ASTM A395/A395M-99(2014)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Ferritic Ductile Iron Pressure-Retaining Castings for Use at Elevated Temperatures
Standard Specification for Ferritic Ductile Iron Pressure-Retaining Castings for Use at Elevated Temperatures
ABSTRACT
This specification covers standard requirements for ductile iron castings for pressure-retaining parts for use at elevated temperatures. Castings are classified by grades based on mechanical property requirements. These iron castings shall meet the specified values of tensile strength, yield strength, elongation and hardness. Chemical analysis shall be performed wherein the casting shall conform to the required chemical composition for carbon, silicon, and phosphorous. The material shall meet the required tensile properties, hardness, and microstructure. The iron casting shall undergo pressure test after machining. The thickness of any repaired section in relation to the size of the plug used shall be indicated. The minimum radius of repaired sections of cylinders or cones in relation to the size of plug used shall not exceed the prescribed limit. Other defective areas may also be repaired by plugging provided the minimum ligament between plugs in adjacent areas shall not be less than twice the distance from the nearest plug. Three Y-blocks shall be utilized as test coupons. The material shall undergo the following test methods: tension test, chemical analysis, yield strength test, and hardness test.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers ductile iron castings for pressure-retaining parts for use at elevated temperatures. Castings of all grades are suitable for use up to 450°F. For temperatures above 450°F and up to 650°F, only Grade 60–40–18 castings are suitable (Note 1).
1.2 Valves, flanges, pipe fittings, pumps, and other piping components are generally manufactured in advance and supplied from stock by the manufacturer, jobber, or dealer.
1.3 For supplemental casting requirements, Specification A834 may be utilized.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.Note 1—For service other than as specified in this section, reference should be made to Specification A536 for Ductile Iron Castings.2
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A395/A395M −99 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Specification for
Ferritic Ductile Iron Pressure-Retaining Castings for Use at
Elevated Temperatures
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA395/A395M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope A834 Specification for Common Requirements for Iron
Castings for General Industrial Use
1.1 This specification covers ductile iron castings for
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
pressure-retaining parts for use at elevated temperatures. Cast-
E10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
ings of all grades are suitable for use up to 450°F. For
E186 Reference Radiographs for Heavy-Walled (2 to 4 ⁄2-in.
temperatures above 450°F and up to 650°F, only Grade
(50.8 to 114-mm)) Steel Castings
60–40–18 castings are suitable (Note 1).
E280 Reference Radiographs for Heavy-Walled (4 ⁄2 to 12-
1.2 Valves, flanges, pipe fittings, pumps, and other piping
in. (114 to 305-mm)) Steel Castings
components are generally manufactured in advance and sup-
E446 Reference Radiographs for Steel Castings Up to 2 in.
plied from stock by the manufacturer, jobber, or dealer.
(50.8 mm) in Thickness
1.3 For supplemental casting requirements, Specification E689 Reference Radiographs for Ductile Iron Castings
E1806 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determina-
A834 may be utilized.
tion of Chemical Composition
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
F1476 Specification for Performance of Gasketed Mechani-
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
cal Couplings for Use in Piping Applications
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
F1548 SpecificationforPerformanceofFittingsforUsewith
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
Gasketed Mechanical Couplings Used in Piping Applica-
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
tions
with the standard.
2.2 Manufacturer’sStandardizationSocietyoftheValveand
NOTE 1—For service other than as specified in this section, reference
Fittings Industry Standard:
should be made to Specification A536 for Ductile Iron Castings.
SP 25 Standard Marking Systems for Valves, Flanges, Pipe
Fittings, and Unions
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3. Classification
A247 Test Method for Evaluating the Microstructure of
3.1 Castings ordered to this specification are classified by
Graphite in Iron Castings
grades based on mechanical property requirements, as listed in
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
Table 1. See note following Table 1.
of Steel Products
A536 Specification for Ductile Iron Castings
4. Ordering Information
A732/A732M Specification for Castings, Investment, Car-
4.1 Orders for material under this specification shall include
bon and Low Alloy Steel for General Application, and
the following applicable information:
Cobalt Alloy for High Strength at Elevated Temperatures
4.1.1 Drawing, catalog number, or part identifications,
4.1.1.1 For grade 65-45-15, drawing indicating critical ar-
ea(s) of casting (see 7.2.2 and 7.3.2).
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A04 on Iron
4.1.2 Quantity (weight or number of pieces),
Castings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A04.02 on Malleable and
Ductile Iron Castings.
4.1.3 ASTM designation and year of issue,
Current edition approved April 1, 2014. Published April 2014. Originally
4.1.4 Grade (See Table 1), if a Grade is not specified, the
approved in 1955. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as A395/A395M – 99
manufacturer shall supply grade 60-40-18.
(2009). DOI: 10.1520/A0395_A0395M-99R14.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on AvailablefromManufacturersStandardizationSocietyoftheValveandFittings
the ASTM website. Industry (MSS), 127 Park St., NE,Vienna,VA22180-4602, http://www.mss-hq.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A395/A395M − 99 (2014)
TABLE 1 Mechanical Property Requirements
7.1.1 The ductile iron as represented by the test specimens
Property Grade 60-40-18 Grade 65-45-15 shallconformtothemechanicalpropertyrequirementsinTable
Tensile Strength Minimum, psi [MPa] 60 000 [415] 65 000 [450]
1.
Yield Strength Minimum, psi [MPa] 40 000 [275] 45 000 [310]
Elongation in 2 in. Minimum, % 18 15
7.2 Hardness:
Hardness HB, 3000 kgf Load 143-187 156-201
7.2.1 For Grade 60–40–18, the hardness of the castings and
test specimens shall be within the limits in Table 1.
7.2.2 For Grade 65–45–15, the hardness of test specimen
4.1.5 Heat-treating requirements (see 5.2.1),
and the critical area(s) of the casting, as identified on the
4.1.6 Pressure test requirements (see 7.4.3),
casting drawing, shall be within the limits in Table 1. If the
4.1.7 Test samples from castings (see 11.1.1 and 12.1.1),
grade 65–45–15 casting drawing does not have critical area(s)
4.1.8 Test coupons size (see 11.2),
of the casting identified, all areas of the casting shall be within
4.1.9 Metallographic option (see 12.1.1),
the hardness limits in Table 1.
4.1.10 Place of inspection (see 16.1),
4.1.11 Certification requirements (see 17.1),
7.3 Microstructure:
4.1.12 Identification marking (see 18.2), and
7.3.1 For Grade 60-40-18, the microstructure of the sepa-
4.1.13 Supplemental Requirements (see 1.4, 7.4.2,S1and
rately cast test coupon or the casting shall be essentially ferritic
S2).
and contain no massive carbides, and have a minimum of 90 %
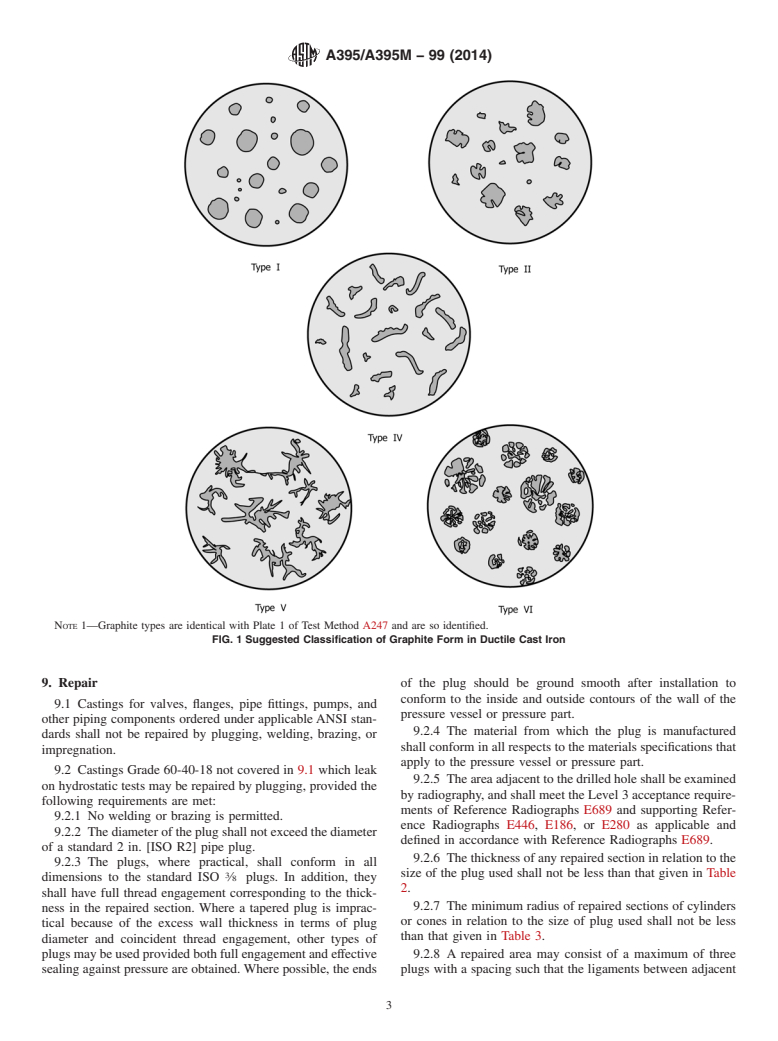
Type I and Type II Graphite as in Fig. 1 or Plate I of Test
5. Materials and Manufacture
Method A247.
5.1 The melting method and the nodularizing practice shall
7.3.2 For Grade 65-45-15, the microstructure of the critical
be optional with the foundry.
areas of the casting, as identified on the casting drawing, shall
5.2 Except as provided in 5.2.1, all castings Grade 60-40-18
be 45 % pearlitic, maximum, contain no massive carbides, and
shall be given a ferritizing heat treatment that produces
have a minimum 90 % Type I and Type II Graphite as in Fig.
essentially a ferritic structure that contains no massive car-
1 or Plate I of Test Method A247.
bides.
5.2.1 When specified in the purchase order, Grade 60-40-18 7.4 Pressure Test Requirements :
castings may be provided in an as-cast condition provided they
7.4.1 Each pressure retaining Grade 60-40-18 casting shall
comply with the requirements of 7.1 and 7.2.1.
be tested after machining to the test pressure specified by the
5.2.2 Castings supplied in accordance with 5.2.1 may be
applicable standard of ANSI, ASME Boiler and Pressure
stress relieved by agreement between the manufacturer and
Vessel Code, or other pertinent code, and shall show no leaks.
purchaser.
7.4.2 Castings Grade 65-45-15 manufactured under this
5.3 Castings Grade 65-45-15 may be provided in as-cast
specification shall be capable of passing hydrostatic test(s)
condition or heat treated, provided they comply with the
compatible with the rating of the finished cast component.
requirements of 7.1, 7.2.2, and 7.3.2.
Such tests shall be conducted by the casting manufacturer only
when Supplementary Requirement S2 is specified.
6. Chemical Requirements
7.4.3 Castings Grade 60-40-18, ordered under this specifi-
6.1 The casting shall conform to the following requirements
cation not covered by ANSI standards and ASME Pressure
for chemical composition (Note 2):
VesselCode,andcastingsforspecialserviceapplications,shall
Total carbon, min, % 3.00
be tested to such pressures as may be agreed upon by the
Silicon, max, % 2.50
manufacturer and the purchaser.
Phosphorus, max, % 0.08
7.4.4 For castings Grade 60-40-18, it is realized that the
6.1.1 The chemical analysis for total carbon shall be made
foundry may be unable to perform the hydrostatic test prior to
on chilled cast pencil type specimens or from thin wafers
shipment, or that the purchaser may wish to defer testing until
approximately ⁄32 in. [0.8 mm] thick cut from test coupons.
additional work or machining has been performed on the
Drillings are not reliable because of the probable loss of
graphite. casting. Castings ordered in the rough state for final machining
by the purchaser may be tested hydrostatically prior to ship-
6.1.2 For each reduction of 0.01 % below the maximum
specified phosphorus content, an increase of 0.08 % silicon ment by the manufacturer at pressures to be agreed upon with
above the specified maximum will be permitted up to a the purchaser. However, the foundry is responsible for the
maximum of 2.75 %.
satisfactory performance of the castings under the final hydro-
static test.
NOTE 2—Silicon contents above 2.75 %, or phosphorus contents above
0.08 % have a tendency to lower the impact resistance of the material. If
the carbon content is below 3.00 %, excess cementite may form during 8. Workmanship and Finish
cooling and if this is not removed during heat treatment, the impact
8.1 The surface of the casting shall be examined visually
resistance of the material may be lowered.
and shall be free from adhering sand, scale, cracks, and hot
7. Requirements
tears. Any other surface discontinuities shall meet visual
7.1 Tensile Properties: acceptance standards specified in the order.
A395/A395M − 99 (2014)
NOTE 1—Graphite types are identical with Plate 1 of Test Method A247 and are so identified.
FIG. 1 Suggested Classification of Graphite Form in Ductile Cast Iron
9. Repair of the plug should be ground smooth after installation to
conform to the inside and outside contours of the wall of the
9.1 Castings for valves, flanges, pipe fittings, pumps, and
pressure vessel or pressure part.
other piping components ordered under applicable ANSI stan-
9.2.4 The material from which the plug is manufactured
dards shall not be repaired by plugging, welding, brazing, or
shall conform in all respects to the materials specifications that
impregnation.
apply to the pressure vessel or pressure part.
9.2 Castings Grade 60-40-18 not covered in 9.1 which leak
9.2.5 The area adjacent to the drilled hole shall be examined
on hydrostatic tests may be repaired by plugging, provided the
by radiography, and shall meet the Level 3 acceptance require-
following requirements are met:
ments of Reference Radiographs E689 and supporting Refer-
9.2.1 No welding or brazing is permitted.
ence Radiographs E446, E186,or E280 as applicable and
9.2.2 The diameter of the plug shall not exceed the diameter
defined in accordance with Reference Radiographs E689.
of a standard 2 in. [ISO R2] pipe plug.
9.2.6 The thickness of any repaired section in relation to the
9.2.3 The plugs, where practical, shall conform in all
size of the plug used shall not be less than that given in Table
dimensions to the standard ISO ⁄8 plugs. In addition, they
2.
shall have full thread engagement corresponding to the thick-
9.2.7 The minimum radius of repaired sections of cylinders
ness in the repaired section. Where a tapered plug is imprac-
or cones in relation to the size of plug used shall not be less
tical because of the excess wall thickness in terms of plug
than that given in Table 3.
diameter and coincident thread engagement, other types of
plugsmaybeusedprovidedbothfullengagementandeffective 9.2.8 A repaired area may consist of a maximum of three
sealing against pressure are obtained. Where possible, the ends plugs with a spacing such that the ligaments between adjacent
A395/A395M − 99 (2014)
TABLE 2 Minimum Thickness of Repaired Sections
10.1.3 All the metal poured from a continuous melting
Minimum Thickness Repaired furnace for a given period of time between changes in charge,
Iron Pipe Size Plug, in.
Section, in. [mm]
processing conditions, or aim-for chemistry, or 8 h, whichever
1 11
⁄8 ⁄32 [8]
is the shorter period.
1 7
⁄4 ⁄16 [10]
3 1
⁄8 ⁄2 [13]
1 21 11. Test Coupon
⁄2 ⁄32 [17]
3 3
⁄4 ⁄4 [19]
11.1 The separately cast test coupons poured from the same
1 ⁄16 [21]
1 7
1 ⁄4 ⁄8 [23] lot as the castings they represent from which the tension test
1 15
1 ⁄2 ⁄16 [24]
specimenismachinedshallbecasttothesizeandshapeshown
2 1 [26]
in Fig. 2, Fig. 3,or Fig. 4. Cast coupons shall be identified with
the castings they represent. Sectioning procedure for removing
test specimens from Y-blocks is shown in Fig. 5.
TABLE 3 Minimum Radius of Repaired Sections
11.1.1 Test samples may be removed from castings at
Minimum Radius of Cylinder
Iron Pipe Size Plug, in.
locations designated on a drawing or as agreed to by manu-
or Cone, in. [mm]
1 9 facturer and purchaser.
⁄8 ⁄16 [15]
1 11
⁄4 ⁄16 [18] 11.1.2 Test bars removed from castings shall conform to
3 1
⁄8 1 ⁄16 [28]
Fig. 6. The testing diameter shall be ⁄2 in. [12.5 mm] if
1 1
⁄2 1 ⁄4 [32]
possible. Smaller diameters shall be utilized if necessary.
⁄4 2 [52]
12 ⁄2 [64]
11.2 The test coupon size shall be as mutually agreed upon
1 ⁄4 4 [104]
1 1
between the manufacturer and purchaser. In the absence of
1 ⁄2 5 ⁄4 [136]
28 ⁄8 [208]
agreement, it shall be the option of the manufacturer.
11.3 The test coupons shall be cast in molds made of
suitable core sand having a minimum wall thickness of 1 ⁄2 in.
[38 mm] for the ⁄2 in. [12.5 mm], 1 in. [25 mm] sizes, and 3
plugs shall not be less than listed in Table 4. Other defective
in. [75 mm] for the 3 in. [75 mm] size. The coupons shall be
areas may also be repaired by plugging provided the minimum
left in the mold until they have changed to a black color
ligament between plugs in adjacent areas is not less than twice
(approximately 900°F [480°C] or less). The keel block as
the distance from the nearest plug, the values for which are
shown in Fig. 2 or the modified keel block produced from the
listed in Table 4.
mold shown in Fig. 4 may be substituted for the 1 in. [25 mm]
9.3 Surface imperfections in castings Grade 60-40-18 other block shown in Fig. 3.
than valves, flanges, pipe fittings, pumps, and other piping
11.4 When investment castings are made to this
componentsmayberepairedbypluggingprovidedthedepthof
specification, the manufacturer may use test specimens cast to
the plug is not greater than 20 % of the thickness of the casting
size incorporated in the mold with the
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.