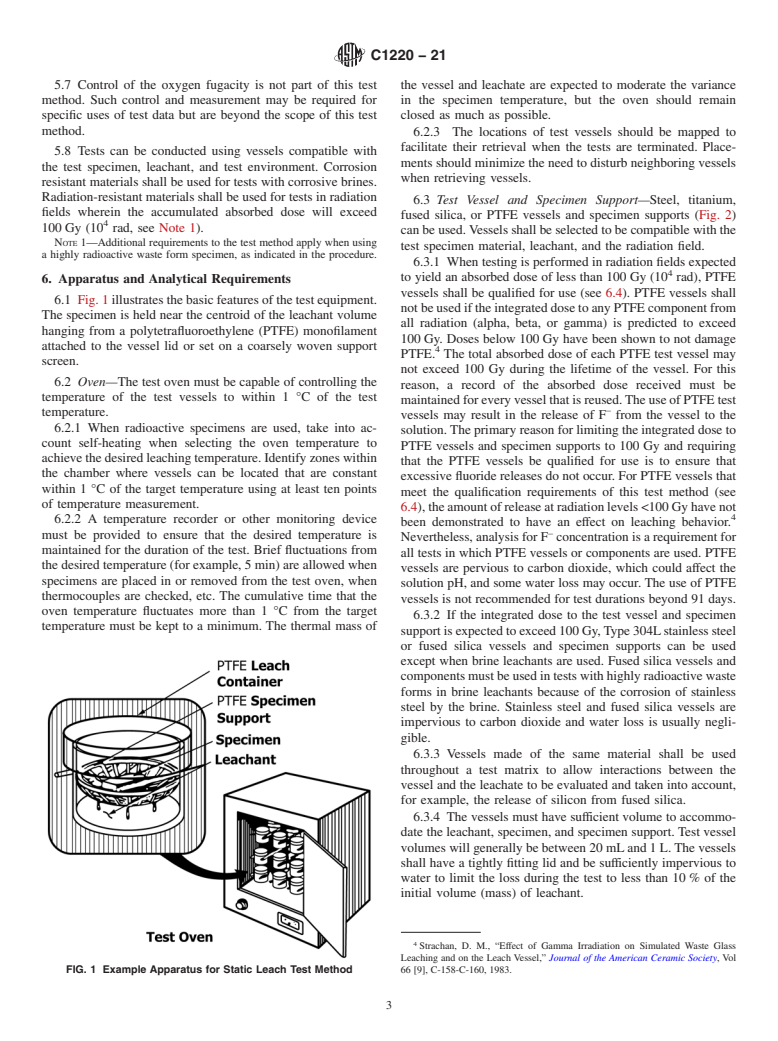
1.3 The test is conducted under static conditions in a
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
constant solution volume and at a constant temperature. The
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
reactivity of the test specimen is determined from the amounts
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
of components released and accumulated in the solution over
For a specific hazard statement, see 7.3.2.
thetestduration.Awiderangeoftestconditionscanbeusedto
1.10 This international standard was developed in accor-
study material behavior, including various leachant
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
composition, specimen surface area-to-leachant volume ratios,
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
temperatures, and test durations.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.4 Three leachant compositions and four reference test
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
matrices of test conditions are recommended to characterize
materials behavior and facilitate interlaboratory comparisons
2. Referenced Documents
of tests results.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.5 Specimen surfaces may become altered during this test.
C859Terminology Relating to Nuclear Materials
Although not part of the test method, it is recommended that
C1109Practice for Analysis of Aqueous Leachates from
these altered surface regions be examined to characterize
Nuclear Waste Materials Using Inductively Coupled
chemical and physical changes due to the reaction of waste
Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectroscopy
forms during static exposure to solutions.
C1174Guide for Evaluation of Long-Term Behavior of
1.6 This test method is not recommended for evaluating
Materials Used in Engineered Barrier Systems (EBS) for
metallicmaterials,thedegradationofwhichincludesoxidation
Geological Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Waste
reactions that are not controlled by this test method.
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
D1293Test Methods for pH of Water
E3Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC26onNuclear
Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.13 on Spent Fuel
2
and High Level Waste. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2021. Published December 2021. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as C1220–17. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/C1220-21. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1220 − 17 C1220 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Static Leaching of Monolithic Waste Forms for Disposal of
1
Radioactive Waste
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1220; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method provides a measure of the chemical durability of a simulated or radioactive monolithic waste form, such as
a glass, ceramic, cement (grout), or cermet, in a test solution at temperatures <100°C <100 °C under low specimen surface-
area-to-leachant volume (S/V) ratio conditions.
1.2 This test method can be used to characterize the dissolution or leaching behaviors of various simulated or radioactive waste
forms in various leachants under the specific conditions of the test based on analysis of the test solution. Data from this test are
used to calculate normalized elemental mass loss values from specimens exposed to aqueous solutions at temperatures
<100°C.<100 °C.
1.3 The test is conducted under static conditions in a constant solution volume and at a constant temperature. The reactivity of
the test specimen is determined from the amounts of components released and accumulated in the solution over the test duration.
A wide range of test conditions can be used to study material behavior, including various leachant composition, specimen surface
area-to-leachant volume ratios, temperatures, and test durations.
1.4 Three leachant compositions and four reference test matrices of test conditions are recommended to characterize materials
behavior and facilitate interlaboratory comparisons of tests results.
1.5 Specimen surfaces may become altered during this test. Although not part of the test method, it is recommended that these
altered surface regions be examined to characterize chemical and physical changes due to the reaction of waste forms during static
exposure to solutions.
1.6 This test method is not recommended for evaluating metallic materials, the degradation of which includes oxidation reactions
that are not controlled by this test method.
1.7 This test method must be performed in accordance with all applicable quality assurance requirements for acceptance of the
data.
1.8 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other Other units of measurement are included in this
standard.for reference only, with the following exceptions:
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C26 on Nuclear Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.13 on Spent Fuel and
High Level Waste.
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2017Oct. 1, 2021. Published December 2017December 2021. Originally approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 20102017
as C1220 – 10.C1220 – 17. DOI: 10.1520/C1220-17.10.1520/C1220-21.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1220 − 21
1.8.1 Grit size used in this standard can be converted to the corresponding μm values using the current revision of Guide E3.
1.8.2 Appendix X2 describes the usage of a model of saw for which components and instruments are imperial unit based; imperial
units are used in this section.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific hazard statement, see 7.3.2.
1.10 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C859 Terminology Relating to Nuclear Materials
C1109 Practice for Analysis of Aqueous Leachates from Nuclear Waste Materials Using Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic
Emission Spectroscopy
C1174 Guide for Evaluation of Long-Term Behavior of Materials Used in Engineered Barrier Systems (EBS) for Geological
Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Waste
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.