ASTM D7833-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Hydrocarbons and Non-Hydrocarbon Gases in Gaseous Mixtures by Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Determination of Hydrocarbons and Non-Hydrocarbon Gases in Gaseous Mixtures by Gas Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The hydrocarbon component distribution of gaseous mixtures is often required for end-use sale of this material. Applications such as chemical feedstock or fuel require precise compositional data to ensure uniform quality. Trace amounts of some hydrocarbon impurities in these materials can have adverse effects on their use and processing. Certain regulations may require use of such method.
5.2 The component distribution data of gaseous mixtures can be used to calculate physical properties such as relative density, vapor pressure, and heating value calculations found in Practice D3588. Precision and accuracy of compositional data is extremely important when this data is used to calculate various properties of petroleum products.
SCOPE
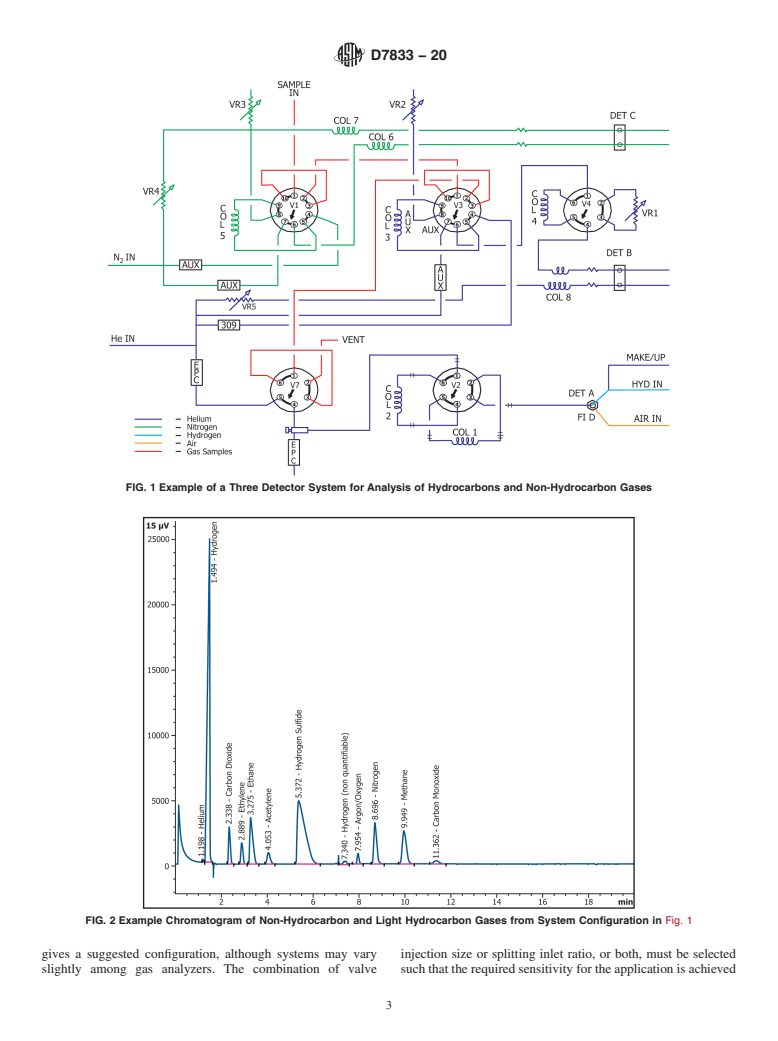
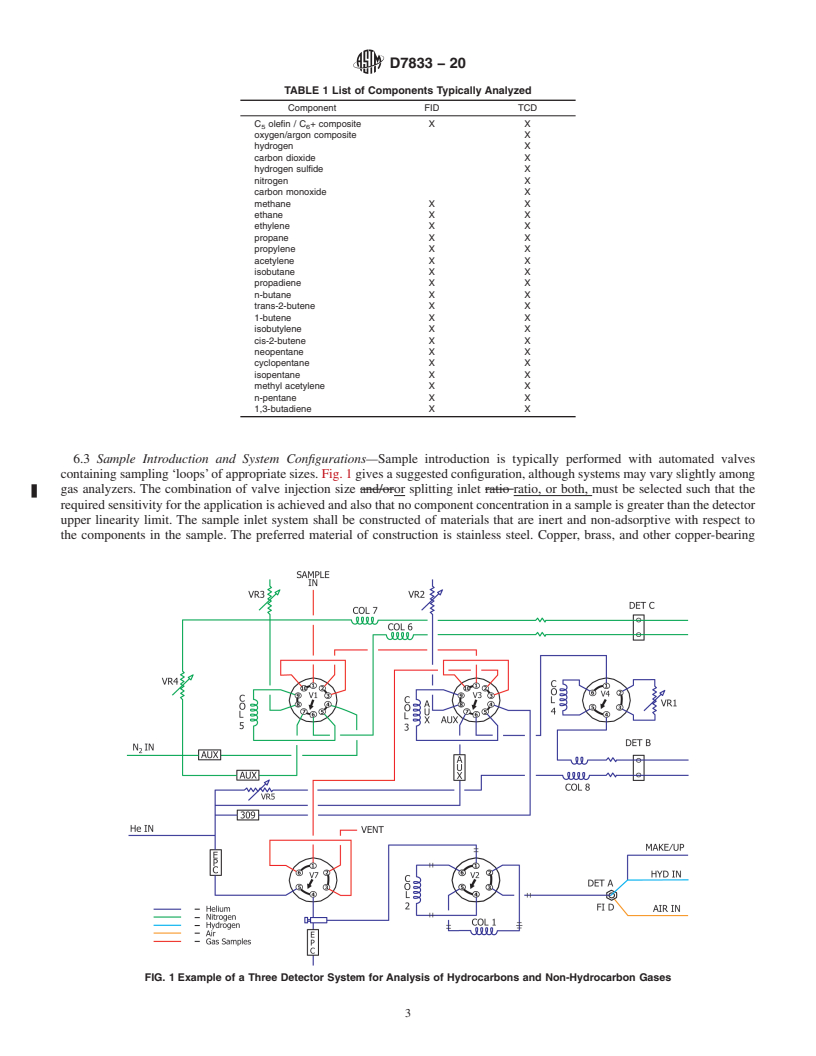
1.1 This test method is intended to quantitatively determine the non-condensed hydrocarbon gases with carbon numbers from C1 to C5+ and non-hydrocarbon gases, such as H2, CO2, O2, N2, and CO, in gaseous samples. This test method is a companion standard test method to Test Method D1945 and Practice D1946, differing in that it incorporates use of capillary columns instead of packed columns and allows other technological differences.
1.2 Hydrogen sulfide can be detected but may not be accurately determined by this procedure due to loss in sample containers or sample lines and possible reactions unless special precautions are taken.
1.3 Non-hydrocarbon gases have a lower detection limit in the concentration range of 0.03 to 100 mole percent using a thermal conductivity detector (TCD), and C1 to C6 hydrocarbons have a lower detection limit in the range of 0.005 to 100 mole percent using a flame ionization detector (FID); using a TCD may increase the lower detection limit to approximately 0.03 mole percent.
1.3.1 Hydrocarbon detection limits can be reduced with the use of pre-concentration techniques or cryogenic trapping, or both.
1.4 This test method does not fully determine individual hydrocarbons heavier than benzene, which are grouped together as C7+. When detailed analysis is not required, the compounds with carbon number greater than C5 may be grouped as either C6+ or C7+. Accurate analysis of C5+ components depends on proper vaporization of these compounds during sampling at process unit sources as well as in the sample introduction into the analyzer in the laboratory.
1.5 Water vapor may interfere with the C6+ analysis if a TCD detector is used.
1.6 Helium and argon may interfere with the determination of hydrogen and oxygen respectively. Depending on the analyzer used, pentenes, if present, may either be separated or grouped with the C6+ components.
1.7 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.9 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D7833 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Hydrocarbons and Non-Hydrocarbon
1
Gases in Gaseous Mixtures by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7833; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.6 Helium and argon may interfere with the determination
of hydrogen and oxygen respectively. Depending on the
1.1 This test method is intended to quantitatively determine
analyzer used, pentenes, if present, may either be separated or
the non-condensed hydrocarbon gases with carbon numbers
grouped with the C + components.
6
from C to C + and non-hydrocarbon gases, such as H , CO ,
1 5 2 2
1.7 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
O , N , and CO, in gaseous samples. This test method is a
2 2
as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
companion standard test method to Test Method D1945 and
standard.
Practice D1946, differing in that it incorporates use of capillary
columns instead of packed columns and allows other techno-
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
logical differences.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
1.2 Hydrogen sulfide can be detected but may not be
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
accurately determined by this procedure due to loss in sample
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
containers or sample lines and possible reactions unless special
1.9 This international standard was developed in accor-
precautions are taken.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.3 Non-hydrocarbon gases have a lower detection limit in
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
the concentration range of 0.03 to 100 mole percent using a
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
thermal conductivity detector (TCD), and C to C hydrocar-
1 6 mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
bons have a lower detection limit in the range of 0.005 to 100
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
mole percent using a flame ionization detector (FID); using a
2. Referenced Documents
TCD may increase the lower detection limit to approximately
2
0.03 mole percent.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.3.1 Hydrocarbon detection limits can be reduced with the D1945 Test Method for Analysis of Natural Gas by Gas
use of pre-concentration techniques or cryogenic trapping, or Chromatography
both. D1946 Practice for Analysis of Reformed Gas by Gas
Chromatography
1.4 This test method does not fully determine individual
D3588 Practice for Calculating Heat Value, Compressibility
hydrocarbons heavier than benzene, which are grouped to-
Factor, and Relative Density of Gaseous Fuels
gether as C +. When detailed analysis is not required, the
7
E355 Practice for Gas Chromatography Terms and Relation-
compounds with carbon number greater than C may be
5
ships
grouped as either C + or C +. Accurate analysis of C +
6 7 5
E1510 Practice for Installing Fused Silica Open Tubular
components depends on proper vaporization of these com-
Capillary Columns in Gas Chromatographs
pounds during sampling at process unit sources as well as in
F307 Practice for Sampling Pressurized Gas for Gas Analy-
the sample introduction into the analyzer in the laboratory.
sis
3
1.5 Water vapor may interfere with the C + analysis if a 2.2 ASTM Publication:
6
TCD detector is used.
ASTM DS 4B, 1991 Physical Constants of Hydrocarbon and
Non-Hydrocarbon Compounds
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.06.01 on Analysis of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Major Constituents by Gas Chromatography. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved June 1, 2020. Published June 2020. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 2012. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D7833 – 14. DOI: Available from the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer
10.1520/D7833-20. Service at service@astm.org
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page:
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7833 − 14 D7833 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Hydrocarbons and Non-Hydrocarbon
1
Gases in Gaseous Mixtures by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7833; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is intended to quantitatively determine the non-condensed hydrocarbon gases with carbon numbers from
C to C + and non-hydrocarbon gases, such as H , CO , O , N , and CO, in gaseous samples. This test method is a companion
1 5 2 2 2 2
standard test method to Test Method D1945 and Practice D1946, differing in that it incorporates use of capillary columns instead
of packed columns and allows other technological differences.
1.2 Hydrogen sulfide can be detected but may not be accurately determined by this procedure due to loss in sample containers
or sample lines and possible reactions unless special precautions are taken.
1.3 Non-hydrocarbon gases have a lower detection limit in the concentration range of 0.03 to 100 mole percent using a thermal
conductivity detector (TCD)(TCD), and C to C hydrocarbons have a lower detection limit in the range of 0.005 to 100 mole
1 6
percent using a flame ionization detector (FID); using a TCD may increase the lower detection limit to approximately 0.03 mole
percent.
1.3.1 Hydrocarbon detection limits can be reduced with the use of pre-concentration techniques and/or cryogenic trapping.or
cryogenic trapping, or both.
1.4 This test method does not fully determine individual hydrocarbons heavier than benzene, which are grouped together as
C ++. When detailed analysis is not required, the compounds with carbon number greater than C may be grouped as either C +,+
7 5 6
or C +. Accurate analysis of C + components depends on proper vaporization of these compounds during sampling at process unit
7 5
sources as well as in the sample introduction into the analyzer in the laboratory.
1.5 Water vapor may interfere with the C + analysis if a TCD detector is used.
6
1.6 Helium and argon may interfere with the determination of hydrogen and oxygen respectively. Depending on the analyzer
used, pentenes, if present, may either be separated or grouped with the C + components.
6
1.7 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.9 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1945 Test Method for Analysis of Natural Gas by Gas Chromatography
D1946 Practice for Analysis of Reformed Gas by Gas Chromatography
D3588 Practice for Calculating Heat Value, Compressibility Factor, and Relative Density of Gaseous Fuels
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.07 on Analysis of Chemical
Composition of Gaseous Fuels.
Current edition approved June 1, 2014June 1, 2020. Published June 2014June 2020. Originally approved in 2012. Last previous edition approved in 20122014 as
D7833D7833 – 14.-12. DOI: 10.1520/D7833-14.10.1520/D7833-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7833 − 20
E355 Practice for Gas Chromatography Terms and Relationships
E1510 Practice for Installing Fused Silica Open Tubular Capillary Columns in Gas Chromatographs
F307 Practice for Sampling
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.