ASTM F81-01
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring Radial Resistivity Variation on Silicon Wafers (Withdrawn 2003)
Standard Test Method for Measuring Radial Resistivity Variation on Silicon Wafers (Withdrawn 2003)
SCOPE
This standard was transferred to SEMI (www.semi.org) May 2003
1.1 This test method provides procedures for the determination of relative radial variation of resistivity of semiconductor wafers cut from silicon single crystals grown either by the Czochralski or floating-zone technique.
1.2 This test method provides procedures for using Test Method F84 for the four-point probe measurement of radial resistivity variation.
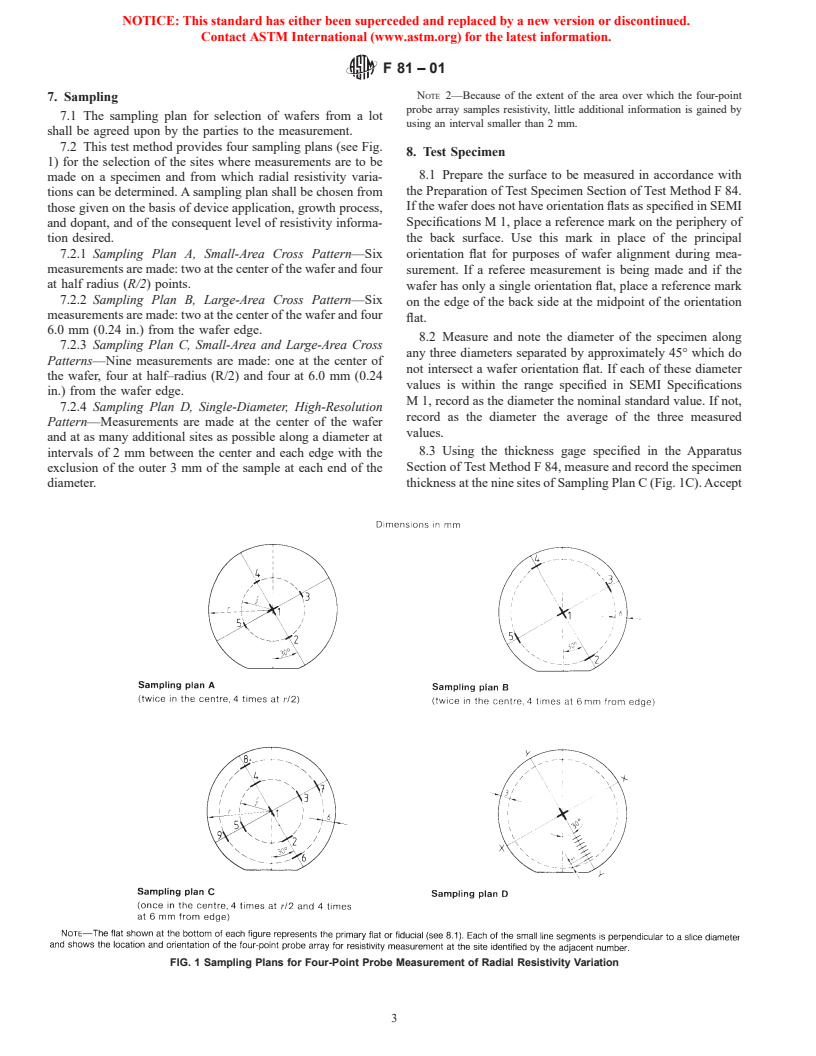
1.3 This test method yields a measure of the variation in resistivity between the center and selected outer regions of the specimen. The amount of information obtained regarding the magnitude and form of the variation in the intervening regions when using the four-point probe array depends on the sampling plan chosen (see 7.2). The interpretation of the variations measured as radial variations may be in error if azimuthal variations on the wafer or axial variations along the crystal length are not negligible.
1.4 This test method can be applied to single crystals of silicon in circular wafer form, the thickness of which is less than one-half of the average probe spacing, and the diameter of which is at least 15 mm (0.6 in.). Measurements can be made on any specimen for which reliable resistivity measurements can be obtained. The resistivity measurement procedure of Test Method F84 has been tested on specimens having resistivities between 0.0008 and 2000 cm for p-type silicon and between 0.0008 and 6000 cm for n-type silicon. Geometrical correction factors required for these measurements are included for the case of standard wafer diameters, and are available in tabulated form for other cases.
Note 1--In the case of wafers whose thickness is greater than the average spacing of the measurement probes, no geometrical correction factor is available except for measurement at the center of the wafer face.
1.5 Several sampling plans are given which specify sets of measurement sites on the wafers being tested. The sampling plans allow differing levels of detail of resistivity variation to be obtained. One of these sampling plans shall be selected and agreed upon by the parties to the measurement. The basic resistivity measurements of Test Method F 84 are then applied at each site specified in the chosen sampling plan.
1.6 Results are expressed as relative changes in resistivity between the several measurement sites. To obtain absolute values of resistivity it is necessary to measure and correct for specimen temperature (see 11.1.4).
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
DIN 50435
Designation: F 81 – 01
Standard Test Method for
1
Measuring Radial Resistivity Variation on Silicon Wafers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 81; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
average spacing of the measurement probes, no geometrical correction
1. Scope
factor is available except for measurement at the center of the wafer face.
2
1.1 This test method provides procedures for the determi-
1.5 Several sampling plans are given which specify sets of
nation of relative radial variation of resistivity of semiconduc-
measurement sites on the wafers being tested. The sampling
tor wafers cut from silicon single crystals grown either by the
plans allow differing levels of detail of resistivity variation to
Czochralski or floating-zone technique.
be obtained. One of these sampling plans shall be selected and
1.2 This test method provides procedures for using Test
agreed upon by the parties to the measurement. The basic
Method F 84 for the four-point probe measurement of radial
resistivity measurements of Test Method F 84 are then applied
resistivity variation.
at each site specified in the chosen sampling plan.
1.3 This test method yields a measure of the variation in
1.6 Results are expressed as relative changes in resistivity
resistivity between the center and selected outer regions of the
between the several measurement sites. To obtain absolute
specimen. The amount of information obtained regarding the
values of resistivity it is necessary to measure and correct for
magnitude and form of the variation in the intervening regions
specimen temperature (see 11.1.4).
when using the four-point probe array depends on the sampling
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
plan chosen (see 7.2). The interpretation of the variations
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
measured as radial variations may be in error if azimuthal
only.
variations on the wafer or axial variations along the crystal
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
length are not negligible.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.4 This test method can be applied to single crystals of
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
silicon in circular wafer form, the thickness of which is less
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
than one-half of the average probe spacing, and the diameter of
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
which is at least 15 mm (0.6 in.). Measurements can be made
on any specimen for which reliable resistivity measurements
2. Referenced Documents
can be obtained. The resistivity measurement procedure of Test
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Method F 84 has been tested on specimens having resistivities
F 84 Test Method for Measuring Resistivity of Silicon
between 0.0008 and 2000 V·cm for p-type silicon and between
4
Wafers with an In-Line Four-Point Probe
0.0008 and 6000 V·cm for n-type silicon. Geometrical correc-
2.2 SEMI Standard:
tion factors required for these measurements are included for
Specifications M 1, for Polished Monocrystalline Silicon
the case of standard wafer diameters, and are available in
5
3
Wafers
tabulated form for other cases.
NOTE 1—In the case of wafers whose thickness is greater than the
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 Resistivity measurements are made at specified sites
1 along one or two diameters of a semiconductor specimen in
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F1 on
accordance with a sampling plan selected from the four given.
Electronics, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F01.06 on Silicon
Materials and Process Control.
Choice among the sampling plans is made on the basis of the
Current edition approved June 10, 2001. Published August 2001. Originally
extent of information required regarding possible resistivity
published as F 81 – 67 T. Last previous edition F 81 – 00.
2
variations. The measured resistivity values are corrected for
DIN 50435 is an equivalent method. It is the responsibility of DIN Committee
NMP 221, with which Committee F-1 maintains close liaison. DIN 50435, specimen geometry and, if desired, for temperature, and
Determination of the Radial Resistivity Variation of Silicon or Germanium Slices by
suitable differences are taken to obtain the resistivity variation.
Means of a Four-Point DC-Probe, is available from Beuth Verlag GmbH, Burg-
grafenstrasse 4-10, D-1000 Berlin 30,
3
Swartzendruber, L. J., “Correction Factor Tables for Four-Point Probe Resis-
4
tivity Measurement
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.