ASTM F1252-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring Optical Reflectivity of Transparent Materials
Standard Test Method for Measuring Optical Reflectivity of Transparent Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Reflections from aircraft transparencies of instrument lights and other cockpit objects have been a concern to many pilots. Attempts to reduce these reflections have been hampered by the lack of a repeatable measurement method and variances in reflection measuring instrumentation.
4.2 This test method reduces the instrument variations by standardizing the light source, calculation method, and area of specimen surface being measured; a brand of instrumentation is not specified. Since the reflectivity is defined as the ratio of two luminance measurements and does not depend on an absolute measurement, dependence upon the accuracy of the calibration of the measuring instrument is reduced.
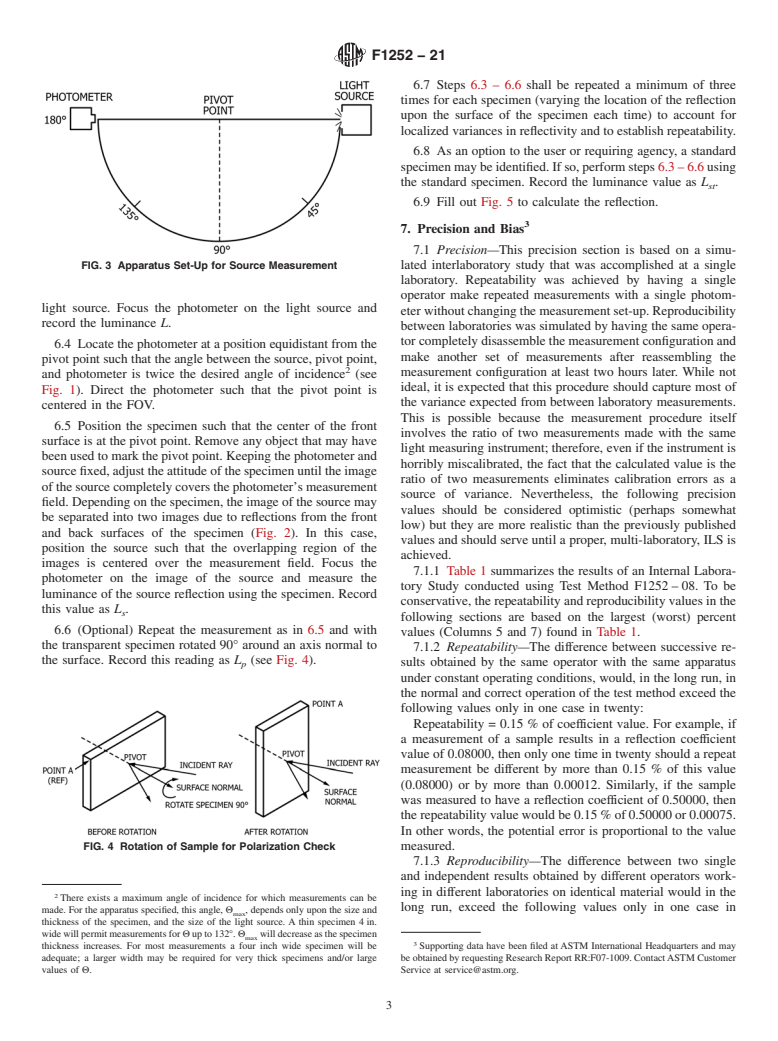
4.3 The test method may be used to objectively compare the reflection characteristics of various transparent materials. Furthermore, the test method may be used to evaluate reflections of a specified spectral distribution light source (for example, a monochromatic light-emitting diode) by using that source in place of the standard light source.
4.4 Provisions are made to check for polarization effects of the sample and to record the reflectivity of a standard specimen. These provisions are offered as an option to the tester; it is up to the user or the requiring agency to determine the significance and use of these data.
4.5 Since the reflections are measured photopically, the results are representative of what the pilot would visually perceive.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for measuring the reflectivity of transparent materials, hereafter known as specimens. The results are repeatable without specifying a particular brand name of instrumentation.
1.2 This test method applies to substantially flat parts. Errors in measurement can occur if the parts being measured are not substantially flat.
1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:F1252 −21
Standard Test Method for
1
Measuring Optical Reflectivity of Transparent Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1252; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.1.3 light source, n—unless otherwise specified, the Na-
tional Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) diffused
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for measuring the
nonpolarized Standard IlluminanceAor C light source shall be
reflectivity of transparent materials, hereafter known as speci-
used. The light source size shall be such that there shall be
mens.The results are repeatable without specifying a particular
sufficient overlap of the front and rear images on the specimen
brand name of instrumentation.
to overfill the measurement field size of the photometer. This
1.2 This test method applies to substantially flat parts.
measurement field size, and front and back reflected image
Errors in measurement can occur if the parts being measured
overlap, are illustrated in Fig. 2. (As angle of incidence and
are not substantially flat.
specimen thickness increase, the two images will diverge.)The
light source used shall be specified and reported as part of the
1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this test results.
standard.
2.1.4 measurement field size, n—the angular extent, in
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the degrees or arc minutes, of the measurement aperture of the
photometer.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
2.1.5 photometer, n—any commercial photometer or pho-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
topic filtered radiometer with a suitable measurement field size
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
(1° or smaller is recommended). A model with a viewfinder is
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
recommended.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
2.1.6 pivot point, n—the point in space at which the incident
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
light ray and reflected light ray are to intersect (see Fig. 1).
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
2.1.7 reflectivity, adj—the reflectivity of a transparent speci-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
men is defined as the ratio of the luminance of the reflected
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
image of a light source to the luminance of the light source.
2. Terminology The reflectivity will depend upon several factors: the angle at
which the reflected light is measured, the thickness, surface
2.1 Definitions:
quality, and type of material of the specimen, whether the
2.1.1 angle of incidence (Θ ), n—in the plane of the light
i
specimen is coated, the spectral distribution of the light source,
source, specimen, and photometer, the angle of incidence is the
and the spectral sensitivity of the measurement device. The
angle between the incident light ray and the normal to the
reflectivity, as defined here, includes the small amount of
surface (see Fig. 1).
scattered light that contributes to the luminance of the reflected
2.1.2 angle of reflection (Θ ), n—in the plane of the light
r
image.
source, specimen, and photometer, the angle of reflection is the
angle between the reflected light ray and the normal to the
3. Summary of Test Method
surface (see Fig. 1).
3.1 The luminance of the standard source is determined by
measuring it directly with the photometer. The luminance of
1
the reflection of the source, from both the front and back
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F07 on
Aerospace and Aircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F07.08 on
surfaces of the specimen, is then measured off the specimen at
Transparent Enclosures and Materials.
aspecifiedgeometry.Theluminanceofthereflectionisdivided
Current edition approved May 1, 2021. Published May 2021. Originally
by the luminance of the source to obtain the reflectivity of the
approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as F1252 – 16. DOI:
10.1520/F1252-21. specimen.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1252−21
is up to
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F1252 − 16 F1252 − 21
Standard Test Method for
1
Measuring Optical Reflectivity of Transparent Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1252; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for measuring the reflectivity of transparent materials, hereafter known as specimens. The
results are repeatable without specifying a particular brand name of instrumentation.
1.2 This test method applies to substantially flat parts. Errors in measurement can occur if the parts being measured are not
substantially flat.
1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Terminology
2.1 Definitions:
2.1.1 angle of incidence (Θ ), n—in the plane of the light source, specimen, and photometer, the angle of incidence is the angle
i
between the incident light ray and the normal to the surface (see Fig. 1).
2.1.2 angle of reflection (Θ ), n—in the plane of the light source, specimen, and photometer, the angle of reflection is the angle
r
between the reflected light ray and the normal to the surface (see Fig. 1).
2.1.3 light source, n—unless otherwise specified, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) diffused nonpolarized
Standard Illuminance A or C light source shall be used. The light source size shall be such that there shall be sufficient overlap
of the front and rear images on the specimen to overfill the measurement field size of the photometer. This measurement field size,
and front and back reflected image overlap, are illustrated in Fig. 2. (As angle of incidence and specimen thickness increase, the
two images will diverge.) The light source used shall be specified and reported as part of the test results.
2.1.4 measurement field size, n—the angular extent, in degrees or arc minutes, of the measurement aperture of the photometer.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F07 on Aerospace and Aircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F07.08 on Transparent
Enclosures and Materials.
Current edition approved April 1, 2016May 1, 2021. Published April 2016May 2021. Originally approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 20102016 as
F1252 – 10.F1252 – 16. DOI: 10.1520/F1252-16.10.1520/F1252-21.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1252 − 21
FIG. 1 Apparatus Set-Up
FIG. 2 Photometer Measurement Field Size (Aperture) Compared to Specimen Front and Back Surface Reflections
2.1.5 photometer, n—any commercial photometer or photopic filtered radiometer with a suitable measurement field size (1° or
smaller is recommended). A model with a viewfinder is recommended.
2.1.6 pivot point, n—the point in space at which the incident light ray and reflected light ray are to intersect (see Fig. 1).
2.1.7 reflectivity, adj—the reflectivity of a transparent specimen is defined as the ratio of the luminance of the reflected image of
a light source to the luminance of the light source. The reflectivity will depend upon several factors: the angle at which the reflected
light is measured, the thickness, surface quality, and type of material of the specimen, whether the specimen is coated, the spectral
distribution of the light source, and the spectral sensitivity of the measurement device. The reflectivity, as defined here, includes
the small amount of scattered light that contributes to the luminance of the reflected image.
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 The luminance of the standard source is determined
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.