ASTM D1777-96(2007)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Thickness of Textile Materials
Standard Test Method for Thickness of Textile Materials
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the thickness of most textile materials.
1.2 This test method applies to most fabrics including woven fabrics, air bag fabrics, blankets, napped fabrics, knitted fabrics, layered fabrics, and pile fabrics. The fabrics may be untreated, heavily sized, coated, resin-treated, or otherwise treated. Instructions are provided for testing thickness, except as provided for in another standard such as listed in Section .
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values stated in inch-pound may be approximate.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D1777 – 96 (Reapproved 2007)
Standard Test Method for
Thickness of Textile Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1777; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope TEX-PAC
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the thick-
3. Terminology
ness of most textile materials.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of other textile terms used
1.2 This test method applies to most fabrics including
in this test method, see Terminology D123.
wovenfabrics,airbagfabrics,blankets,nappedfabrics,knitted
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
fabrics, layered fabrics, and pile fabrics. The fabrics may be
3.2.1 cross-machine direction, CD, n—the direction in the
untreated, heavily sized, coated, resin-treated, or otherwise
plane of the fabric perpendicular to the direction of manufac-
treated. Instructions are provided for testing thickness, except
ture.
as provided for in another standard such as listed in Section 2.
3.2.1.1 Discussion—This term is used to refer to the direc-
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
tion analogous to coursewise or filling direction in knitted or
standard.Thevaluesstatedininch-poundmaybeapproximate.
woven fabrics, respectively.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2.2 machine direction, MD, n—the direction in the plane
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
of the fabric parallel to the direction of manufacture.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2.2.1 Discussion—This term is used to refer to the direc-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
tion analogous to walewise or warp direction in knitted or
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
woven fabrics, respectively.
2. Referenced Documents 3.2.3 pressure, n—the force exerted to a surface per unit
area.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2.3.1 Discussion—Pressure may be expressed in any ap-
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
propriate or specified units, such as pascals (Pa), newtons per
D1776 Practice for Conditioning and Testing Textiles
square metre (N/m ), or pounds-force per square inch (psi).
D2904 Practice for Interlaboratory Testing of a Textile Test
3.2.4 thickness, n—the distance between one surface of a
Method that Produces Normally Distributed Data
material and its opposite.
D2906 Practice for Statements on Precision and Bias for
3.2.4.1 Discussion—In textiles, thickness is the distance
Textiles
between the upper and lower surfaces of the material as
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
measuredunderaspecifiedpressure.Itisusuallydeterminedas
the distance between an anvil or base and a presser foot used
1 to apply the specified pressure.
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 onTextiles
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.59 on Fabric Test Methods,
4. Summary of Test Method
General.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2007. Published January 2007. Originally
4.1 A specimen is placed on the base of a thickness gauge
approved in 1960. Discontinued in November 1995 and reinstated as D1777 – 96.
and a weighted presser foot lowered. The displacement be-
Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2002asD1777 – 96(2002).DOI:10.1520/D1777-
96R07. tweenthebaseandthepresserfootismeasuredasthethickness
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
of the specimen.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. A PC program on floppy disk for analyzing Committee D13 interlaboratory
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced data are available from ASTM Headquarters. For a 3 ⁄2-in. disk, request PCN:12-
on www.astm.org. 429040-18. For a 5 ⁄4-in. disk, request PCN:12-429041-18.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D1777 – 96 (2007)
5. Significance and Use shall take precedence over the directions described in this test
method, unless specifically provided for in that test method.
5.1 This test method is considered satisfactory for accep-
This test method is used in its entirety when no test method for
tance testing of commercial shipments since current estimates
measuring thickness is available for the specific material to be
of between-laboratory precision are acceptable, and this test
tested or unless otherwise specified in a material specification
method is used extensively in the trade for acceptance testing.
or contract order.
5.1.1 In case of a dispute arising from differences in
reported test results when using this test method for acceptance
6. Apparatus
testing of commercial shipments, the purchaser and the sup-
plier should conduct comparative tests to determine if there is
6.1 Thickness Gauge, having dimensions appropriate to the
a statistical bias between their laboratories. Competent statis-
material to be tested as specified in Table 1, unless otherwise
tical assistance is recommended for the investigation of bias.
specifiedinamaterialspecificationorcontractorder.Acircular
As a minimum, the two parties should take a group of test
presserfootcommonlyisusedformostmaterials;however,for
specimens that are as homogeneous as possible and that are
certain materials, such as narrow tapes, a rectangular foot is
from a lot of material of the type in question. Test specimens
moreappropriatewhenagreeduponbetweenthepurchaserand
then should be randomly assigned in equal numbers to each
the supplier.
laboratory for testing. The average results from the two
6.1.1 Automatic Microprocessor Data Gathering Systems,
laboratories should be compared using the appropriate statis-
optional.
tical analysis and an acceptable probability level chosen by the
6.1.2 Spring Force or Compression Test Apparatus, may be
two parties before testing is begun. If a bias is found, either its
substituted for the dead-weight-type thickness gauge providing
cause must be found and corrected, or the purchaser and the
they meet the specified conditions cited in Table 1.
supplier must agree to interpret future test results with consid-
6.2 Cutting Dies or Templates, to cut specimens having
eration to the known bias.
minimum dimensions at least 20 % greater than any dimension
5.2 Thickness is one of the basic physical properties of
of the presser foot to be used in measuring the thickness
textile materials. In certain industrial applications, the thick-
(optional).
ness may require rigid control within specified limits. Bulk and
warmth properties of textile materials are often estimated from
7. Sampling and Test Specimens
theirthicknessvalues,andthicknessisalsousefulinmeasuring
7.1 Lot Sample—As a lot sample for acceptance testing,
some performance characteristics, such as before and after
randomly select the number of rolls or pieces of fabric directed
abrasion and shrinkage.
in an applicable material specification or other agreement
5.3 The thickness value of most textile materials will vary
between the purchaser and the supplier. Consider the rolls or
considerably depending on the pressure applied to the speci-
pieces of fabric to be the primary sampling units. In the
men at the time the thickness measurement is taken. In all
absence of such an agreement, take the number of fabric rolls
cases, the apparent thickness varies inversely with the pressure
specifed in Table 2.
applied. For this reason, it is essential that the pressure be
specified when discussing or listing any thickness value.
NOTE 1—An adequate specification or other agreement between the
5.4 Whenusingthistestmethodformeasuringthethickness
purchaser and the supplier requires taking into account the variability
of textile materials, the primary method for the specific
between rolls or pieces of fabric and between specimens from a swatch
material such as listed in the Referenced Document section from a roll or piece of fabric to provide a sampling plan with a meaningful
TABLE 1 Designated Gauges and Gauge Specifications for Measuring Thickness of Textiles
Testing Material Gauge Presser Foot Anvil/Foot Foot to Anvil
Anvil Applied Pressure Readability
A B
Option Type Type Diameter Parallelism Surface Parallelism
1 Woven fabrics dead-weight 28.7 6 0.02 mm 38 mm D, or greater 0.01 mm 0.002 mm 4.14 6 0.21 kPa 0.02 mm
Knitted fabrics (1.129 6 0.001 in.) (1.629 in. D, or greater) (0.0005 in.) (0.0001 in.) (0.60 6 0.03 psi) (0.001 in.)
Textured fabrics
2 Coated fabrics dead-weight 9.5 6 0.02 mm 38 mm D, or greater 0.01 mm 0.002 mm 23.4 6 0.7 kPa 0.02 mm
Narrow fabrics (0.375 6 0.001 in.) (1.629 in. D, or greater) (0.0005 in.) (0.0001 in.) (3.46 0.1 psi) (0.001 in.)
Webbings
Tapes
Ribbons
Braids
3 Films dead-weight 6.3 6 0.02 mm 19 mm D, or greater 0.002 mm 0.002 mm 172 6 14 kPa 0.002 mm
Glass cloths (0.250 6 0.001 in.) (0.750 in. D, or greater) (0.0001 in.) (0.0001 in.) (25 6 2 psi) (0.0001 in.)
Glass tapes
4 Glass fiber mat dead-weight (2.25 6 0.001 in.) (2.75 in. D, or greater) 0.01 mm 0.002 mm 18.9 6 0.7 kPa 0.02 mm
(0.0005 in.) (0.0001 in.) (2.75 6 0.1 psi) (0.001 in.)
5 Blankets dead-weight 28.7 6 0.02 mm 38 mm D, or greater 0.01 mm 0.002 mm 0.7 6 0.07 kPa 0.02 mm
Pile fabrics (1.129 6 0.001 in.) (1.629 in. D, or greater) (0.0005 in.) (0.0001 in.) (0.1 6 0.01 psi) (0.001 in.)
Napped fabrics also 7.58 6 0.21
kPa (1.1 6 0.03 psi)
A
When testing fabrics made with textured yarns or open-end spun yarns, primary consideration should be given to the pressure applied in Option 1, with respect to the
size of the presser foot used.
B
Other spring force or compression test apparatus that meet the stated specifications can be used.
D1777 – 96 (2007)
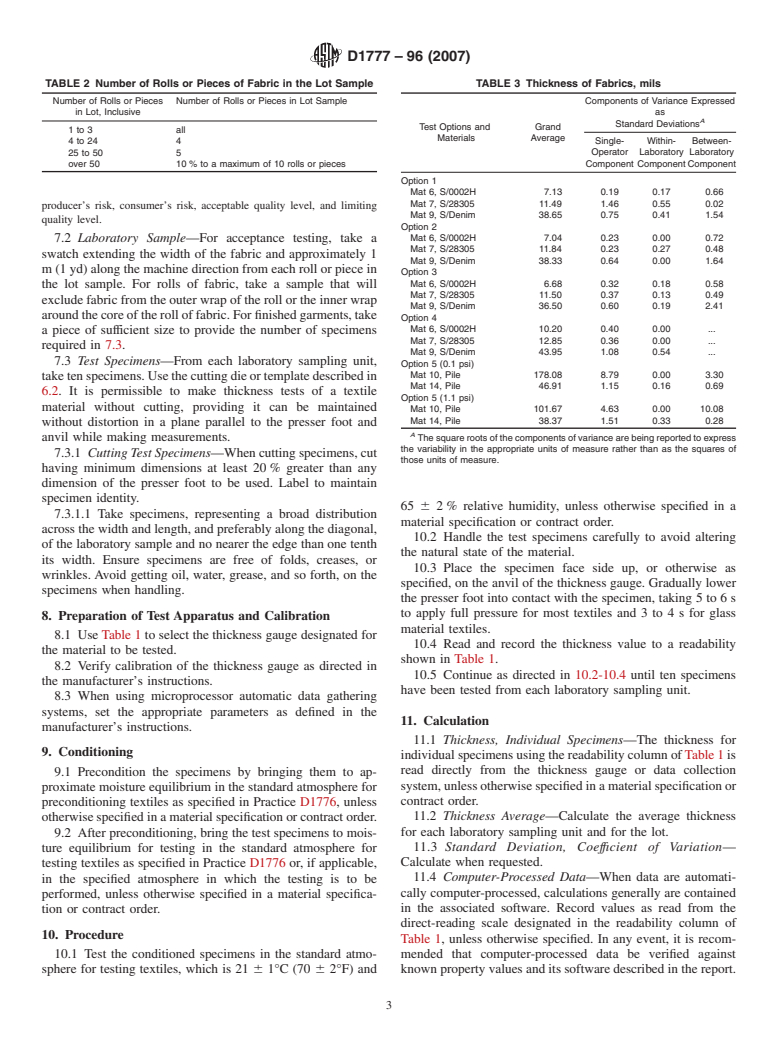
TABLE 2 Number of Rolls or Pieces of Fabric in the Lot Sample TABLE 3 Thickness of Fabrics, mils
Number of Rolls or Pieces Number of Rolls or Pieces in Lot Sample Components of Variance Expressed
in Lot, Inclusive as
A
Standard Deviations
Test Options and Grand
1to3 all
Materials Average
4to24 4 Single- Within- Between-
25 to 50 5 Operator Laboratory Laboratory
over 50 10 % to a maximum of 10 rolls or pieces Component ComponentComponent
Option 1
Mat 6, S/0002H 7.13 0.19 0.17 0.66
Mat 7, S/28305 11.49 1.46 0.55 0.02
producer’s risk, consumer’s risk, acceptable quality level, and limiting
Mat 9, S/Denim 38.65 0.75 0.41 1.54
quality level.
Option 2
Mat 6, S/0002H 7.04 0.23 0.00 0.72
7.2 Laboratory Sample—For acceptance testing, take a
Mat 7, S/28305 11.84 0.23 0.27 0.48
swatch extending the width of the fabric and approximately 1
Mat 9, S/Denim 38.33 0.64 0.00 1.64
m (1 yd) along the machine direction from each roll or piece in
Option 3
Mat 6, S/0
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.