ASTM D2919-01(2007)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Durability of Adhesive Joints Stressed in Shear by Tension Loading
Standard Test Method for Determining Durability of Adhesive Joints Stressed in Shear by Tension Loading
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The combination of stress and moisture decreases the durability of most adhesive joints. Stresses in the presence of water or water vapor may cause some adhesive joints to fail at some small fraction of the stress required to break the dry joint. The time to failure for a given adhesive joint generally decreases with increasing stress, temperature, and relative humidity.
This test method may be used as an accelerated screening test for assessing the durability of adhesive joints. It may be used to measure durability of adhesive joints exposed outdoors or to environmental conditions experienced by adhesive joints in service. The tests may also be used to determine the effects of various surface preparations or substrates on durabilities of adhesive joints.
The durability performance of various adhesives may be compared by using this test method under uniform sets of conditions. To assess the overall durability of a given adhesive, lap-shear joints should be tested under a range of stress, relative humidity, and temperature. For a specific end use it may be possible to obtain the needed durability data using only one set of test conditions.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers data for assessing the durability of adhesive lap-shear joints while stressed in contact with air, air in equilibrium with certain solutions, water, aqueous solutions, or other environments at various temperatures.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in .
1.2 The values stated in SI units are considered to be the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2919 − 01 (Reapproved2007)
Standard Test Method for
Determining Durability of Adhesive Joints Stressed in Shear
by Tension Loading
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2919; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
Durability Test Apparatus Drawings
1.1 This test method covers data for assessing the durability
of adhesive lap-shear joints while stressed in contact with air,
3. Terminology
air in equilibrium with certain solutions, water, aqueous
3.1 Definitions—Definitions of terms in this test method
solutions, or other environments at various temperatures.
may be found in Terminology D907.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 4. Significance and Use
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 The combination of stress and moisture decreases the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
durability of most adhesive joints. Stresses in the presence of
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precau-
water or water vapor may cause some adhesive joints to fail at
tionary statements are given in 7.4.
some small fraction of the stress required to break the dry joint.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are considered to be the
The time to failure for a given adhesive joint generally
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
decreases with increasing stress, temperature, and relative
humidity.
2. Referenced Documents
4.2 This test method may be used as an accelerated screen-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ingtestforassessingthedurabilityofadhesivejoints.Itmaybe
D907 Terminology of Adhesives
used to measure durability of adhesive joints exposed outdoors
D1002 Test Method for Apparent Shear Strength of Single-
or to environmental conditions experienced by adhesive joints
Lap-Joint Adhesively Bonded Metal Specimens by Ten-
in service. The tests may also be used to determine the effects
sion Loading (Metal-to-Metal)
of various surface preparations or substrates on durabilities of
D1828 Practice for Atmospheric Exposure of Adhesive-
adhesive joints.
Bonded Joints and Structures
4.3 The durability performance of various adhesives may be
D2294 Test Method for Creep Properties of Adhesives in
compared by using this test method under uniform sets of
Shear by Tension Loading (Metal-to-Metal)
conditions.To assess the overall durability of a given adhesive,
D3165 Test Method for Strength Properties of Adhesives in
lap-shear joints should be tested under a range of stress,
Shear by Tension Loading of Single-Lap-Joint Laminated
relative humidity, and temperature. For a specific end use it
Assemblies
may be possible to obtain the needed durability data using only
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
one set of test conditions.
5. Apparatus
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D14 on
Adhesives and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D14.80 on Metal
5.1 Fixture, as shown in Fig. 1, is required for this test
Bonding Adhesives
method, although a fixture such as described in Test Method
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2007. Published October 2007. Originally
´1
approved in 1971. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D2919 – 01 . DOI:
D2294 may also be suitable for the performance of this test.
10.1520/D2919-01R07.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Detailed working drawings for the construction of the durability test apparatus
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on are available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No.
the ASTM website. ADJD2919. Original adjunct produced in 1980.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D2919 − 01 (2007)
FIG. 1 Durability Test Apparatus
5.2 Testing Machine, or other suitable machine capable of 6. Test Specimens
applying measured compressive loads. Force measurements
6.1 The successful use of this test method depends on
have an accuracy of 61 % of any reading when calibrated in
preparing good quality lap-shear joints. The test joints must be
compliance with Practices E4 requirements. Machine that is
prepared carefully in accordance with the adhesive manufac-
equipped with a suitable loading base as shown in Fig. 1, shall
turer’s directions or in accordance with some other specified
be used as a loading mechanism.
set of conditions agreed upon between the manufacturer and
5.3 Outdoor Weathering Racks (Standard) are recom- the purchaser. It is recommended that the test joints be
mended (Practice D1828), but any stable frame may be used prepared in accordance with Test Method D1002, except that
(for example, galvanized pipe or painted steel channel). No the dimensions of the test specimens shall be as shown in Fig.
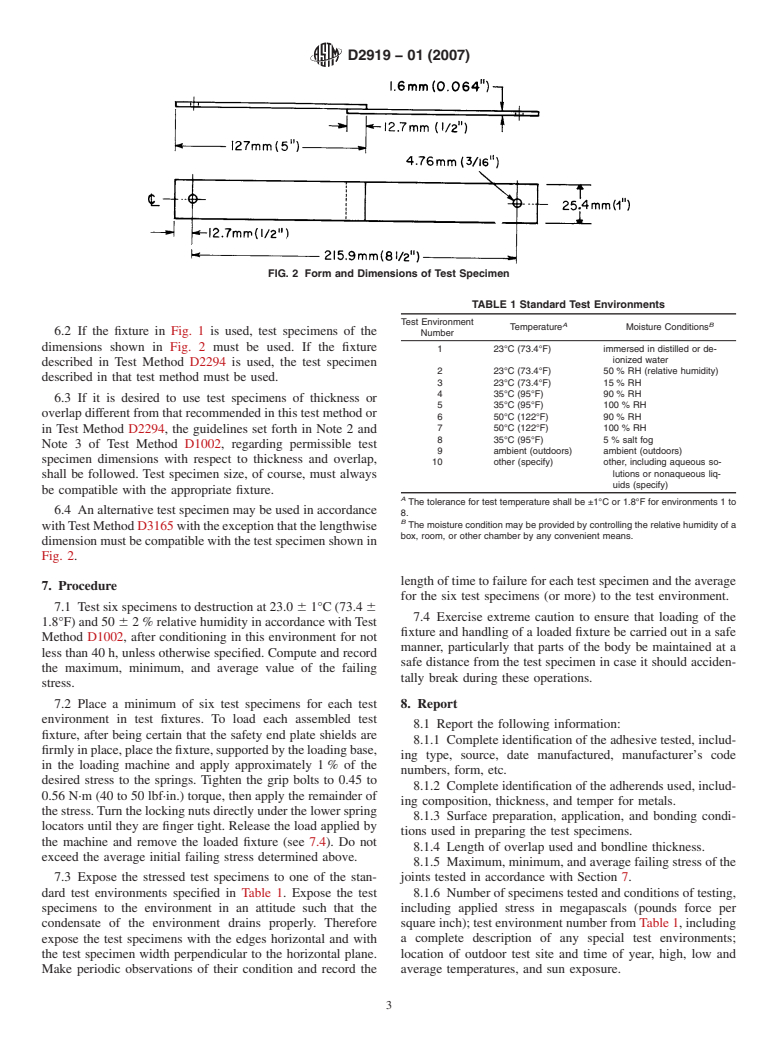
other special apparatus is required for outdoor tests. 2.
D2919 − 01 (2007)
FIG. 2 Form and Dimensions of Test Specimen
TABLE 1 Standard Test Environments
Test Environment
A B
Temperature Moisture Conditions
6.2 If the fixture in Fig. 1 is used, test specimens of the
Number
dimensions shown in Fig. 2 must be used. If the fixture
1 23°C (73.4°F)
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.