ASTM D5132-11
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Horizontal Burning Rate of Polymeric Materials Used in Occupant Compartments of Motor Vehicles
Standard Test Method for Horizontal Burning Rate of Polymeric Materials Used in Occupant Compartments of Motor Vehicles
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method provides a standard laboratory procedure for measuring and comparing the burning rates of polymeric materials under specified controlled conditions.
The rate of burning is affected by such factors as density, direction of rise, and type and amount of surface treatments. The thickness of the finished specimens must also be taken into account. These factors must be considered in order to compare materials on the same basis.
In this procedure, the specimens are subjected to one or more specific sets of laboratory test conditions. If different test conditions are substituted or the end-use conditions are changed, it is not always possible by or from this test method to predict changes in the fire-test-response characteristics measured. Therefore, the results are valid only for the fire test exposure conditions described in this procedure.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is intended for use as a small-scale laboratory procedure for comparing the relative horizontal burning rates of polymeric materials used in occupant compartments of motor vehicles.
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.3 This test method, Federal Safety Standard MVSS 302, SAE J369, and ISO 3795 address the same subject matter, but differ in technical content.
1.4 This standard is used to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire hazards or fire risk assessment of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 7.
1.6 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safeguards for personnel and property shall be employed in conducting these tests.
Note 1—This standard and ISO 3795 address the same subject matter, but differ in technical content.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5132 − 11
Standard Test Method for
Horizontal Burning Rate of Polymeric Materials Used in
1
Occupant Compartments of Motor Vehicles
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5132; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.1 This test method is intended for use as a small-scale
2.2 Federal Safety Standard:
laboratory procedure for comparing the relative horizontal
MVSS 302 (49 CFR 571.302) Flammability of Interior
burning rates of polymeric materials used in occupant com-
Materials-Passenger Cars, Multipurpose Passenger
partments of motor vehicles.
3
Vehicles, Trucks and Buses
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
2.3 SAE Standard:
as standard.
SAE J369 Flammability of Polymeric Interior Materials -
4
1.3 This test method, Federal Safety Standard MVSS 302, Horizontal Test Method
2.4 ISO Standard:
SAE J369, and ISO 3795 address the same subject matter, but
differ in technical content. ISO 3795 Road vehicles, and tractors and machinery for
agriculture and forestry—Determination of burning be-
1.4 This standard is used to measure and describe the
5
havior of interior materials
responseofmaterials,products,orassembliestoheatandflame
under controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate
3. Terminology
all factors required for fire hazards or fire risk assessment of
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of fire-related terms used in
materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
this test method, refer to Terminology E176.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
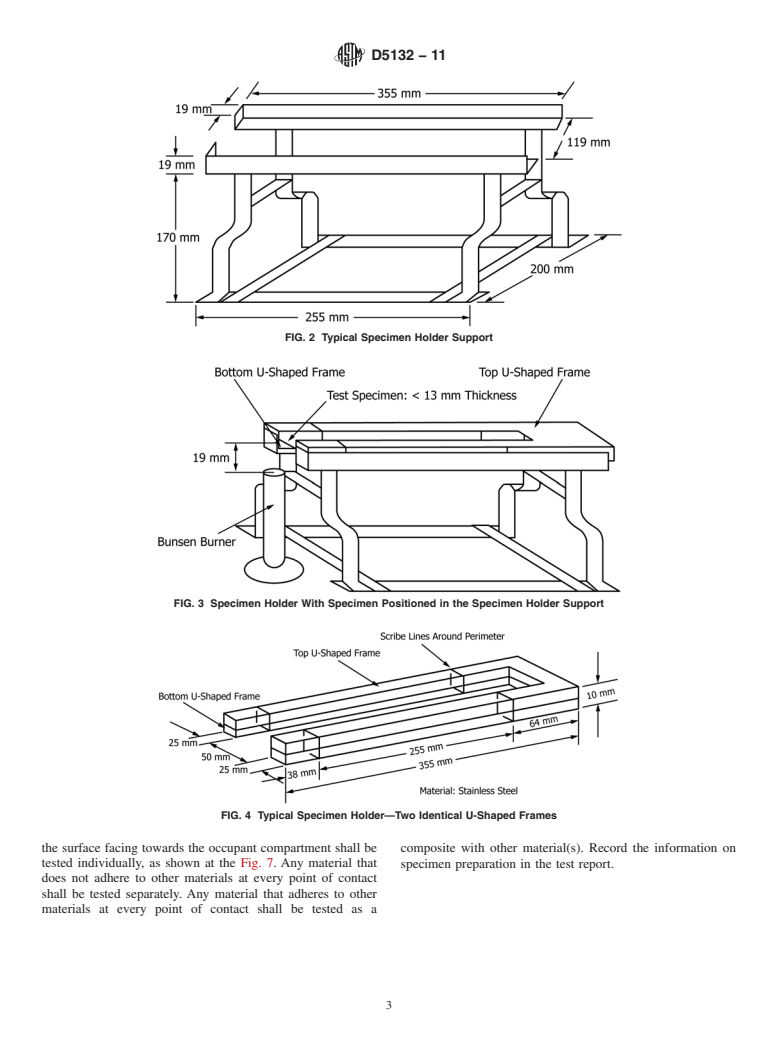
4.1 This test method employs a standard test specimen (100
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
by 356 mm) with a thickness up to 13 mm, mounted in a
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard
U-shaped metal frame. The specimen is ignited by means of a
statements are given in Section 7.
38 mm high flame from an appropriate burner, and the burning
1.6 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safe-
rate of the material is determined.
guards for personnel and property shall be employed in
4.2 The rate of burning is determined by measurements of
conducting these tests.
the horizontal distance burned in relation to the time of
NOTE 1—This standard and ISO 3795 address the same subject matter,
but differ in technical content.
burning, and reported for each set of specimens.
5. Significance and Use
2. Referenced Documents
2
5.1 This test method provides a standard laboratory proce-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
dure for measuring and comparing the burning rates of
D5025 Specification for Laboratory Burner Used for Small-
Scale Burning Tests on Plastic Materials polymeric materials under specified controlled conditions.
E176 Terminology of Fire Standards
5.2 Therateofburningisaffectedbysuchfactorsasdensity,
direction of rise, and type and amount of surface treatments.
Thethicknessofthefinishedspecimensmustalsobetakeninto
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.30 on Thermal Properties.
3
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2011. Published February 2011. Originally United States Code of Federal Regulations, 49 CFR 571.302, 36 FR 28991,
approved in 1990. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D5132 – 04. DOI: available from Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office,
10.1520/D5132-11. Washington, DC 20402.
2 4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001.
5
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1 rue de
the ASTM website. Varembé, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5132 − 11
account. These factors must be considered in order to compare 330 mm long.Aspecimen that softens and bends at the flaming
materials on the same basi
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D5132–04 Designation:D5132–11
Standard Test Method for
Horizontal Burning Rate of Polymeric Materials Used in
1
Occupant Compartments of Motor Vehicles
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5132; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope *
1.1 Thistestmethodisintendedforuseasasmall-scalelaboratoryprocedureforcomparingtherelativehorizontalburningrates
of polymeric materials used in occupant compartments of motor vehicles.
1.2Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.3This test method, Federal Safety Standard MVSS 302, SAE J369, and ISO 3795 Standards are technically equivalent.
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.3 This test method, Federal Safety Standard MVSS 302, SAE J369, and ISO 3795 address the same subject matter, but differ
in technical content.
1.4 This standard is used to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under
controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire hazards or fire risk assessment of materials,
products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 7.
1.6 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safeguards for personnel and property shall be employed in conducting these
tests.
NOTE 1—This standard and ISO 3795 address the same subject matter, but differ in technical content.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D5025 Specification for Laboratory Burner Used for Small-Scale Burning Tests on Plastic Materials
E176 Terminology of Fire Standards
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
2.2 Federal Safety Standard:
MVSS 302Flammability of Interior Materials-Passenger Cars, Multipurpose Passenger Vehicles, Trucks and Buses
MVSS 302 (49 CFR 571.302) Flammability of Interior Materials-Passenger Cars, Multipurpose PassengerVehicles,Trucks and
3
Buses
2.3 SAE Standard:
4
SAE J369 Flammability of Polymeric Interior Materials - Horizontal Test Method
2.4 ISO Standard:
ISO 3795 Road vehicles, and tractors and machinery for agriculture and forestry—Determination of burning behavior of
5
interior materials
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of fire-related terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology E176.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.30 on Thermal Properties.
Current edition approved JulyFeb. 1, 2004.2011. Published July 2004.February 2011. Originally approved in 1990. Last previous edition approved in 20032004 as
D5132 – 034. DOI: 10.1520/D5132-04.10.1520/D5132-11.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
United States Code of Federal Regulations, 49 CFR 571.302, 36 FR 28991, available from Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington,
DC 20402.
4
Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001.
5
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1 rue de Varembé, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5132–11
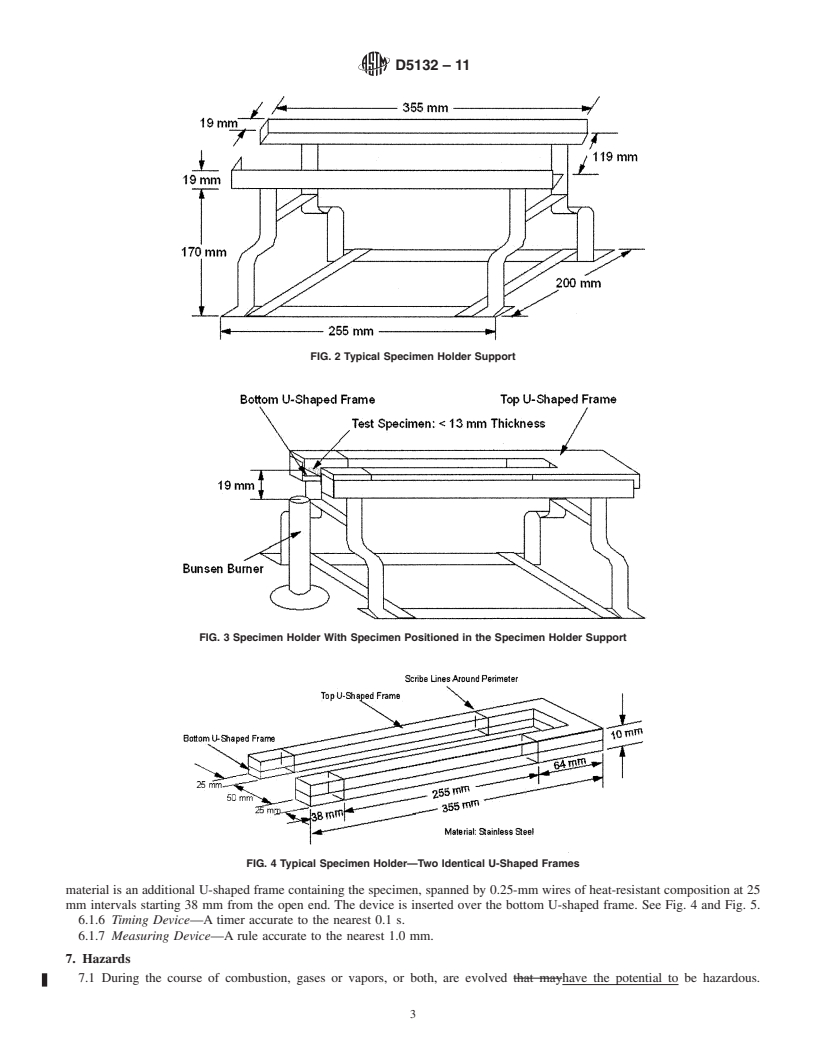
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 This test method employs a standard test specimen (100 by 356) mm356 mm) with a thickness up to 13 mm, mounted in
a U-shaped metal frame. The specimen is ignited by means of a 38-mm38 mm high flame from an appropriate burner, and the
burning rate of the material is determined.
4.2 The rate of burning is determined by measureme
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.