ASTM D7-27
(Test Method)Test Method for Sieve Analysis of Fine and Aggregates (Withdrawn 1938)
Test Method for Sieve Analysis of Fine and Aggregates (Withdrawn 1938)
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
•
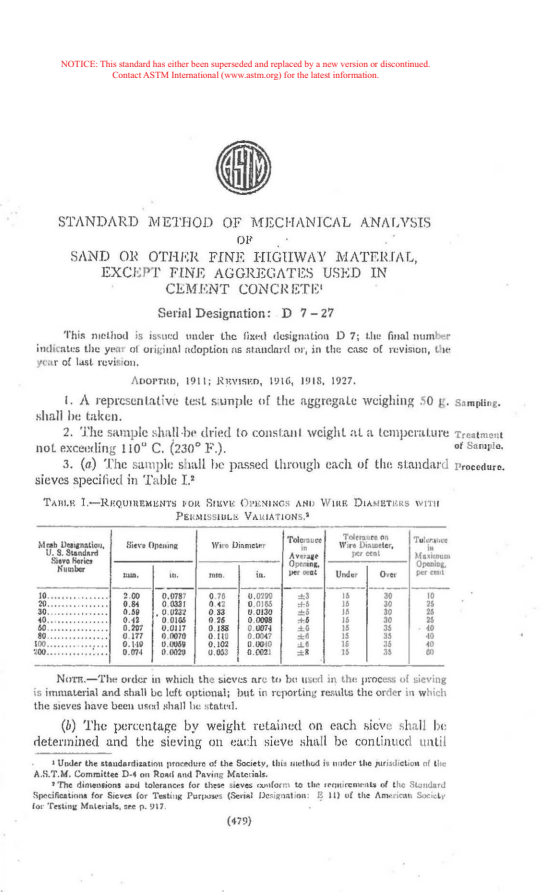
STANDARD METHOD OF 1\'.fECHANlCJ\L AN/\LY~TS
OP
SAND 01< OTI·lft:R FINE HIGHWAY MATF.lUJ\L,
EXCEPT FJNE AGGREGATES USED IN
1
Cl!.1\fENT CON CJ~ gTE
Serini Designation: D 7 - 27
This niclhotl is is~w:tl uutler the fi:u,ll 1lcsii;natio11 D 7; I.he final numl ·r
ind1rnt1:s the yt•n- ol origiunl ndoption ns r,tnndnrcl nr, in the c:isc o( revision, t 1e
lt'·u· oC l.tsl rcvit.•on.
Aoormo, 1911; H iw1s1m, l!>lIS, 1927.
I. A reprcsenlalivc lest s unplc of lht! aggregalc weighing SO b.· Sampling.
sha ll he taken.
2. The sample sha!l ·lw drit~d lo r.omta11 I weight al a lcmpcml.ure Treatment
not exr.el!ding 110° C. (230° F.). of Snm11lo,
3. (a) '.l.'hc sample s •mll lie passed through each of the standard Proccdur~.
sieves specified in Ta ble I.2
TATll.1' I.-RHQ.Ullll!MIH'11'S J· Oll 8rnv1~ 0l'E:-llNGS Mill Wurn D1AM1n1ms w n 11
P1m.,11ss1ut.i. VA1t1A T10Ns.'
Tnltl'Qllt~ on
Tolcrou~ Tu!t:tahce
Me1h Vt.111nA,io1J, Sit\"t Opcrnncr: Wiro Uinmclor Wire Di.iutcr,
i•
U. S. Stand•nl per ctnl
'"
Aver>1t MuiU>u Ill
Sl"o fiorico
Opemn~
Oi-i•c.
N'u01bcr
per ttUI
llWI. lfl, min. in. Undor Over
l.>et °""'
--------- ---
--- ---
10 . . . . . . 2.00 0.0787 0.10 0.021Xl ::3 16 30 10
20 . . . . . . . O.SI 0 .0331 0 42 0 .0l&S :H 16 30 26
30 . . . . . . 11.58 . o.u2ai 0 83 IJ.0130 J6 30 u
:H
•o . . O.i2 0 0106 () 26 0 .0098 :H 16 30 26
60 . . . 0 . 207 U.0117 0 .188 O.IXIH .:l.G 16 36
•o
80 . . . . . 0 171 0 .0070 0 110 0.0047 15 36 40
:H
1
...
This May Also Interest You
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The primary use of these test methods is testing to determine the specified mechanical properties of steel, stainless steel, and related alloy products for the evaluation of conformance of such products to a material specification under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 and its subcommittees as designated by a purchaser in a purchase order or contract.
4.1.1 These test methods may be and are used by other ASTM Committees and other standards writing bodies for the purpose of conformance testing.
4.1.2 The material condition at the time of testing, sampling frequency, specimen location and orientation, reporting requirements, and other test parameters are contained in the pertinent material specification or in a general requirement specification for the particular product form.
4.1.3 Some material specifications require the use of additional test methods not described herein; in such cases, the required test method is described in that material specification or by reference to another appropriate test method standard.
4.2 These test methods are also suitable to be used for testing of steel, stainless steel and related alloy materials for other purposes, such as incoming material acceptance testing by the purchaser or evaluation of components after service exposure.
4.2.1 As with any mechanical testing, deviations from either specification limits or expected as-manufactured properties can occur for valid reasons besides deficiency of the original as-fabricated product. These reasons include, but are not limited to: subsequent service degradation from environmental exposure (for example, temperature, corrosion); static or cyclic service stress effects, mechanically-induced damage, material inhomogeneity, anisotropic structure, natural aging of select alloys, further processing not included in the specification, sampling limitations, and measuring equipment calibration uncertainty. There is statistical variation in all aspects of mechanical testin...
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods2 cover procedures and definitions for the mechanical testing of steels, stainless steels, and related alloys. The various mechanical tests herein described are used to determine properties required in the product specifications. Variations in testing methods are to be avoided, and standard methods of testing are to be followed to obtain reproducible and comparable results. In those cases in which the testing requirements for certain products are unique or at variance with these general procedures, the product specification testing requirements shall control.
1.2 The following mechanical tests are described:
Sections
Tension
7 to 14
Bend
15
Hardness
16
Brinell
17
Rockwell
18
Portable
19
Impact
20 to 30
Keywords
32
1.3 Annexes covering details peculiar to certain products are appended to these test methods as follows:
Annex
Bar Products
Annex A1
Tubular Products
Annex A2
Fasteners
Annex A3
Round Wire Products
Annex A4
Significance of Notched-Bar Impact Testing
Annex A5
Converting Percentage Elongation of Round Specimens to
Equivalents for Flat Specimens
Annex A6
Testing Multi-Wire Strand
Annex A7
Rounding of Test Data
Annex A8
Methods for Testing Steel Reinforcing Bars
Annex A9
Procedure for Use and Control of Heat-cycle Simulation
Annex A10
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 When these test methods are referenced in a metric product specification, the yield and tensile values may be determined in inch-pound (ksi) units then converted into SI (MPa) units. The elongation determined in inch-pound gauge lengths of 2 in. or 8 in. may be report...
- Standard51 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Standard51 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 This practice is intended to confirm the method of obtaining and evaluating the fluorescent penetrant indications on metallic surgical implants.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice is intended as a standard for fluorescent penetrant inspection of metallic surgical implants.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Standard2 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Standard2 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method was developed to evaluate the ability of a heavy-duty diesel engine coolant to provide protection against damage resulting from a phenomenon known as cylinder liner cavitation corrosion.
5.2 This test method may be used for engine coolant specification acceptance when all details of this test method are in compliance.
5.3 The design of the engine used in this test method is a production OEM diesel engine modified to consistently produce the operating conditions that accelerate damage from cylinder liner cavitation. This factor, along with the accelerated operating conditions needs to be considered when extrapolating test results.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is commonly referred to as the John Deere Cavitation Test.2 The test method defines a heavy-duty diesel engine to evaluate coolant protection as related to cylinder liner pitting caused by cavitation.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only. The only exception is where there is no direct SI equivalent such as screw threads, national pipe threads/diameters, and tubing sizes.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See Annex A1 for general safety precautions.
1.4 Table of Contents:
Scope
1
Referenced Documents
2
Terminology
3
Summary of Test Method
4
Significance and Use
5
Apparatus
6
Test Engine Configuration
6.1
Test Engine
6.1.1
Test Stand Configuration
6.2
Engine Mounting
6.2.1
Intake Air System
6.2.2
Aftercooler
6.2.3
Exhaust System
6.2.4
Fuel System
6.2.5
Coolant System
6.2.6
Oil System
6.2.7
Oil Volume
6.2.7.1
Pressurized Oil Fill System
6.2.7.2
External Oil System
6.2.7.3
Oil Sample Valve Location
6.2.7.4
Unacceptable Oil System Materials
6.2.7.5
Crankcase Aspiration
6.3
Blowby Rate
6.4
System Time Responses
6.5
Clearance Measurements
6.6
Engine and Cleaning Fluids
7
Engine Oil
7.1
Test Fuel
7.2
Test Coolant
7.3
Solvent
7.4
Preparation of Apparatus
8
Cleaning of Parts
8.1
General
8.1.1
Engine Block
8.1.2
Cylinder Head
8.1.3
Rocker Cover and Oil Pan
8.1.4
External Oil System
8.1.5
Rod Bearing Cleaning and Measurement
8.1.6
Ring Cleaning and Measurement
8.1.7
Injector Nozzle
8.1.8
Pistons
8.1.9
Engine Assembly
8.2
General
8.2.1
Parts Reuse and Replacement
8.2.2
Build-Up Oil
8.2.3
Coolant Thermostat
8.2.4
Fuel Injectors
8.2.5
New Parts
8.2.6
Operational Measurements
8.3
Units and Formats
8.3.1
Instrumentation Calibration
8.3.2
Fuel Consumption Rate Measurement Calibration
8.3.2.1
Temperature Measurement Calibration
8.3.2.2
Pressure Measurement Calibration
8.3.2.3
Temperatures
8.3.3
Measurement Location
8.3.3.1
Coolant Out Temperature
8.3.3.2
Coolant In Temperature
8.3.3.3
Fuel In Temperature
8.3.3.4
Oil Gallery Temperature
8.3.3.5
Intake Air Temperature
8.3.3.6
Intake Air after Compressor Temperature
8.3.3.7
Intake Manifold Temperature
8.3.3.8
Exhaust Temperature
8.3.3.9
Exhaust after Turbo Temperature
8.3.3.10
Additional Temperatures
8.3.3.11
Pressures
8.3.4
Measurement Location and Equipment
8.3.4.1
Condensation Trap
8.3.4.2
Coolant Pressure
8.3.4.3
Fuel Pressure
8.3.4.4
Oil Gallery Pressure
8.3.4.5
Intake Air Pressure
8.3.4.6
Intake Air after Comp...
- Standard24 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is designed to determine the temperature at which the Wet Blue or Wet White specimen experiences shrinkage. In this test method, shrinkage occurs as a result of hydrothermal denaturation of the collagen protein molecules which make up the fiber structure of the Wet Blue or Wet White. The shrinkage temperature of Wet Blue or Wet White is influenced by many different factors, most of which appear to affect the number and nature of crosslinking interactions between adjacent polypeptide chains of the collagen protein molecules. The value of the shrinkage temperature of Wet Blue or Wet White is commonly used as an indicator of the type of tannage or the degree of tannage, or both, of that particular Wet Blue or Wet White (especially for the more hydrothermally stable tannages such as chrome tannage).
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the shrinkage temperature of all types of Wet Blue and Wet White. The heating medium is water when the shrinkage temperature is at or below 98 °C. The heating medium is a glycerine-water solution when the shrinkage temperature is above 98 °C.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Standard3 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This standard provides guidance to obtain data that is the most representative of the material’s characteristics and performance. To properly evaluate EPDM, tests should be performed in accordance with specific test methods and procedures.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers and provides recommendations for the selection of appropriate test methods for Ethylene Propylene Diene Terpolymer (EPDM) geomembranes used in geotechnical and geoenvironmental applications.
1.2 This guide includes test methods for three different types of EPDM geomembranes including: scrim-reinforced membranes, composite membranes, and smooth, nonreinforced membranes.
1.3 The test methods are divided into three categories including manufacturing quality control, optional performance tests, and seam testing.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Guide3 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
ABSTRACT
This specification contains the general requirements for the 245/7OR19.5 136/134M radial truck standard reference test. Provided in this specification is a 19.5 rim diameter code standard truck design and construction, standard dimensions, and standard conditions of storage. A reference tire is covered in this specification for braking traction, snow traction, wear evaluations pavement roughness, noise and other forms of test requiring a reference tire. Test methods of the tensile sheet cure, the 300% stress elongation, and tensile sheet strength should be in accordance to the specified testing requirements presented in D3182, and D412. The testing procedure also includes using of Type A durometer centred at the presser foot at a minimum of 6.0 mm, chaking the durometer operation and the state of durometer calibration with rubber reference, determining tire tread hardness by four readings and quickly applying the presser foot to the tire tread without inducing shock.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the general requirements for the 245/70R19.5 136/134M radial truck standard reference test tire. The tire covered by this specification is primarily for use as a reference tire for braking traction, snow traction, and wear performance evaluations, but may also be used for other evaluations, such as pavement roughness, noise, or other tests that require a reference tire.
1.1.1 Other standard reference test tires are also used for these purposes and are referenced in Section 2.
1.2 This specification provides a 19.5 rim diameter code standard truck tire design and construction, standard dimensions, and specifies the conditions of storage.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to inch-pound units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Technical specification5 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Technical specification5 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method may be used to evaluate the difference in gloss of dried films of emulsion floor polishes when the light reflected at a 60° angle is measured. Extremely high- or low-gloss polishes may not be differentiated at a 60° angle. A20° angle measured in accordance with Test Method D523 may give better definition of gloss.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the 60° specular gloss of films of emulsion floor polish after application to a substrate.
Note 1: Specular gloss is one of several related appearance attributes that produce the sensation of glossiness. For this reason, specular gloss measurements may not always correlate well with visual rankings of glossiness.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Standard2 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The properties determined by these test methods are of value in material specifications, qualifications, data base generation, certification, research, and development.
5.2 These test methods are intended for the testing of fibers that have been specifically developed for use as reinforcing agents in advanced composite structures. The test results of an impregnated and consolidated fiber should be representative of the strength and modulus that are available in the material when used as intended. The performance of fibers in different resin systems can vary significantly so that correlations between results using these test methods and composite testing may not always be obtained.
5.3 The reproducibility of test results is dependent upon precise control over all test conditions. Resin type, content and distribution, curing process, filament alignment, gripping in the testing machine, and alignment in the testing machine are of special importance.
5.4 The measured strengths of fibers are not unique quantities and test results are strongly dependent on the test methods used. Therefore the test method described here will not necessarily give the same mean strengths or standard deviations as those obtained from single filaments, dry fibers, composite laminas, or composite laminates.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the preparation and tensile testing of resin-impregnated and consolidated test specimens made from continuous filament carbon and graphite yarns, rovings, and tows to determine their tensile properties.
1.2 These test methods also cover the determination of the density and mass per unit length of the yarn, roving, or tow to provide supplementary data for tensile property calculation.
1.3 These test methods include a procedure for sizing removal to provide the preferred desized fiber samples for density measurement. This procedure may also be used to determine the weight percent sizing.
1.4 These test methods include a procedure for determining the weight percent moisture adsorption of carbon or graphite fiber.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Standard8 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Standard8 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Use of the SIM decreases the time required for creep to occur and the obtaining of the associated data.
5.2 The statements set forth in 1.5 are very important in the context of significance and use, as well as scope of the standard.
5.3 Creep test data are used to calculate the creep modulus of materials as a function of time. These data are then used to predict the long-term creep deformation expected of geosynthetics used in drainage applications.
Note 1: Currently, SIM testing has focused mainly on geonets made from high-density polyethylene. Additional testing on other materials is ongoing.
5.4 R+H testing is done to establish the range of creep strains experienced in the brief period of very rapid response following the peak of the load ramp.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers accelerated testing for compressive creep properties using the stepped isothermal method (SIM).
1.2 The test method is focused on geosynthetic drainage materials such as HDPE geonet specimens.
1.3 The SIM tests are laterally unconfined tests based on time-temperature superposition procedures.
1.4 Ramp and hold (R+H) tests may be completed in conjunction with SIM tests. They are designed to provide additional estimates of the initial rapid compressive creep strain levels appropriate for the SIM results.
1.5 This method can be used to establish the sustained load compressive creep characteristics of a geosynthetic that demonstrates a relationship between time-dependent behavior and temperature. Results of this method are to be used to augment results of compressive creep tests performed at 20 ± 1 °C and may not be used as the sole basis for determination of long-term compressive creep behavior of geosynthetic material.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Standard8 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 This test method provides the means to determine nitrogen containing water extractable materials such as excess and loosely bound tannins, ammonium salts, and nitrates.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers quantitatively determining the water extractable nitrogen in leather.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Standard2 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.