ASTM B438-08
(Specification)Standard Specification for Bronze-Base Powder Metallurgy (PM) Bearings (Oil-Impregnated)
Standard Specification for Bronze-Base Powder Metallurgy (PM) Bearings (Oil-Impregnated)
ABSTRACT
This specification covers sintered bronze, oil-impregnated bearings made primarily from elemental copper, tin, lead, and graphite powders. This specification covers the following variables: Grades (available in three bronze base compositions identifiable by different graphite contents and one leaded bronze grade) and Type (Grades 1 and 2 are available in four types described by specific density ranges. Grade 3 is available in two types and Grade 4 is available in one type). Sintered bronze bearings shall be made by molding or briquetting metal powder mixtures to the proper density. The material shall conform to the required chemical composition for copper, tin, graphite, iron, lead, zinc, nickel, and antimony. The density of bearings supplied impregnated with lubricant shall be within the prescribed limits. Oil content of bearings shall not be less than the prescribed value for each grade and type of material. The material of different grades and types shall conform to the prescribed radial crushing strength requirements. An acceptance specification for the minimum bearing breaking load may be established for any specific standard oil-impregnated bearing. Chemical analysis shall be made for each representative sample of chips, which may be obtained by milling, drilling, filing, or crushing a bearing with clean dry tools without lubrication.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers porous metallic sleeve, flange, thrust and spherical bronze-base bearings that are produced from mixed metal powders utilizing powder metallurgy (PM) technology and then impregnated with oil to supply operating lubrication.
1.2 Included are the specifications for the chemical, physical and mechanical requirements of those bronze-base PM materials that have been developed and standardized specifically for use in the manufacture of these self-lubricating bearings.
1.3 This specification is applicable to the purchase of bronze-base bearings (oil-impregnated) that were formerly covered by military specifications and are intended for government or military applications. Those additional government requirements that only apply to military bearings are listed in the Supplementary Requirements section of this specification.
1.4 This specification acccompanies Specification B 439 that covers the requirements for Iron-Base Powder Metallurgy (PM) Bearings, (Oil-Impregnated).
1.5 Typical applications for bronze-base bearings are listed in Appendix X1.
1.6 Bearing dimensional tolerance data are shown in Appendix X2, while engineering information regarding installation and operating parameters of PM bearings is included in Appendix X3. Additional useful information on self-lubricating bearings can be found in MPIF Standard 35 and the technical literature.
1.7 With the exception of density values for which the g/cm3 unit is the industry standard, the values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The SI equivalents of inch-pound units, shown in parenthesis, have been converted in accordance with IEEE/ASTM SI 10, may be approximate and are only for information.
1.8 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods described in this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:B438 −08
StandardSpecification for
Bronze-Base Powder Metallurgy (PM) Bearings (Oil-
Impregnated)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B438; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* beenconvertedinaccordancewithIEEE/ASTMSI10,maybe
approximate and are only for information.
1.1 This specification covers porous metallic sleeve, flange,
1.8 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
thrust and spherical bronze-base bearings that are produced
test methods described in this specification. This standard does
from mixed metal powders utilizing powder metallurgy (PM)
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
technology and then impregnated with oil to supply operating
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
lubrication.
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
1.2 Included are the specifications for the chemical, physi-
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
cal and mechanical requirements of those bronze-base PM
to use.
materials that have been developed and standardized specifi-
cally for use in the manufacture of these self-lubricating
2. Referenced Documents
bearings.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.3 This specification is applicable to the purchase of
B243Terminology of Powder Metallurgy
bronze-base bearings (oil-impregnated) that were formerly
B328Test Method for Density, Oil Content, and Intercon-
coveredbymilitaryspecificationsandareintendedforgovern-
nected Porosity of Sintered Metal Structural Parts and
ment or military applications. Those additional government
Oil-Impregnated Bearings (Withdrawn 2009)
requirements that only apply to military bearings are listed in
B439Specification for Iron-Base Powder Metallurgy (PM)
the Supplementary Requirements section of this specification.
Bearings (Oil-Impregnated)
1.4 ThisspecificationacccompaniesSpecificationB439that
B939Test Method for Radial Crushing Strength, K,of
covers the requirements for Iron-Base Powder Metallurgy
Powder Metallurgy (PM) Bearings and Structural Materi-
(PM) Bearings, (Oil-Impregnated).
als
B946Test Method for Surface Finish of Powder Metallurgy
1.5 Typical applications for bronze-base bearings are listed
(PM) Products
in Appendix X1.
E9Test Methods of Compression Testing of Metallic Mate-
1.6 Bearing dimensional tolerance data are shown in Ap-
rials at Room Temperature
pendix X2, while engineering information regarding installa-
E29Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
tion and operating parameters of PM bearings is included in
Determine Conformance with Specifications
Appendix X3. Additional useful information on self-
E1019Test Methods for Determination of Carbon, Sulfur,
lubricatingbearingscanbefoundinMPIFStandard35andthe
Nitrogen, and Oxygen in Steel, Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt
technical literature.
Alloys by Various Combustion and Fusion Techniques
1.7 With the exception of density values for which the
2.2 MPIF Standard:
g/cm unit is the industry standard, the values stated in
MPIF Standard 35 Materials Standards for PM Self-
inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The SI
Lubricating Bearings
equivalents of inch-pound units, shown in parenthesis, have
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee B09 on Metal contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Powders and Metal Powder Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcom- Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
mittee B09.04 on Bearings. the ASTM website.
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2008.PublishedJuly2008.Originallyapproved The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as B438/B438M–05. DOI: www.astm.org.
10.1520/B0438-08. Available from MPIF, 105 College Road East, Princeton, NJ 08540, telephone
Machine Design Magazine, Vol 54, #14, June 17, 1982, pp. 130-142. (609) 452-7700.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
B438−08
2.3 IEEE/ASTM Standard:
CTG-1004-K10—Bronze, 4 % graphite with 11 % oil
CTG-1004-K15—Bronze, 4 % graphite with a trace or up to8%oil
SI 10American National Standard for Use of the Interna-
tional System of Units (SI): The Modernized Metric
4.2.4 Prefix CTG-MOD—Bronze-Lead-Graphite (Military
System Grade):
2.4 ISO Standard:
CTG-1001-K23-MOD—Bronze, 3 % lead, 1 % graphite with 17 % oil
ISO 2795Plain Bearings Made from Sintered Metal—
4.2.5 Prefix CFTG—Bronze-Iron-Graphite (Diluted
Dimensions and Tolerances
Bronze):
2.5 Government Standards:
CFTG-3806-K14—Bronze, 40 % iron, 0.75 % graphite with 22 % oil
MIL-PRF-6085Lubricating Oil: Instrument, Aircraft, Low
CFTG-3806-K22—Bronze, 40 % iron, 0.75 % graphite with 17 % oil
Volatility
QPL-6085Lubricating Oil: Instrument, Aircraft, Low Vola-
5. Ordering Information
tility
5.1 Purchase orders or contracts for bronze-base, oil-
MIL-PRF-17331Lubrication Oil, Steam Turbine and Gear,
impregnated bearings covered by this purchasing specification
Moderate Service
shall include the following information:
QPL-17331Lubricating Oil, SteamTurbine and Gear, Mod-
5.1.1 A copy of the bearing print showing dimensions and
erate Service
tolerances (Section 10),
MIL-B-5687Bearings, Sleeve, Washers, Thrust, Sintered,
5.1.2 Reference to this ASTM Standard, including date of
Metal Powder, Oil-Impregnated, General Specification
issue,
For
5.1.3 Identification of bearing material by the PM Material
MS17795Bearing, Sleeve, Plain, Sintered Bronze, Oil-
Designation Code (section 4.2),
Impregnated
5.1.4 Request for Certification and Test Report documents,
MS17796Bearing, Sleeve, Flanged, Sintered Bronze, Oil-
if required (Section 16),
Impregnated
5.1.5 Type and grade of special Lubricating Oil, if required
MS21783Bearing, Washer, Thrust, Sintered Bronze, Oil-
(section 6.2 or S2.2),
Impregnated
5.1.6 Instructions for Special Packaging, if required (Sec-
tion 17).
3. Terminology
5.2 Thoseadditionalgovernmentrequirementsnecessaryon
3.1 Definitions—The definitions of the terms used in this
orders for military bearings are prescribed in the Supplemen-
specification are found in Terminology B243. Additional de-
tary Requirements section.
scriptive information is available in the Related Materials
section of Volume 02.05 of the Annual Book of ASTM
6. Materials and Manufacture
Standards .
6.1 Porous Metallic Bearing:
4. Classification
6.1.1 Sintered bronze-base bearings shall be produced by
firstcompactingpre-alloyedbronzeorelementalcopperandtin
4.1 This specification uses the established three-part alpha-
powders and any other additives appropriate for the composi-
numeric PM Material Designation Code to identify the non-
tion to the proper density and bearing configuration.
ferrous materials used for self-lubricating PM bearings. The
6.1.2 The green bearings shall then be sintered in a protec-
complete explanation of this classification system is presented
tiveatmospherefurnaceforatimeandtemperaturerelationship
in Annex A1.
that will produce the required sintered bronze-base PM mate-
4.2 The following standard oil-impregnated bronze-base
rial.
bearing material compositions are contained in this specifica-
6.1.3 After sintering, the bronze-base bearings are normally
tion:
sized to achieve the density, dimensional characteristics, con-
4.2.1 Prefix CT—Bronze:
centricity and surface finish required of the metallic bearing.
CT-1000-K19—Bronze with 24 % oil
CT-1000-K26—Bronze with 19 % oil 6.2 Oil for Operating Lubrication:
CT-1000-K37—Bronze with 12 % oil
6.2.1 The interconnected or open porosity in the bearings
CT-1000-K40—Bronze with9%oil
shallbefilledtotherequiredvolumewithlubricatingoil,either
4.2.2 Prefix CTG—Bronze-Graphite :
byanextendedsoakinginthehotoilorpreferablybyavacuum
CTG-1001-K17—Bronze, 1 % graphite with 22 % oil
impregnation operation.
CTG-1001-K23—Bronze, 1 % graphite with 17 % oil
6.2.2 Amediumviscositypetroleumoilisnormallyusedfor
CTG-1001-K30—Bronze, 1 % graphite with9%oil
CTG-1001-K34—Bronze, 1 % graphite with7%oil most bearing applications, but extreme operating conditions
such as elevated temperatures, intermittent rotation, extremely
4.2.3 Prefix CTG—Bronze-High Graphite:
low speeds or heavy loads may require a synthetic lubricant or
an oil with a different viscosity.
ISO standards are available from the American National Standards Institute
6.2.3 Unless otherwise specified by the purchaser, a high-
(ANSI), 16 West 42nd Street, New York, NY 10036, (212) 642-4900.
grade turbine oil with antifoaming additives and containing
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg 4, Sec. D, 700
corrosion and oxidation inhibitors, having a kinematic viscos-
Robbins Ave, Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094. Electronic copies of military specifi-
-6 -6 2
cations may be obtained from http://assist.daps.dla.mil/. ity of 280 to 500 SSU [(60 × 10 to110×10 m /s), (60 to
B438−08
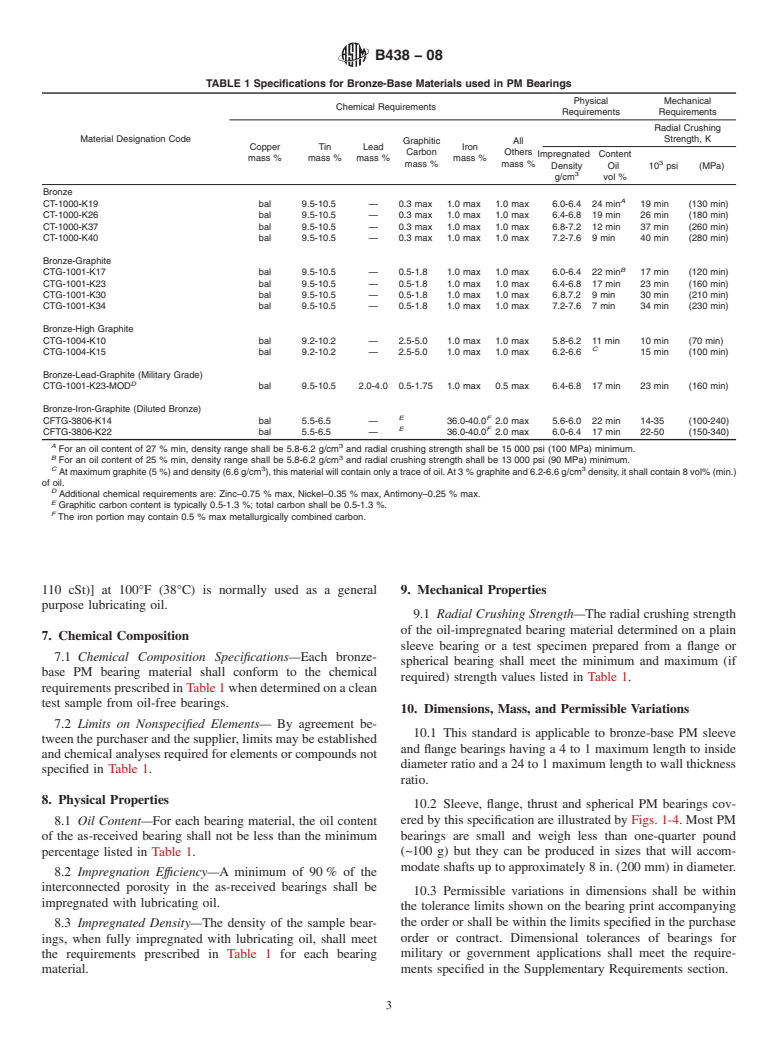
TABLE 1 Specifications for Bronze-Base Materials used in PM Bearings
Physical Mechanical
Chemical Requirements
Requirements Requirements
Radial Crushing
Material Designation Code Strength, K
Graphitic All
Copper Tin Lead Iron
Carbon Others
Impregnated Content
mass % mass % mass % mass %
mass % mass %
Density Oil 10 psi (MPa)
g/cm vol %
Bronze
A
CT-1000-K19 bal 9.5-10.5 — 0.3 max 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.0-6.4 24 min 19 min (130 min)
CT-1000-K26 bal 9.5-10.5 — 0.3 max 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.4-6.8 19 min 26 min (180 min)
CT-1000-K37 bal 9.5-10.5 — 0.3 max 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.8-7.2 12 min 37 min (260 min)
CT-1000-K40 bal 9.5-10.5 — 0.3 max 1.0 max 1.0 max 7.2-7.6 9 min 40 min (280 min)
Bronze-Graphite
B
CTG-1001-K17 bal 9.5-10.5 — 0.5-1.8 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.0-6.4 22 min 17 min (120 min)
CTG-1001-K23 bal 9.5-10.5 — 0.5-1.8 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.4-6.8 17 min 23 min (160 min)
CTG-1001-K30 bal 9.5-10.5 — 0.5-1.8 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.8.7.2 9 min 30 min (210 min)
CTG-1001-K34 bal 9.5-10.5 — 0.5-1.8 1.0 max 1.0 max 7.2-7.6 7 min 34 min (230 min)
Bronze-High Graphite
CTG-1004-K10 bal 9.2-10.2 — 2.5-5.0 1.0 max 1.0 max 5.8-6.2 11 min 10 min (70 min)
C
CTG-1004-K15 bal 9.2-10.2 — 2.5-5.0 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.2-6.6 15 min (100 min)
Bronze-Lead-Graphite (Military Grade)
D
CTG-1001-K23-MOD bal 9.5-10.5 2.0-4.0 0.5-1.75 1.0 max 0.5 max 6.4-6.8 17 min 23 min (160 min)
Bronze-Iron-Graphite (Diluted Bronze)
E F
CFTG-3806-K14 bal 5.5-6.5 — 36.0-40.0 2.0 max 5.6-6.0 22 min 14-35 (100-240)
E F
CFTG-3806-K22 bal 5.5-6.5 — 36.0-40.0 2.0 max 6.0-6.4 17 min 22-50 (150-340)
A 3
For an oil content of 27 % min, density range shall be 5.8-6.2 g/cm and radial crushing strength shall be 15 000 psi (100 MPa) minimum.
B 3
For an oil content of 25 % min, density range shall be 5.8-6.2 g/cm and radial crushing strength shall be 13 000 psi (90 MPa) minimum.
C 3 3
At maximum graphite (5 %) and density (6.6 g/cm ), this material will contain only a trace of oil. At3%graphite and 6.2-6.6 g/cm density, it shall contain 8 vol% (min.)
of oil.
D
Additional chemical requirements are: Zinc–0.75 % max, Nickel–0.35 % max, Antimony–0.25 % max.
E
Graphitic carbon content is typically 0.5-1.3 %; total carbon shall be 0.5-1.3 %.
F
The iron portion may contain 0.5 % max metallurgically combined carbon.
110 cSt)] at 100°F (38°C) is normally used as a general 9. Mechanical Properties
purpose lubricating oil.
9.1 Radial Crushing Strength—The radial crushing strength
of the oil-impregnated bearing material determined on a plain
7. Chemical Composition
sleeve bearing or a test specimen prepared from a flange or
7.1 Chemical Composition Specifications—Each bronze-
spherical bearing shall meet the minimum and maximum (if
base PM bearing material shall conform to the chemical
required) strength values listed in Table 1.
requirementsprescribedinTable1whendeterminedonaclean
test sample from oil-free bearings.
10. Dimensions, Mass, and Permissible Variations
7.2 Limits on Nonspecified Elements— By agreement be-
10.1 This standard is applicable to bronze-base PM sleeve
tweenthepurchaserandthesupplier,limitsmaybeestablished
and flange bearings havinga4to1 maximum length to inside
andchemicalanalysesrequiredforelementsorcompoundsnot
diameter ratio and a 24 to 1 maximum length to wall thickness
specified in Table 1.
ratio.
8. Physical Properties
10.2 Sleeve, flange, thrust and spherical PM bearings cov-
ered by this specification are illustrated by Figs. 1-4. Most PM
8.1 Oil Content—For each bearing material, the oil content
of the as-received bearing shall not be less than the minimum bearings are small and weigh less than one-quarter pound
percentage listed in Table 1. (~100 g) but they can be produced in sizes that will accom-
modate shafts up to approximately 8 in. (200 mm) in diameter.
8.2 Impregnation Effıciency—A minimum of 90% of the
interconnected porosity in the as-received bearings shall be
10.3 Permissible variations in dimensions shall be within
impregnated with lubricating oil.
the tolerance limits shown on the bearing print accompanying
the order or shall be within the limits specified in the purchase
8.3 Impregnated Density—The density of the sample bear-
order or contract. Dimensional tolerances of bearings for
ings, when fully impregnated with lubricating oil, shall meet
military or government applications shall meet the require-
the requirements prescribed in Table 1 for each bearing
material. ments specified in the Supplementary Requirements section.
B438−08
FIG. 1Standard Sleeve Bearing
FIG. 4Standard Spherical Bearing
11.2 When cut or fractured, the exposed surface of the
bearings should exhibit a uniform visual appearance.
11.3 If metallographic examination is performed to deter-
mine degree of sintering, it should be done at 200-400×
magnification. In 90Cu-10Sn bronze bearings, the microstruc-
ture should be alpha bronze with no silver-gray tin-rich copper
compounds and with a minimum of reddish copper-rich areas.
The structure should have a very minimum number of original
particle boundaries. Diluted Bronze material should show a
bronze phase with no visible free tin, dispersed throughout an
iron matrix.
FIG. 2Standard Flange Bearing
11.4 To verify that oil is present, heat the bearing to about
300°F (150°C) for 5 minutes. If oil is
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B438/B438M–05 Designation: B 438 – 08
Standard Specification for
Bronze Powder Metallurgy (P/M) Bearings (Oil-
Impregnated)Bronze-Base Powder Metallurgy (PM) Bearings
(Oil-Impregnated)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B438/B438M;B 438; the number immediately following the designation indicates
the year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1This specification covers sintered bronze, oil-impregnated bearings made primarily from elemental copper, tin, lead, and
graphite powders. The manufacturer may, at his discretion, use prealloyed bronze powder in the mixed powder.
1.2This specification covers the following variables:
1.2.1Grades—Available in three bronze base compositions identifiable by different graphite contents and one leaded bronze
grade.
1.2.2Type—Grades 1 and 2 are available in four types described by specific density ranges. Grade 3 is available in two types
and Grade 4 is available in one type.
1.3Bearings ordered to this specification will normally be sized after sintering and will be impregnated with a lubricating oil
unless otherwise specified by the print.
1.4The values stated in either inch-pound or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system
are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems
may result in nonconformance with this specification.
1.5The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods described in this specification. This standard does not
purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers porous metallic sleeve, flange, thrust and spherical bronze-base bearings that are produced from
mixed metal powders utilizing powder metallurgy (PM) technology and then impregnated with oil to supply operating lubrication.
1.2 Included are the specifications for the chemical, physical and mechanical requirements of those bronze-base PM materials
that have been developed and standardized specifically for use in the manufacture of these self-lubricating bearings.
1.3 This specification is applicable to the purchase of bronze-base bearings (oil-impregnated) that were formerly covered by
military specifications and are intended for government or military applications. Those additional government requirements that
only apply to military bearings are listed in the Supplementary Requirements section of this specification.
1.4 This specification acccompanies Specification B 439 that covers the requirements for Iron-Base Powder Metallurgy (PM)
Bearings, (Oil-Impregnated).
1.5 Typical applications for bronze-base bearings are listed in Appendix X1.
1.6 Bearing dimensional tolerance data are shown in Appendix X2, while engineering information regarding installation and
operating parameters of PM bearings is included in Appendix X3. Additional useful information on self-lubricating bearings can
be found in MPIF Standard 35 and the technical literature.
1.7 With the exception of density values for which the g/cm unit is the industry standard, the values stated in inch-pound units
are to be regarded as standard. The SI equivalents of inch-pound units, shown in parenthesis, have been converted in accordance
with IEEE/ASTM SI 10, may be approximate and are only for information.
1.8 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods described in this specification. This standard does not
purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B09 on Metal Powders and Metal Powder Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
B09.04 on Bearings.
Current edition approved Nov.June 1, 2005.2008. Published November 2005.July 2008. Originally approved in 1966. Last previous edition approved in 20042005 as
B 438/B 438M – 045.
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Machine Design Magazine, Vol 54, #14, June 17, 1982, pp. 130-142.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
B438–08
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B 243 Terminology of Powder Metallurgy
B 328 Test Method for Density, Oil Content, and Interconnected Porosity of Sintered Metal Structural Parts and Oil-
Impregnated Bearings
B 439 Specification for Iron-Base Powder Metallurgy (PM) Bearings (Oil-Impregnated)
B 939Test Method for Radial Crushing Strength, K, of Powder Metallurgy (P/M), Bearings and Structural Materials
Test Method for Radial Crushing Strength,K, of Powder Metallurgy (P/M) Bearings and Structural Materials
B 946 Test Method for Surface Finish of Powder Metallurgy (P/M) Products
E 9Test Methods of Compression Testing of Metallic Materials at Room Temperature Test Methods of Compression Testing
of Metallic Materials at Room Temperature
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E 1019 TestMethodsforDeterminationofCarbon,Sulfur,Nitrogen,andOxygeninSteelandinIron,Nickel,andCobaltAlloys
2.2 Government Standards: MPIF Standard:
MIL-PRF-6085Lubricating Oil: Instrument, Aircraft, Low Volatility MPIF Standard 35 Materials Standards for PM Self-
Lubricating Bearings
2.3 IEEE/ASTM Standard:
MIL-PRF-17331Lubrication Oil: SteamTurbine and Gear, Moderate Service SI 10 American National Standard for Use of the
International System of Units (SI): The Modernized Metric System
2.4 ISO Standard:
FED-STD-151 Metals Test Method
2.3 MPIF Standard:
MPIF Standard 35Materials Standards for P/M Self-Lubricating Bearings ISO 2795 Plain Bearings Made from Sintered
Metal—Dimensions and Tolerances
2.5 Government Standards:
MIL-PRF-6085 Lubricating Oil: Instrument, Aircraft, Low Volatility
QPL-6085 Lubricating Oil: Instrument, Aircraft, Low Volatility
MIL-PRF-17331 Lubrication Oil, Steam Turbine and Gear, Moderate Service
QPL-17331 Lubricating Oil, Steam Turbine and Gear, Moderate Service
MIL-B-5687 Bearings, Sleeve, Washers, Thrust, Sintered, Metal Powder, Oil-Impregnated, General Specification For
MS17795 Bearing, Sleeve, Plain, Sintered Bronze, Oil-Impregnated
MS17796 Bearing, Sleeve, Flanged, Sintered Bronze, Oil-Impregnated
MS21783 Bearing, Washer, Thrust, Sintered Bronze, Oil-Impregnated
3. Ordering Information
3.1Orders for bearings under this specification shall include the following information:
3.1.1Dimensions and tolerances (Section 9Terminology
3.1 Definitions—The definitions of the terms used in this specification are found in Terminology B 243.Additional descriptive
information is available in the Related Materials section of Volume 02.05 of the Annual Book of ASTM Standards .
4. Classification
4.1 This specification uses the established three-part alphanumeric PM Material Designation Code to identify the nonferrous
materials used for self-lubricating PM bearings. The complete explanation of this classification system is presented inAnnexA1.
4.2 The following standard oil-impregnated bronze-base bearing material compositions are contained in this specification:
4.2.1 Prefix CT—Bronze:
CT-1000-K19—Bronze with 24 % oil
CT-1000-K26—Bronze with 19 % oil
CT-1000-K37—Bronze with 12 % oil
CT-1000-K40—Bronze with9%oil
4.2.2 Prefix CTG—Bronze-Graphite :
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111–5094, Attn: NPODS.
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Available from Metal Powders Industries Federation (MPIF), 105 College Road East, Princeton, NJ 08540–6692, USA.
Available from MPIF, 105 College Road East, Princeton, NJ 08540, telephone (609) 452-7700.
ISO standards are available from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 16 West 42nd Street, New York, NY 10036, (212) 642-4900.
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg 4, Sec. D, 700 RobbinsAve, Philadelphia, PA19111-5094. Electronic copies of military specifications may
be obtained from http://assist.daps.dla.mil/.
B438–08
CTG-1001-K17—Bronze, 1 % graphite with 22 % oil
CTG-1001-K23—Bronze, 1 % graphite with 17 % oil
CTG-1001-K30—Bronze, 1 % graphite with9%oil
CTG-1001-K34—Bronze, 1 % graphite with7%oil
4.2.3 Prefix CTG—Bronze-High Graphite:
CTG-1004-K10—Bronze, 4 % graphite with 11 % oil
CTG-1004-K15—Bronze, 4 % graphite with a trace or up to8%oil
4.2.4 Prefix CTG-MOD—Bronze-Lead-Graphite (Military Grade):
CTG-1001-K23-MOD—Bronze, 3 % lead, 1 % graphite with 17 % oil
4.2.5 Prefix CFTG—Bronze-Iron-Graphite (Diluted Bronze):
CFTG-3806-K14—Bronze, 40 % iron, 0.75 % graphite with 22 % oil
CFTG-3806-K22—Bronze, 40 % iron, 0.75 % graphite with 17 % oil
5. Ordering Information
5.1 Purchase orders or contracts for bronze-base, oil-impregnated bearings covered by this purchasing specification shall
include the following information:
5.1.1 A copy of the bearing print showing dimensions and tolerances (Section 10),
3.1.2Grade and type (see Tables 1-5
5.1.2 Reference to this ASTM Standard, including date of issue,
5.1.3 Identification of bearing material by the PM Material Designation Code (section 4.2),
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements (Composition, %)
Chemical Requirements Physical Requirements Mechanical Require
Radial Crushin
Graphitic All
Material Designation Code Strength, K
Copper Tin Lead Iron
Carbon Others
mass % mass % mass % mass %
EleImpregnated DensityContent Oil
mass % mass %
10 psi (MP
g/cm vol %
Bronze
A
CT-1000-K19 bal 9.5-10.5 Grade 1 0.3 max 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.0-6.4 24 min 19 min (130 min
CT-1000-K26 bal 9.5-10.5 Grade 2 Grade3 Gradex 1.0 max 6.4-6.8 19 min 26 min (180 min
CT-1000-K26 bal 9.5-10.5 Grade 2 0.3 max 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.4-6.8 19 min 26 min (180 min
Copper 87.2–90.5 85.7–90.082.8–88.3 80 max 6.9–88.2 12 min 37 min (260
CT-1000-K37 bal 9.5-10.5 — 0.3 max 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.8-7.2 12 min 37 min (260 min
Tin 9.5–10.5 9.5–10.5 9.2–10.2 9.5–10 max 7.52-7.6 9min 40 min (280 min
CT-1000-K40 bal 9.5-10.5 — 0.3 max 1.0 max 1.0 max 7.2-7.6 9min 40 min (280 min
Graphite 0–0.3 0.5–1.8 2.5–5.0 0.50–1.75
Bronze-Graphite
B
Iron, max 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 max 6.0-6.4 22 min 17 min (120 min
B
CTG-1001-K17 bal 9.5-10.5 — 0.5-1.8 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.0-6.4 22 min 17 min (120 min
TotG-1001-K23 bal other elements9.5-10.5 by difference, max1.0 1.0 1.0 17 min 23 min (160.5
CTG-1001-K23 bal 9.5-10.5 by difference, max0.5-1.8 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.4-6.8 17 min 23 min (160 min
Lead 2.0–4 max 6.8.7.2 9min 30 min (210 min
CTG-1001-K30 bal 9.5-10.5 — 0.5-1.8 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.8.7.2 9min 30 min (210 min
Zinc, max 0 max 7.75.6 7min 34 min (230 min
CTG-1001-K34 bal 9.5-10.5 — 0.5-1.8 1.0 max 1.0 max 7.2-7.6 7min 34 min (230 min
Nickel, max 0.35
Bronze-High Graphite
Antimony, max 0 max 5.2 11 min 10 min (70 min)
CTG-1004-K10 bal 9.2-10.2 — 2.5-5.0 1.0 max 1.0 max 5.8-6.2 11 min 10 min (70 min)
C
CTG-1004-K15 bal 9.2-10.2 — 2.5-5.0 1.0 max 1.0 max 6.2-6.6 15 min (100 min
Bronze-Lead-Graphite (Military Grade)
D
CTG-1001-K23-MOD bal 9.5-10.5 2.0-4.0 0.5-1.75 1.0 max 0.5 max 6.4-6.8 17 min 23 min (160 min
Bronze-Iron-Graphite (Diluted Bronze)
E F
CFTG-3806-K14 bal 5.5-6.5 — 36.0-40.0 2.0 max 5.6-6.0 22 min 14-35 (100-240
E F
CFTG-3806-K22 bal 5.5-6.5 — 36.0-40.0 2.0 max 6.0-6.4 17 min 22-50 (150-340
A3
and radial crushing strength shall be 15 000 psi (100 MPa) minimum.
B 3
For an oil content of 25 % min, density range shall be 5.8-6.2 g/cm and radial crushing strength shall be 13 000 psi (90 MPa) minimum.
C 3 3
At maximum graphite (5 %) and density (6.6 g/cm ), this material will contain only a trace of oil. At3%graphite and 6.2-6.6 g/cm density, it shall contain 8 vol% (min.)
of oil.
D
Additional chemical requirements are: Zinc–0.75 % max, Nickel–0.35 % max, Antimony–0.25 % max.
E
Graphitic carbon content is typically 0.5-1.3 %; total carbon shall be 0.5-1.3 %.
F
The iron portion may contain 0.5 % max metallurgically combined carbon.
NOTE—Grade 4 to be used for special government needs.
B438–08
3.1.3Wet density specification (Table 2 and Table 3), and
3.1.4Oil type.
4.
5.1.4 Request for Certification and Test Report documents, if required (Section 16),
5.1.5 Type and grade of special Lubricating Oil, if required (section 6.2 or S2.2),
5.1.6 Instructions for Special Packaging, if required (Section 17).
5.2 Those additional government requirements necessary on orders for military bearings are prescribed in the Supplementary
Requirements section.
6. Materials and Manufacture
4.1Sintered bronze bearings shall be made by molding or briquetting metal powder mixtures to the proper density. The green
bearing shall be sintered at a time–temperature relationship to produce a microstructure that is essentially alpha bronze and
containsnotin-richphasesvisibleat3003.Sinteredbronzebearingsarenormallysizedaftersinteringtomaintainthedimensional
characteristics required of the bearing. After sizing and inspection, they are impregnated with a lubricating oil unless otherwise
specified.
5.
6.1 Porous Metallic Bearing:
6.1.1 Sintered bronze-base bearings shall be produced by first compacting pre-alloyed bronze or elemental copper and tin
powders and any other additives appropriate for the composition to the proper density and bearing configuration.
6.1.2 The green bearings shall the
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.