ASTM A439-83(1999)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Austenitic Ductile Iron Castings
Standard Specification for Austenitic Ductile Iron Castings
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers austenitic ductile iron castings which are used primarily for their resistance to heat, corrosion, and wear, and for other special purposes.
1.2 Austenitic ductile iron, also known as austenitic nodular iron or austenitic spheroidal iron, is characterized by having its graphite substantially in a spheroidal form and substantially free of flake graphite. It contains some carbides and sufficient alloy content to produce an austenitic structure.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A 439 – 83 (Reapproved 1999)
Standard Specification for
Austenitic Ductile Iron Castings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 439; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.4 If repair of castings is permitted (see 4.5),
3.1.5 Size and number of test bars required (see 9.1 through
1.1 This specification covers austenitic ductile iron castings
9.4 and 10.1),
which are used primarily for their resistance to heat, corrosion,
3.1.6 Special tests, if required (see 12.1),
and wear, and for other special purposes.
3.1.7 Certification, if required (see 14.1), and
1.2 Austenitic ductile iron, also known as austenitic nodular
3.1.8 Different preparation for delivery requirements, if
iron or austenitic spheroidal iron, is characterized by having its
needed (see 15.1).
graphite substantially in a spheroidal form and substantially
free of flake graphite. It contains some carbides and sufficient
4. Manufacture
alloy content to produce an austenitic structure.
4.1 Melting may be done in any furnaces that produce
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
castings meeting the chemical and mechanical requirements
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
outlined in this specification. These include cupolas, air fur-
information only.
naces, electric furnaces, crucible furnaces, etc.
2. Referenced Documents 4.2 By agreement between the manufacturer and the pur-
chaser, the castings may be stress relieved by heating to 1150
2.1 ASTM Standards:
to 1200°F (621 to 650°C) for not less than 1 h nor more than
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
2 h per inch of thickness in the thickest section. Heating and
of Steel Products
cooling shall be uniform and shall not be more than 400°F
A 732/A 732M Specification for Castings, Investment,
(222°C)/h for castings less than 1 in. (25.4 mm) in maximum
Carbon and Low Alloy Steel for General Application, and
thickness, nor more than 400°F (222°C) divided by the
Cobalt Alloy for High Strength at Elevated Temperatures
maximum section thickness in inches for thicker castings.
E 8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
During the cooling cycle, castings may be cooled in still air
E 30 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Steel, Cast
after the temperature has dropped to 600°F (315°C).
Iron, Open-Hearth Iron, and Wrought Iron
4.3 Whenever dimensional changes in high-temperature
E 59 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determination
service are a problem, by agreement between the manufacturer
of Chemical Composition
and the purchaser, the castings may be stabilized by heating at
E 351 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Cast Iron—
1600°F (870°C) for 1 h per inch of section, with a minimum of
All Types
1 h. Otherwise, the austenite which is super-saturated with
3. Ordering Information
respect to carbon may reject carbon during service and produce
dimensional changes.
3.1 Orders for material to this specification shall include the
4.4 By agreement between the manufacturer and the pur-
following information:
chaser, castings with chilled edges or excessive carbides may
3.1.1 ASTM designation,
be annealed at 1750 to 1900°F (955 to 1040°C) for ⁄2 to5h
3.1.2 Type of austenitic ductile iron required (see 6.1),
followed by uniform cooling, preferably in still air.
3.1.3 Heat treatment required (see 4.2 through 4.4),
4.5 Repair by welding, plugging, or other approved methods
may be done only with written permission from the purchaser.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A-4 on Iron
Castings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A04.02 on Malleable and 5. Magnetic Properties
Ductile Iron Castings.
5.1 In the event that nonmagnetic castings are specified, the
Current edition approved July 29, 1983. Published September 1983. Originally
magnetic permeability test shall be used. The maximum
published as A439–60T. Last previous edition A439–82.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
magnetic permeability value shall be agreed upon between the
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.02.
manufacturer and the purchaser.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.05.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A 439 – 83 (1999)
NOTE 1—A convenient shop test for differentiating the various types of
burnt-on sand and shall be reasonably smooth. Runners, risers,
austenitic ductile iron is based on the fact that a ground face of either the
fins, and other useless cast-on pieces shall be removed. In other
test bar or the castings of Types D-2 and D-2C will not attract a small steel
respects, the castings shall conform to whatever points may be
horseshoe-type magnet which is normally attracted to steel (Alnico
specifically agreed upon between the manufacturer and the
magnet should not be used). Types D-3, D-3A, D-5, and D-5B are
purchaser.
attracted, and types D-2B and D-4 may be slightly attracted. This
nonmagnetic test is a convenient qualitative test only for Types D-2 and
D-2C and shall not be used as a basis for acceptance.
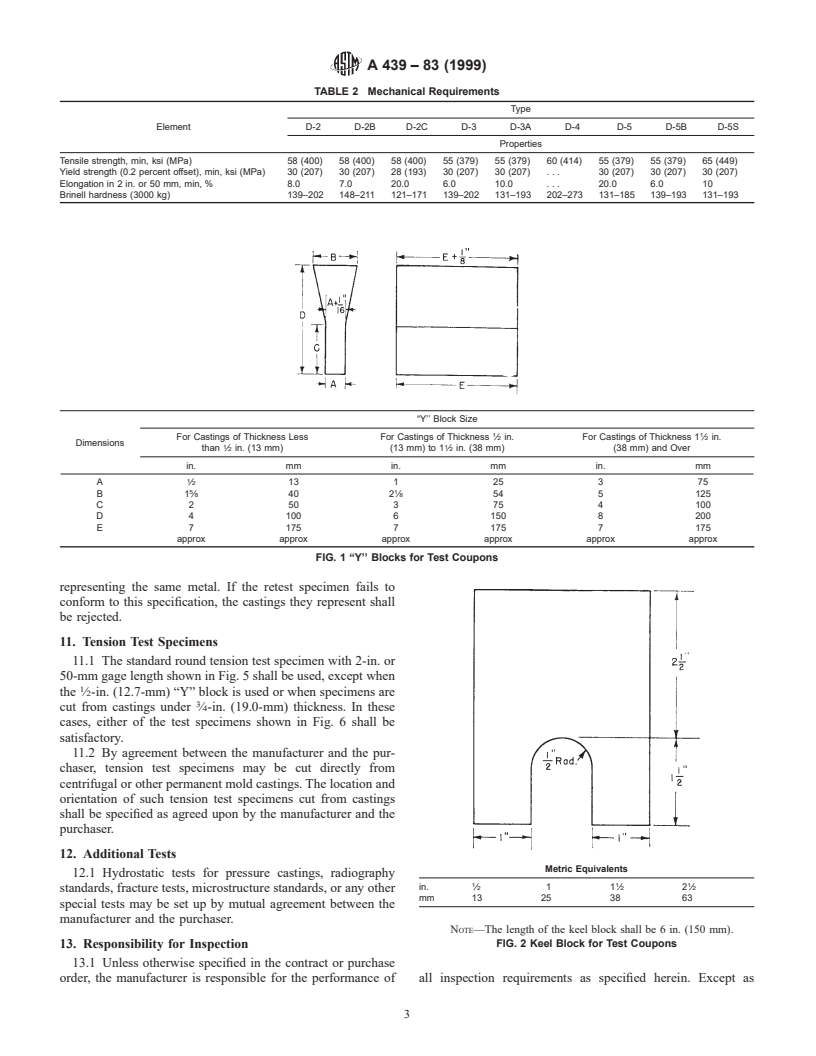
9. Test Bars
9.1 The standard test bars shall be the 1-in. (25.4-mm) “Y”
6. Chemical Requirements
block and 1-in. (25.4-mm) keel block as shown in Fig. 1 and
6.1 Many combinations of alloys can be used to obtain an
Fig. 2, respectively. A modified keel block cast from the mold
austenitic ductile iron. This specification includes nine general
shown in Fig. 3 may be substituted for the 1-in. (25.4-mm) “Y”
types defined by the composition limits in Table 1.
block or the 1-in. keel block.
6.2 Samples taken from test coupons, broken test speci-
9.2 Whenever the section size of the castings is consider-
mens, or castings shall conform to the requirements as to
ably less or greater than 1 in. (25.4 mm) and by agreement
chemical composition prescribed in Table 1. Sampling shall be
between the purchaser and the manufacturer, the ⁄2-in. (12.7-
conducted in accordance with Method E 59 and chemical
mm) or 3-in. (76.2-mm) “Y” blocks shown in Fig. 1 may be
analyses in accordance with Test Methods E 351 and Methods
used.
E 30. Methods E 30 should only be used for analyzing those
9.3 The test bars shall be cast in open molds made of a
elements for which specific coverage is not provided for in Test
suitable core sand with a minimum of 1 ⁄2 in. (38.1 mm) of
Methods E 351.
sand on all sides and bottom of the ⁄2 and 1-in. (12.7 and
6.3 Spectrometric techniques may also be used for analysis,
25.4-mm) test bars and 3 in. (76.2 mm) of sand for the 3-in.
but should a dispute arise concerning chemical composition,
(76.2-mm) test bar.
Test Methods E 351 and Methods E 30 shall be used for referee
9.4 When investment castings are made to this specification,
methods.
the manufacturer may use test specimens cast to size incorpo-
6.4 The chemical analysis for total carbon shall be made on
rated in the mold with the castings, or separately cast to size
either chilled cast pencil-type specimens or thin wafers ap-
using the same type of mold and the same thermal conditions
proximately ⁄32 in. (0.8 mm) thick cut from test coupons.
that are used to produce the castings. These test specimens
Drillings shall not be used because of attendant loss of
shall be made to the dimensions shown in Fig. 1 of Specifica-
graphite.
tion A 732 or Fig. 4 and Fig. 3 of Test Methods and Definitions
A 370.
7. Mechanical Requirements
9.5 It is recommended that test bars be poured immediately
7.1 Test specimens of austenitic ductile iron made according
after the castings and from the same ladle of metal. Test bars
to this specification shall meet the test requirements prescribed
shall be left in the mold until they have coole
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.