ASTM D7770-12(2019)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Collection of Volatile Organic Compounds Emitted During Simulated Manufacturing of Engineered Wood Products Via a Sealed Caul Plate Method
Standard Test Method for Collection of Volatile Organic Compounds Emitted During Simulated Manufacturing of Engineered Wood Products Via a Sealed Caul Plate Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Compliance with national and local air emission regulations create the need to determine volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from adhesive-bonded structural wood products.
5.2 This method has been used to estimate the types and amounts of certain VOC that are emitted during production operations.
5.3 The method was originally developed to measure the methanol, formaldehyde, and phenol emitted in a laboratory setting that is designed to simulate the hot pressing, and post pressing conditions of hot stacking and cool down period for exterior plywood and laminated veneer lumber (LVL) processes. This current method generalizes the concept for adhesive-bonded wood products.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides a method for the collection of volatile organic compounds (VOC) that are emitted during the manufacture of engineered wood products using a laboratory environment designed to simulate a defined production process. The method is used for the determination of the amounts of methanol, formaldehyde, phenol and other VOC that may be emitted during conditions designed to simulate production such as hot pressing, the conditions of ‘hot stacking’ and ‘cool-down’ that occurs post-press.
1.2 The test method was originally developed to measure certain VOC from exterior plywood meeting Voluntary Product Standard PS 1–09 and structural composite lumber products such as laminated veneer lumber (LVL) meeting Specification D5456. Both of these product types are typically manufactured using phenol-formaldehyde resin based adhesives that meet Specification D2559.
1.3 The test method is suitable for many types of wood products bonded with adhesives.
1.4 This test method is specific for collecting VOC during simulated production of wood products and is not designed to determine general organic emissions from all indoor materials or sources.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Some specific hazards statements are given in Section 7 on Hazards.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D7770 − 12 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Method for
Collection of Volatile Organic Compounds Emitted During
Simulated Manufacturing of Engineered Wood Products Via
a Sealed Caul Plate Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7770; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.1 This test method provides a method for the collection of
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
volatile organic compounds (VOC) that are emitted during the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
manufacture of engineered wood products using a laboratory
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
environment designed to simulate a defined production pro-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
cess. The method is used for the determination of the amounts
ofmethanol,formaldehyde,phenolandotherVOCthatmaybe
2. Referenced Documents
emittedduringconditionsdesignedtosimulateproductionsuch
2.1 ASTM Standards:
as hot pressing, the conditions of ‘hot stacking’ and ‘cool-
D2145 Method of Test for Phenol Content of Phenol-Water
down’ that occurs post-press.
Mixtures (Withdrawn 1978)
1.2 The test method was originally developed to measure
D2559 Specification for Adhesives for Bonded Structural
certainVOCfromexteriorplywoodmeetingVoluntaryProduct
Wood Products for Use Under Exterior Exposure Condi-
Standard PS 1–09 and structural composite lumber products
tions
such as laminated veneer lumber (LVL) meeting Specification
D4442 Test Methods for Direct Moisture Content Measure-
D5456. Both of these product types are typically manufactured
ment of Wood and Wood-Based Materials
using phenol-formaldehyde resin based adhesives that meet
D4933 Guide for Moisture Conditioning of Wood and
Specification D2559.
Wood-Based Materials
1.3 The test method is suitable for many types of wood D5456 Specification for Evaluation of Structural Composite
products bonded with adhesives.
Lumber Products
E346 Test Methods for Analysis of Methanol (Withdrawn
1.4 This test method is specific for collecting VOC during
2017)
simulated production of wood products and is not designed to
E1333 Test Method for Determining Formaldehyde Concen-
determine general organic emissions from all indoor materials
trations in Air and Emission Rates from Wood Products
or sources.
Using a Large Chamber
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
2.2 Other Standards:
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
Voluntary Product Standard PS 1–09 Structural Plywood
only.
3. Terminology
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1 Definitions:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.1 target production process—asetofspecifiedmanufac-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
turing parameters that define the production of an adhesive
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
bonded wood product. For the purposes of this standard, those
Some specific hazards statements are given in Section 7 on
parameters are designed to be representative of a specific
Hazards.
production facility and are used to derive the test specimen.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D07 on Wood contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D07.03 on Panel Products. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2019. Published November 2019. Originally the ASTM website.
approved in 2012. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D7770–12. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/D7770-12R19. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D7770 − 12 (2019)
3.1.2 test specimen—a combination of defined wood ele- wood elements, and the concentrations of the VOC detected in
ments with or without applied adhesive that is exposed to the collection solutions are determined to be used to calculate
pressing and post pressing conditions in a defined laboratory the relative amount of methanol, formaldehyde, and phenol
setting that is designed to simulate the Target Production that are emitted during the test.
Process (see 3.1.1).
4.6 At least three test replications shall be conducted and
3.1.3 VOC—forthepurposesofthisstandard,thetermVOC results separately reported for each of the tests.
means the specific volatile organic compounds of
5. Significance and Use
formaldehyde,methanolandphenolthatareemittedfromatest
5.1 Compliance with national and local air emission regu-
specimen during the pressing and post pressing measurements.
lations create the need to determine volatile organic compound
4. Summary of Test Method (VOC) emissions from adhesive-bonded structural wood prod-
ucts.
4.1 A laboratory scale press is used to simulate the target
production process with respect to the key variables that 5.2 This method has been used to estimate the types and
influence the production process and that may affect the amounts of certain VOC that are emitted during production
emission of VOC. The lab press is fitted with a caul system to operations.
createasealaroundthepresssystemtopermitcollectionofthe
5.3 The method was originally developed to measure the
VOC discharged during the process. The sealed caul plate
methanol, formaldehyde, and phenol emitted in a laboratory
contains inlet and outlet ports to permit the controlled collec-
setting that is designed to simulate the hot pressing, and post
tion of the emitted VOC.
pressing conditions of hot stacking and cool down period for
exterior plywood and laminated veneer lumber (LVL) pro-
4.2 During the test, emitted VOC collect in the air space
encompassed within the sealed caul plate. The VOC are cesses. This current method generalizes the concept for
adhesive-bonded wood products.
collected by mixing them into a continuous flow of clean, dry
air that is injected into the sealed space via a controlled,
6. Apparatus
pressurized supply cylinder.
6.1 Laboratory Press. A laboratory scale press shall be
4.3 The VOC within the collected air stream are removed
equipped with automatic temperature (if hot pressing is used)
from the sealed caul system and then condensed into a water
and pressure controls to control the pressing conditions to
solution using impingers submerged into an ice bath.
simulate the production process. If required, the hot press
4.4 The collected solutions are diluted to concentrations
platens can be heated with any suitable means such as
ideally suited for instrumental analysis. They are analyzed to
electrical, hot oil or steam to control the press temperature
determine their methanol, formaldehyde and phenol content.
within 62°C (64°F) during the pressing operation. The hot
Several suitable analytical procedures are referenced in Ap-
pressplatensshallbeatleast600by600mm(24by24in.)and
pendix X1. shall accommodate the sealed caul plate described in 6.2.
4.5 The weight of the wood elements used to assemble the 6.2 Sealed Caul Plate. A machined aluminum caul plate is
wood test specimen, the weight of the adhesive applied to the fabricated to fit within the laboratory press.As shown in Fig. 1,
FIG. 1 Schematic of Sealed Caul Plate and Test Panel
D7770 − 12 (2019)
the outside dimensions of the plate are within 125 mm (5 in.) 6.3.9 Gasket Material.
of the outside dimension of the laboratory press. The sealed 6.3.10 O-ring gaskets.
caul plate is fabricated with holes in the sides to create air
7. Hazards
‘inlet’ and ‘outlet’ paths. The inlet and outlets are tapped to
receive threaded stainless steel tubing. It is permissible to fit
7.1 This test method involves heating, handling of wood
the ‘inlet’and ‘outlet’tubes with quick-disconnect couplings.
and adhesives, pressure, presence and handling of VOC and
The thickness of the sealed caul plate shall be thick enough to
handling of laboratory glassware.
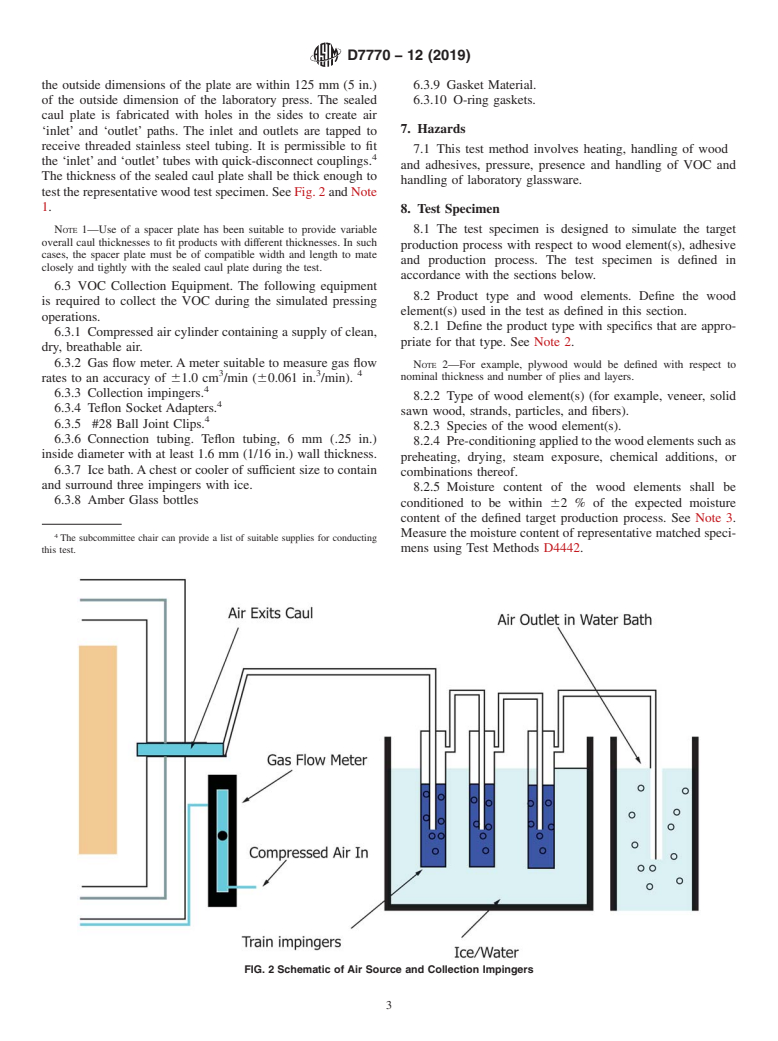
test the representative wood test specimen. See Fig. 2 and Note
1.
8. Test Specimen
NOTE 1—Use of a spacer plate has been suitable to provide variable 8.1 The test specimen is designed to simulate the target
overall caul thicknesses to fit products with different thicknesses. In such
production process with respect to wood element(s), adhesive
cases, the spacer plate must be of compatible width and length to mate
and production process. The test specimen is defined in
closely and tightly with the sealed caul plate during the test.
accordance with the sections below.
6.3 VOC Collection Equipment. The following equipment
8.2 Product type and wood elements. Define the wood
is required to collect the VOC during the simulated pressing
element(s) used in the test as defined in this section.
operations.
8.2.1 Define the product type with specifics that are appro-
6.3.1 Compressed air cylinder containing a supply of clean,
priate for that type. See Note 2.
dry, breathable air.
6.3.2 Gas flow meter. A meter suitable to measure gas flow
NOTE 2—For example, plywood would be defined with respect to
3 3 4
nominal thickness and number of plies and layers.
rates to an accuracy of 61.0 cm /min (60.061 in. /min).
6.3.3 Collection impingers.
8.2.2 Type of wood element(s) (for example, veneer, solid
6.3.4 Teflon Socket Adapters.
sawn wood, strands, particles, and fibers).
6.3.5 #28 Ball Joint Clips.
8.2.3 Species of the wood element(s).
6.3.6 Connection tubing. Teflon tubing, 6 mm (.25 in.)
8.2.4 Pre-conditioningappliedtothewoodelementssuchas
inside diameter with at least 1.6 mm (1/16 in.) wall thickness.
preheating, drying, steam exposure, chemical additions, or
6.3.7 Ice bath.Achest or cooler of sufficient size to contain
combinations thereof.
and surround three impingers with ice.
8.2.5 Moisture content of the wood elements shall be
6.3.8 Amber Glass bottles
conditioned to be within 62 % of the expected moisture
content of the defined target production process. See Note 3.
4 Measure the moisture content
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.