ASTM F2162-01
(Specification)Standard Specification for Bearing, Roller, Needle: Drawn Outer Ring, Full Complement, Without Inner Ring, Open and Closed End, Standard Type
Standard Specification for Bearing, Roller, Needle: Drawn Outer Ring, Full Complement, Without Inner Ring, Open and Closed End, Standard Type
SCOPE
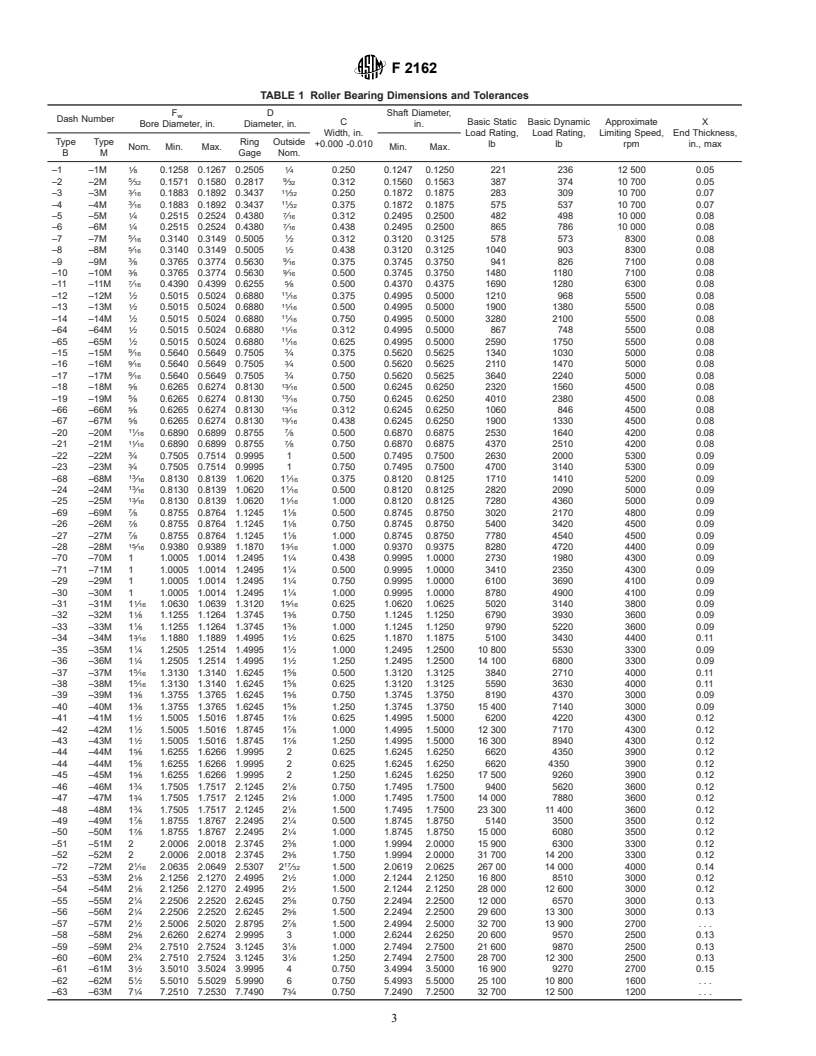
1.1 This specification covers standard-type needle roller bearings having drawn outer rings, full complement, without inner rings, with either open or closed ends.
1.2 The use of recycled materials that meet the requirements of the applicable material specification without jeopardizing the intended use of the item is encouraged.
1.3 The inner rings specified in this specification are not intended for use in flight critical systems of aircraft.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information only.
Note 1—This specification was originally developed by the Department of Defense and maintained by the Defense Supply Center Richmond. It is intended to replicate the requirements of MS 17130.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: F 2162 – 01
Standard Specification for
Bearing, Roller, Needle: Drawn Outer Ring, Full
Complement, Without Inner Ring, Open and Closed End,
1
Standard Type
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 2162; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope MIL-STD-130 Identification Marking of US Military Prop-
5
erty
1.1 This specification covers standard-type needle roller
2.5 American Bearing Manufacturer’s Association (ABMA)
bearings having drawn outer rings, full complement, without
Standard:
inner rings, with either open or closed ends.
STD 4 Tolerance Definitions and Gauging Practices For
1.2 The use of recycled materials that meet the requirements
6
Ball and Roller Bearings
of the applicable material specification without jeopardizing
2.6 ISO Standards:
the intended use of the item is encouraged.
7
ISO 5593 Rolling Bearings—Vocabulary
1.3 The inner rings specified in this specification are not
7
ISO 1132 Rolling Bearings—Tolerances—Definitions
intended for use in flight critical systems of aircraft.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3. Terminology
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this speci-
for information only.
fication, refer to ABMA STD 4 Tolerance Definitions and
NOTE 1—This specification was originally developed by the Depart-
Gauging Practices for Ball and Roller Bearings, ISO 1132
ment of Defense and maintained by the Defense Supply Center Richmond.
Roller Bearings—Tolerances—Definitions, and to ISO 5593
It is intended to replicate the requirements of MS 17130.
Rolling Bearings—Vocabulary
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
2. Referenced Documents
3.2.1 average life (L ), n—for a radial roller bearing, the
50
2.1 ASTM Standards:
number of revolutions that 50 % of a group of bearings will
E 18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness and Rockwell
complete or exceed before the first evidence of fatigue devel-
2
Superficial Hardness of Metallic Materials
ops.
E 140 Standard Hardness Conversion Tables for Metals
3.2.1.1 Discussion—The average life maybe as much as five
(Relationship Among Brinell Hardness, Vickers Hardness,
times the rating life.
Rockwell Hardness, Rockwell Superficial Hardness,
3.2.2 basic dynamic load rating (C ), n—for a radial roller
2
r
Knoop Hardness, and Scleroscope Hardness)
2 bearing, that calculated, constant radial load that a group of
E 384 Test Method for Microindentation Hardness
apparently identical bearings with stationary outer rings can
F 2163 Specification for Ring, Bearing, Inner: for Needle
theoretically endure for a rating life of one million revolutions
2
Roller Bearing With Drawn Outer Ring
of the inner ring.
2.2 ASME Standard:
3.2.2.1 Discussion—Since applied loading as great as the
ASME B 46.1 Surface Texture Surface Roughness, Wavi-
basic dynamic load rating tends to cause local plastic defor-
3
ness, and Lay
mation of the rolling surfaces, it is not anticipated that such
2.3 SAE Standard:
heavy loading would normally be applied.
4
SAE J-404 Chemical Composition of SAE Alloy Steels
3.2.3 basic static load rating (C ), n—for a radial roller
or
2.4 Military Standard:
bearing, that uniformly distributed static radial load which
produces a maximum contact stress of 580 000 psi (4000 Mpa)
1
at the center of the contact of the most heavily loaded rolling
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F34 on Rolling
Element Bearings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F34.01 on
element.
Rolling Element.
Current edition approved Dec. 12, 2001. Published March 2002.
2 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01. Available from USA Information Systems, 1092 Laskin Rd., Ste. 208, Virginia
3
Available from Global Engineering Documents, 15 Inverness Way, East Beach, VA 23451.
6
Englewood, CO 80112. Available from the American Bearing Manufacturer’s Association, 1200 19th
4
Available from SAI International, 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA St. NW, Ste. 300, Washington, DC 20036–2401.
7
15096-0001. Available from ANSI, 1819 L St. NW, Ste. 600, Washington, DC 20036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F 2162
3.2.3.1 Discussion—For this contact stress, total permanent 6.2 Rings—Rings shall be manufactured of steel, alloy, or
deformation of rolling element and raceway occurs which is carbon, carburizing grade 4620, 4720, 8620, 8720, or 1010-
approximately 0.0001 or the
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.