ASTM D6330-20
(Practice)Standard Practice for Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (Excluding Formaldehyde) Emissions from Wood-Based Panels Using Small Environmental Chambers Under Defined Test Conditions
Standard Practice for Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (Excluding Formaldehyde) Emissions from Wood-Based Panels Using Small Environmental Chambers Under Defined Test Conditions
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The effects of VOC sources on the indoor air quality in buildings have not been well established. One basic requirement that has emerged from indoor air quality studies is the need for well-characterized test data on the emission factors of VOCs from building materials. Standard test method and procedure are a requirement for the comparison of emission factor data from different products.
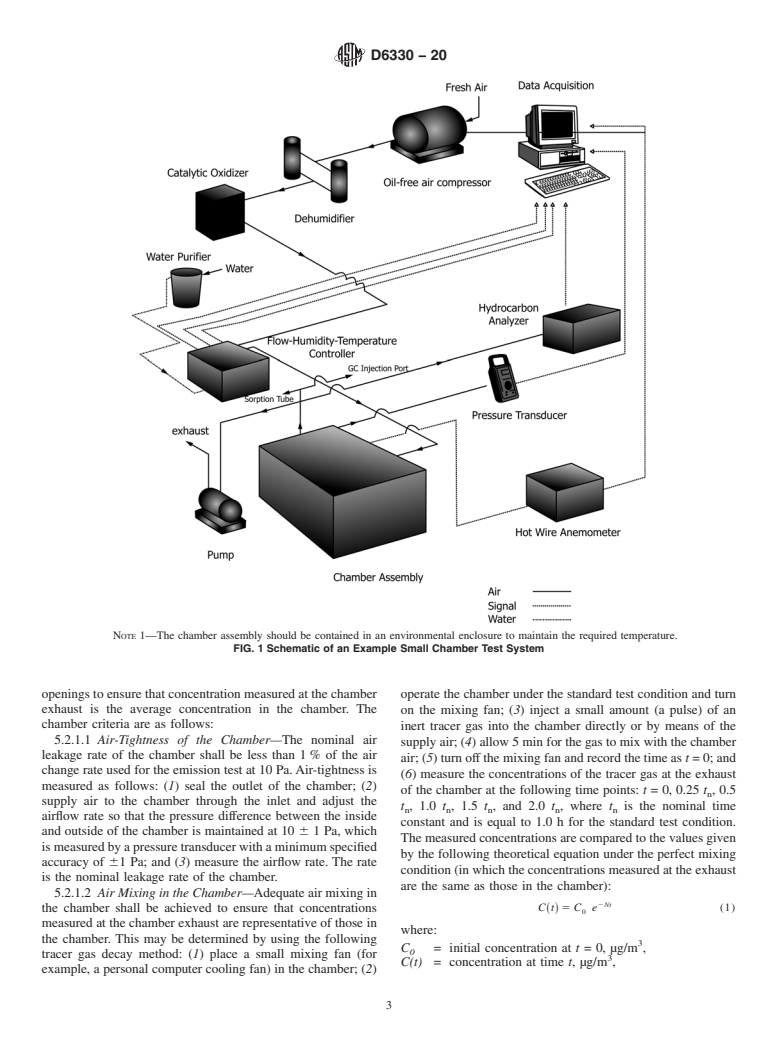
4.2 This practice describes a procedure for using a small environmental test chamber to determine the emission factors of VOCs from wood-based panels over a specified period of time. A pre-screening analysis procedure is also provided to identify the VOCs emitted from the products, to determine the appropriate GC-MS or GC-FID analytical procedure, and to estimate required sampling volume for the subsequent environmental chamber testing.
4.3 Test results obtained using this practice provide a basis for comparing the VOC emission characteristics of different wood-based panel products. The emission data can be used to inform manufacturers of the VOC emissions from their products. The data can also be used to identify building materials with reduced VOC emissions over the time interval of the test.
4.4 While emission factors determined by using this practice can be used to compare different products, the concentrations measured in the chamber shall not be considered as the resultant concentrations in an actual indoor environment.
SCOPE
1.1 The practice measures the volatile organic compounds (VOC), excluding formaldehyde, emitted from manufactured wood-based panels. A pre-screening analysis is used to identify the VOCs emitted from the panel. Emission factors (that is, emission rates per unit surface area) for the VOCs of interest are then determined by measuring the concentrations in a small environmental test chamber containing a specimen. The test chamber is ventilated at a constant air change rate under the standard environmental conditions. For formaldehyde determination, see Test Method D6007.
1.2 This practice describes a test method that is specific to the measurement of VOC emissions from newly manufactured individual wood-based panels, such as particleboard, plywood, and oriented strand board (OSB), for the purpose of comparing the emission characteristics of different products under the standard test condition. For general guidance on conducting small environmental chamber tests, see Guide D5116.
1.3 VOC concentrations in the environmental test chamber are determined by adsorption on an appropriate single adsorbent tube or multi-adsorbent tube, followed by thermal desorption and combined gas chromatograph/mass spectrometry (GC-MS) or gas chromatograph/flame ionization detection (GC-FID). The air sampling procedure and the analytical method recommended in this practice are generally valid for the identification and quantification of VOCs with saturation vapor pressure between 500 and 0.01 kPa at 25°C, depending on the selection of adsorbent(s).
Note 1: VOCs being captured by an adsorbent tube depend on the adsorbent(s) and sampling procedure selected (see Practice D6196). The user should have a thorough understanding of the limitations of each adsorbent used. Although canisters can be used to sample VOCs, this standard is limited to sampling VOCs from the chamber air using adsorbent tubes.
1.4 The emission factors determined using the above procedure describe the emission characteristics of the specimen under the standard test condition. These data can be used directly to compare the emission characteristics of different products and to estimate the emission rates up to one month after the production. They shall not be used to predict the emission rates over longer periods of time (that is, more than one month) or under different environmental conditions.
1.5 Emission data from chamber tests can be used for predicting the impact of wood-based panels on the VOC concentrations...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:D6330 −20
Standard Practice for
Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (Excluding
Formaldehyde) Emissions from Wood-Based Panels Using
Small Environmental Chambers Under Defined Test
1
Conditions
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6330; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.4 The emission factors determined using the above pro-
cedure describe the emission characteristics of the specimen
1.1 The practice measures the volatile organic compounds
under the standard test condition. These data can be used
(VOC), excluding formaldehyde, emitted from manufactured
directly to compare the emission characteristics of different
wood-basedpanels.Apre-screeninganalysisisusedtoidentify
products and to estimate the emission rates up to one month
the VOCs emitted from the panel. Emission factors (that is,
after the production. They shall not be used to predict the
emission rates per unit surface area) for the VOCs of interest
emission rates over longer periods of time (that is, more than
arethendeterminedbymeasuringtheconcentrationsinasmall
one month) or under different environmental conditions.
environmental test chamber containing a specimen. The test
chamber is ventilated at a constant air change rate under the 1.5 Emission data from chamber tests can be used for
standard environmental conditions. For formaldehyde predicting the impact of wood-based panels on the VOC
determination, see Test Method D6007. concentrations in buildings by using an appropriate indoor air
quality model, which is beyond the scope of this practice.
1.2 This practice describes a test method that is specific to
the measurement ofVOC emissions from newly manufactured 1.6 The values stated in SI units shall be regarded as the
individualwood-basedpanels,suchasparticleboard,plywood, standard (see IEEE/ASTM SI-10).
andorientedstrandboard(OSB),forthepurposeofcomparing
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
the emission characteristics of different products under the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
standard test condition. For general guidance on conducting
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
small environmental chamber tests, see Guide D5116.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
1.3 VOC concentrations in the environmental test chamber mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
For specified hazard statements see Section 6.
are determined by adsorption on an appropriate single adsor-
benttubeormulti-adsorbenttube,followedbythermaldesorp- 1.8 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
tionandcombinedgaschromatograph/massspectrometry(GC-
MS) or gas chromatograph/flame ionization detection (GC- ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
FID). The air sampling procedure and the analytical method
recommended in this practice are generally valid for the mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
identificationandquantificationofVOCswithsaturationvapor
pressure between 500 and 0.01 kPa at 25°C, depending on the
selection of adsorbent(s). 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
NOTE 1—VOCs being captured by an adsorbent tube depend on the
adsorbent(s) and sampling procedure selected (see Practice D6196). The
D1356Terminology Relating to Sampling and Analysis of
user should have a thorough understanding of the limitations of each
Atmospheres
adsorbent used. Although canisters can be used to sample VOCs, this
D1914PracticeforConversionUnitsandFactorsRelatingto
standard is limited to sampling VOCs from the chamber air using
Sampling and Analysis of Atmospheres
adsorbent tubes.
1
ThispracticeisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD22onAirQuality
2
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.05 on Indoor Air. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved March 1, 2020. Published May 2020. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D6330–98 (2014). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D6330-20. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM In
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6330 − 98 (Reapproved 2014) D6330 − 20
Standard Practice for
Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds (Excluding
Formaldehyde) Emissions from Wood-Based Panels Using
Small Environmental Chambers Under Defined Test
1
Conditions
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6330; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 The practice measures the volatile organic compounds (VOC), excluding formaldehyde, emitted from manufactured
wood-based panels. A pre-screening analysis is used to identify the VOCs emitted from the panel. Emission factors (that is,
emission rates per unit surface area) for the VOCs of interest are then determined by measuring the concentrations in a small
environmental test chamber containing a specimen. The test chamber is ventilated at a constant air change rate under the standard
environmental conditions. For formaldehyde determination, see Test Method D6007.
1.2 This practice describes a test method that is specific to the measurement of VOC emissions from newly manufactured
individual wood-based panels, such as particleboard, plywood, and oriented strand board (OSB), for the purpose of comparing the
emission characteristics of different products under the standard test condition. For general guidance on conducting small
environmental chamber tests, see Guide D5116.
1.3 VOC concentrations in the environmental test chamber are determined by adsorption on an appropriate single adsorbent tube
or multi-adsorbent tube, followed by thermal desorption and combined gas chromatograph/mass spectrometry (GC/MS)(GC-MS)
or gas chromatograph/flame ionization detection (GC/FID).(GC-FID). The air sampling procedure and the analytical method
recommended in this practice are generally valid for the identification and quantification of VOCs with saturation vapor pressure
between 500 and 0.01 kPa at 25°C, depending on the selection of adsorbent(s).
NOTE 1—VOCs being captured by an adsorbent tube depend on the adsorbent(s) and sampling procedure selected (see Practice D6196). The user should
have a thorough understanding of the limitations of each adsorbent used. Although canisters can be used to sample VOCs, this standard is limited to
sampling VOCs from the chamber air using adsorbent tubes.
1.4 The emission factors determined using the above procedure describe the emission characteristics of the specimen under the
standard test condition. These data can be used directly to compare the emission characteristics of different products and to estimate
the emission rates up to one month after the production. They shall not be used to predict the emission rates over longer periods
of time (that is, more than one month) or under different environmental conditions.
1.5 Emission data from chamber tests can be used for predicting the impact of wood-based panels on the VOC concentrations
in buildings by using an appropriate indoor air quality model, which is beyond the scope of this practice.
1.6 The values stated in SI units shall be regarded as the standard (see IEEE/ASTM SI-10).
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use. For specified hazard statements see Section 6.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D22 on Air Quality and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.05 on Indoor Air.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2014March 1, 2020. Published November 2014May 2020. Originally approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 20082014
as D6330 – 98 (2008).(2014). DOI: 10.1520/D6330-98R14.10.1520/D6330-20.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6330 − 20
2
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.