ASTM D1708-18
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics by Use of Microtensile Specimens
Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics by Use of Microtensile Specimens
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method provides data for quality control and acceptance or rejection under specifications.
4.2 Before proceeding with this test method, reference the ASTM specification of the material being tested. Any test specimen preparation, conditioning, dimensions, or testing parameters, or combination thereof, covered in the materials specification takes precedence over those mentioned in this test method. If there are no material specifications, then the default conditions herein apply. Table 1 of Classification System D4000 lists the ASTM materials standards that currently exist.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers certain material specifications for which a history of data has been obtained using the standard microtensile specimen. In general, this test method is superseded for general use by either Test Method D882 or Test Method D638. The very small Type V specimen in Test Method D638 is the recommended specimen when limited amounts of material are available.
1.2 This test method covers the determination of the comparative tensile strength and elongation properties of plastics in the form of standard microtensile test specimens when tested under defined conditions of pretreatment, temperature, humidity, and testing machine speed. This method is applicable when using specimens of any thickness up to 3.2 mm (1/8 in.), including thin films.
1.3 This test method cannot be used for the determination of modulus of elasticity. For the determination of modulus, see Test Method D638 or Test Methods D882.
1.4 Data obtained by this test method are relevant and appropriate for use in engineering design.
Note 1: Tensile properties provide useful data for plastics engineering design purposes. However, because of the high degree of sensitivity exhibited by many plastics to rate of straining and environmental conditions, data obtained by this test method cannot be considered valid for applications involving load-time scales or environments widely different from those of this test method. In cases of such dissimilarity, no reliable estimation of the limit of usefulness can be made for most plastics. This sensitivity to rate of straining and environment necessitates testing over a broad load-time scale (including impact and creep) and range of environmental conditions if tensile properties are to suffice for engineering design purposes.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 2: There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D1708 − 18
Standard Test Method for
Tensile Properties of Plastics by Use of Microtensile
1
Specimens
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1708; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.1 This test method covers certain material specifications
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
forwhichahistoryofdatahasbeenobtainedusingthestandard
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
microtensile specimen. In general, this test method is super-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
seded for general use by either Test Method D882 or Test
NOTE 2—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
Method D638. The very small Type V specimen in Test
Method D638 is the recommended specimen when limited
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
amounts of material are available.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
1.2 This test method covers the determination of the com-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
parativetensilestrengthandelongationpropertiesofplasticsin
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
the form of standard microtensile test specimens when tested
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
under defined conditions of pretreatment, temperature,
humidity,andtestingmachinespeed.Thismethodisapplicable
2. Referenced Documents
1
when using specimens of any thickness up to 3.2 mm ( ⁄8 in.),
2
including thin films. 2.1 ASTM Standards:
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
1.3 Thistestmethodcannotbeusedforthedeterminationof
D638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
modulus of elasticity. For the determination of modulus, see
D882 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Thin Plastic
Test Method D638 or Test Methods D882.
Sheeting
1.4 Data obtained by this test method are relevant and D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
appropriate for use in engineering design. D4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Materi-
als
NOTE 1—Tensile properties provide useful data for plastics engineering
D5947 Test Methods for Physical Dimensions of Solid
design purposes. However, because of the high degree of sensitivity
Plastics Specimens
exhibited by many plastics to rate of straining and environmental
conditions, data obtained by this test method cannot be considered valid D6988 GuideforDeterminationofThicknessofPlasticFilm
for applications involving load-time scales or environments widely
Test Specimens
different from those of this test method. In cases of such dissimilarity, no
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
reliableestimationofthelimitofusefulnesscanbemadeformostplastics.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
This sensitivity to rate of straining and environment necessitates testing
E2935 Practice for Conducting Equivalence Testing in
over a broad load-time scale (including impact and creep) and range of
environmentalconditionsiftensilepropertiesaretosufficeforengineering Laboratory Applications
design purposes.
3. Terminology
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
3.1 Definitions—Definitions of terms applying to this test
only.
method appear in Terminology D883 and Test Method D638,
Annex A2.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
2
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.10 on Mechanical Properties. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2018. Published October 2018. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1959. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as D1708 - 13. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D1708-18. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 -----------------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D1708 − 13 D1708 − 18
Standard Test Method for
Tensile Properties of Plastics by Use of Microtensile
1
Specimens
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1708; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers certain material specifications for which a history of data has been obtained using the standard
microtensile specimen. In general, this test method is superseded for general use by either Test MethodsMethod D882 or Test
Method D638. The very small Type V specimen in Test Method D638 is the recommended specimen when limited amounts of
material are available.
1.2 This test method covers the determination of the comparative tensile strength and elongation properties of plastics in the
form of standard microtensile test specimens when tested under defined conditions of pretreatment, temperature, humidity, and
1
testing machine speed. This method is applicable when using specimens of any thickness up to 3.2 mm ( ⁄8 in.), including thin
films.
1.3 This test method cannot be used for the determination of modulus of elasticity. For the determination of modulus, see Test
Method D638 or Test Methods D882.
1.4 Test data Data obtained by this test method are relevant and appropriate for use in engineering design.
NOTE 1—Tensile properties provide useful data for plastics engineering design purposes. However, because of the high degree of sensitivity exhibited
by many plastics to rate of straining and environmental conditions, data obtained by this test method cannot be considered valid for applications involving
load-time scales or environments widely different from those of this test method. In cases of such dissimilarity, no reliable estimation of the limit of
usefulness can be made for most plastics. This sensitivity to rate of straining and environment necessitates testing over a broad load-time scale (including
impact and creep) and range of environmental conditions if tensile properties are to suffice for engineering design purposes.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
NOTE 2—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
D882 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Thin Plastic Sheeting
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Materials
D5947 Test Methods for Physical Dimensions of Solid Plastics Specimens
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.10 on Mechanical Properties.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2013Oct. 1, 2018. Published September 2013October 2018. Originally approved in 1959. Last previous edition approved in 20102013
as D1708 - 10.D1708 - 13. DOI: 10.1520/D1708-13.10.1520/D1708-18.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1708 − 18
D6988 Guide for Determination of Thickness of Plastic Film Test Specimens
E691 Practice for Conduc
...








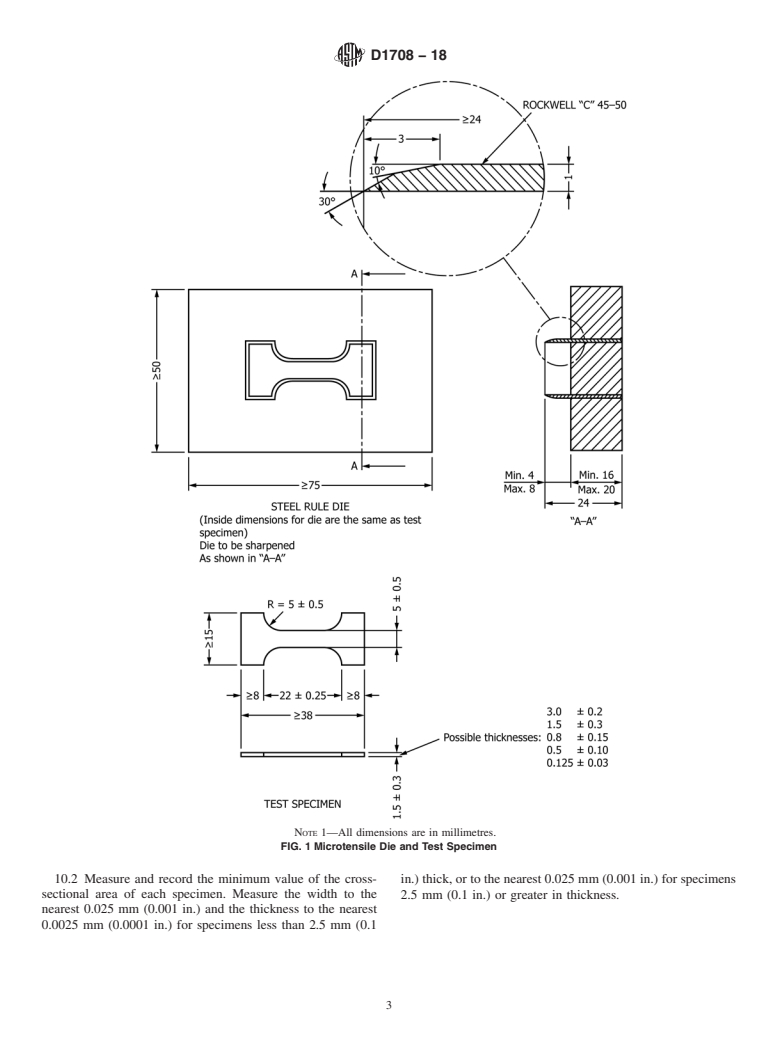

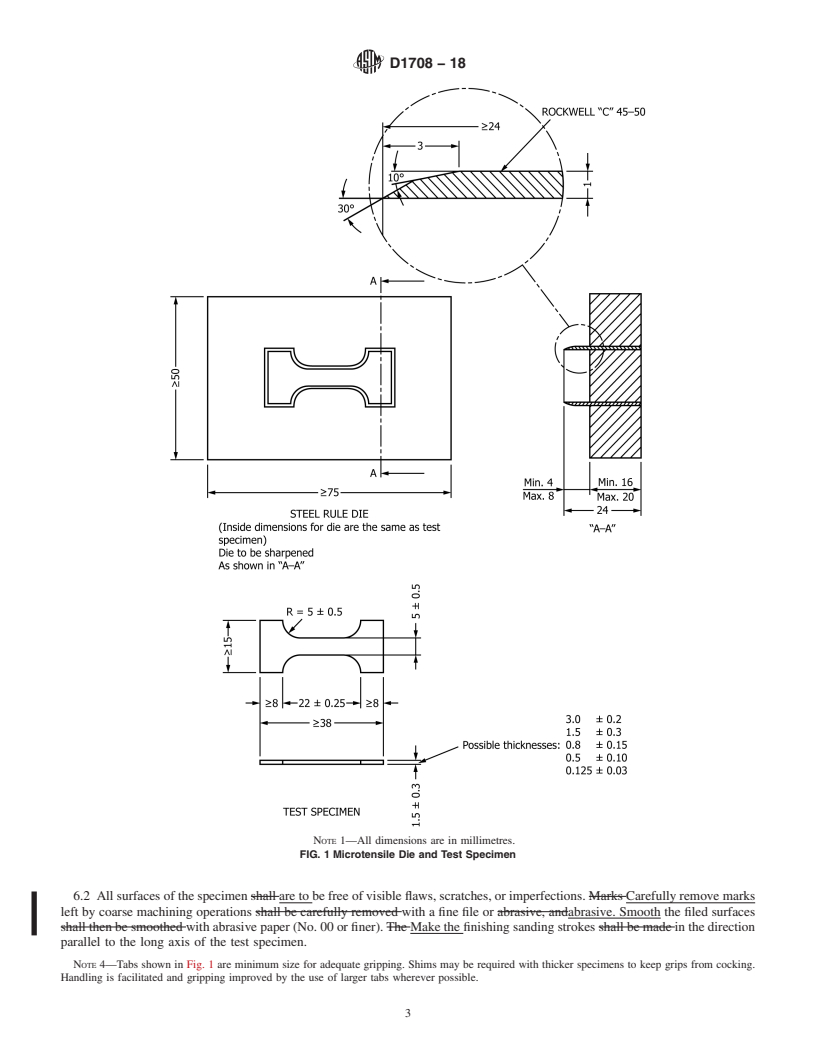
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.