ASTM F2281-04(2017)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Stainless Steel and Nickel Alloy Bolts, Hex Cap Screws, and Studs, for Heat Resistance and High Temperature Applications
Standard Specification for Stainless Steel and Nickel Alloy Bolts, Hex Cap Screws, and Studs, for Heat Resistance and High Temperature Applications
ABSTRACT
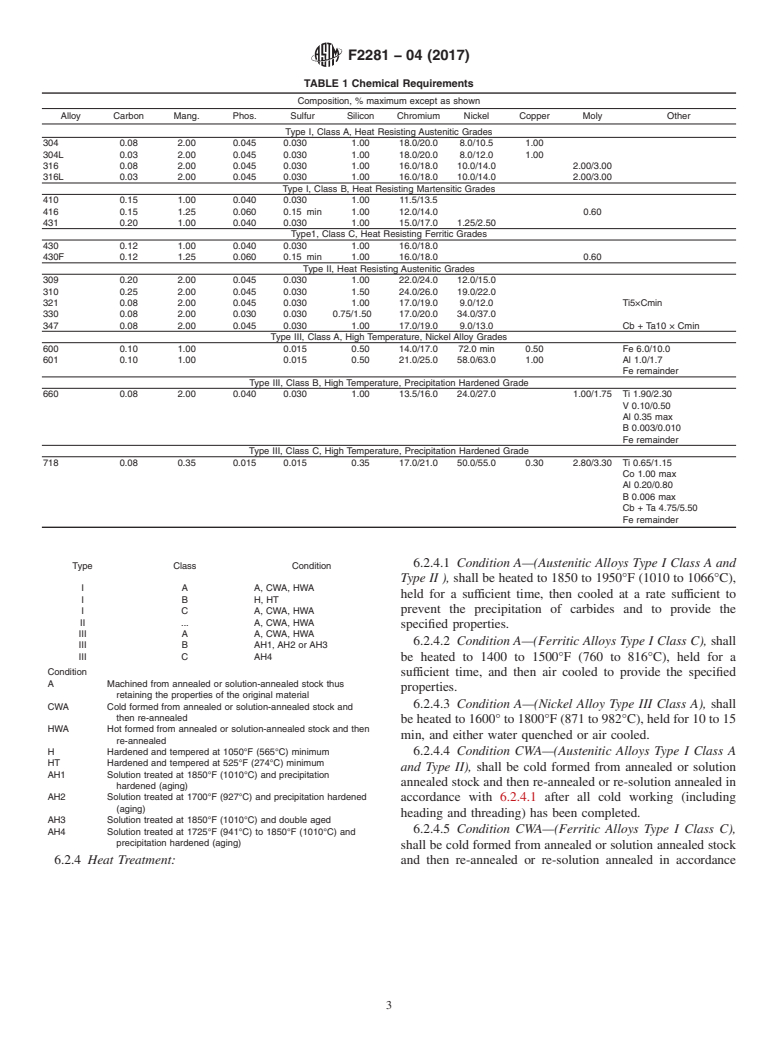
This specification covers the chemical and mechanical requirements for stainless steel and nickel alloy bolts, hex cap screws, and studs intended for use in applications where resistance to heat and the effects of high temperature are to be considered. Three types of materials covered in this specification are: Type I—heat resisting alloys for continuous service applications; Type II—heat resisting alloys for continuous and intermittent service applications; and Type III—high temperature alloys for continuous and intermittent service applications. Type I is classified further into Class A—austenitic grades, Class B—martensitic grades, and Class C—ferritic grades. Type III is also classified further into Class A—nickel based alloy, Class B—precipitation hardened alloy, and Class C—precipitation hardened alloy. The products shall be subject to: chemical analysis; mechanical tests to determine yield strength, wedge tensile strength, or axial tensile strength; and corrosion resistance tests to determine freedom from precipitated carbides.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the chemical and mechanical requirements for stainless steel and nickel alloy bolts, hex cap screws, and studs, 1/4 in. diameter and larger, intended for use at temperatures up to 1800°F (982°C), and in applications where resistance to heat and the effects of high temperature are to be considered. See Appendix X1 for Service Application. A wide variety of materials are covered in this specification which can be used at high temperatures as a function of the specific alloy properties, as well as environmental requirements including corrosive environments.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:F2281 −04 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Specification for
Stainless Steel and Nickel Alloy Bolts, Hex Cap Screws, and
Studs, for Heat Resistance and High Temperature
1
Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2281; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope A276 Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes
A342/A342M Test Methods for Permeability of Weakly
1.1 This specification covers the chemical and mechanical
Magnetic Materials
requirements for stainless steel and nickel alloy bolts, hex cap
A380 Practice for Cleaning, Descaling, and Passivation of
1
screws, and studs, ⁄4 in. diameter and larger, intended for use
Stainless Steel Parts, Equipment, and Systems
at temperatures up to 1800°F (982°C), and in applications
A484/A484M Specification for General Requirements for
where resistance to heat and the effects of high temperature are
Stainless Steel Bars, Billets, and Forgings
to be considered. See Appendix X1 for ServiceApplication.A
A493 Specification for Stainless Steel Wire and Wire Rods
wide variety of materials are covered in this specification
for Cold Heading and Cold Forging
which can be used at high temperatures as a function of the
A564/A564M Specification for Hot-Rolled and Cold-
specific alloy properties, as well as environmental require-
Finished Age-Hardening Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes
ments including corrosive environments.
A582/A582M Specification for Free-Machining Stainless
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
Steel Bars
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
A751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemi-
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
cal Analysis of Steel Products
and are not considered standard.
B637 Specification for Precipitation-Hardening and Cold
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Worked Nickel Alloy Bars, Forgings, and Forging Stock
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the for Moderate or High Temperature Service
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
B880 Specification for General Requirements for Chemical
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
Check Analysis Limits for Nickel, Nickel Alloys and
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Cobalt Alloys
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
D3951 Practice for Commercial Packaging
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- E21 TestMethodsforElevatedTemperatureTensionTestsof
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Metallic Materials
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Determine Conformance with Specifications
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. E76 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel-Copper
3
Alloys (Withdrawn 2003)
2. Referenced Documents
E139 Test Methods for Conducting Creep, Creep-Rupture,
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: and Stress-Rupture Tests of Metallic Materials
E292 Test Methods for Conducting Time-for-Rupture Notch
A262 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular
Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels Tension Tests of Materials
E353 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Stainless,
Heat-Resisting, Maraging, and Other Similar Chromium-
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F16 on
Nickel-Iron Alloys
Fasteners and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F16.04 on Nonferrous
Fasteners. E354 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of High-
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2017. Published December 2017. Originally
Temperature,Electrical,Magnetic,andOtherSimilarIron,
approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as F2281 – 04(2012).
Nickel, and Cobalt Alloys
DOI: 10.1520/F2281-04R17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F2281−04
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.