ASTM E748-19
(Guide)Standard Guide for Thermal Neutron Radiography of Materials
Standard Guide for Thermal Neutron Radiography of Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
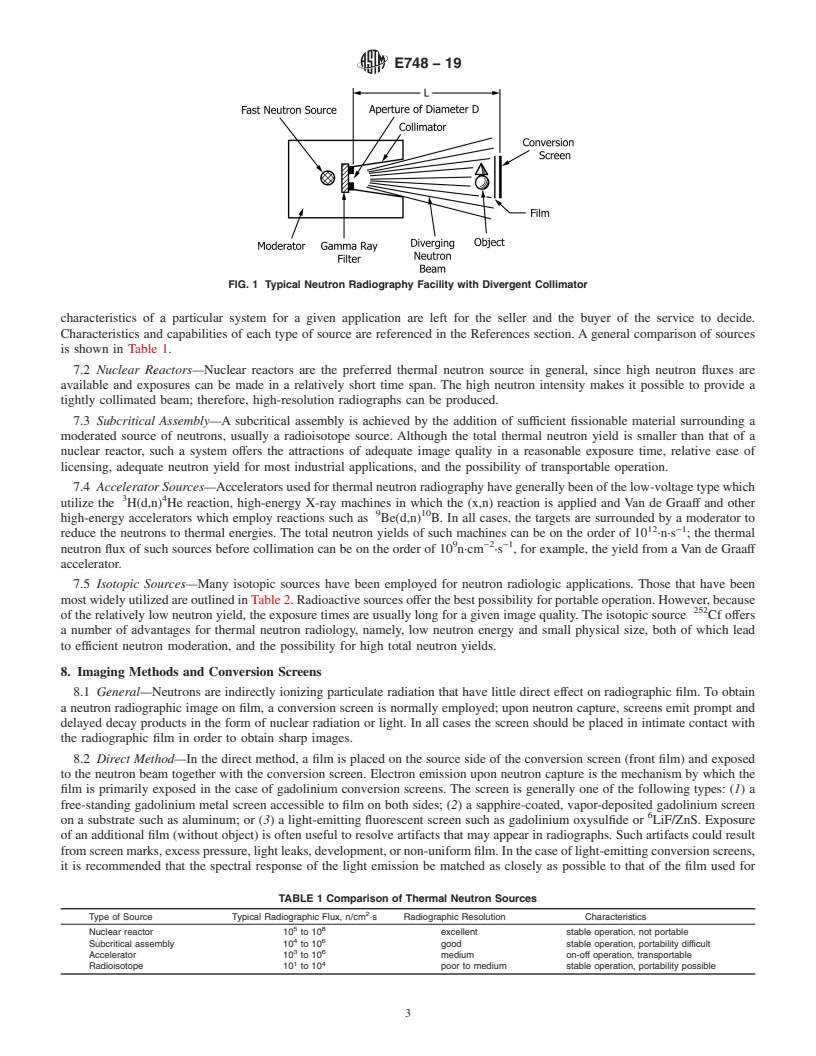
4.1 This guide covers types of materials to be examined, neutron radiographic examination techniques, neutron production and collimation methods, radiographic film, and converter screen selection. Within the present state of the neutron radiologic art, these practices are generally applicable to specific material combinations, processes, and techniques.
SCOPE
1.1 Purpose—Practices to be employed for the radiographic examination of materials and components with thermal neutrons are outlined herein. They are intended as a guide for the production of neutron radiographs that possess consistent quality characteristics, as well as aiding the user to consider the applicability of thermal neutron radiology. Statements concerning preferred practice are provided without a discussion of the technical background for the preference. The necessary technical background can be found in Refs (1-16).2
1.2 Limitations—Acceptance standards have not been established for any material or production process (see Section 5 on Basis of Application). Adherence to the guide will, however, produce reproducible results. Neutron radiography, whether performed by means of a reactor, an accelerator, subcritical assembly, or radioactive source, will be consistent in sensitivity and resolution only if the consistency of all details of the technique, such as neutron source, collimation, geometry, film, etc., are maintained. This guide is limited to the use of photographic or radiographic film in combination with conversion screens for image recording; other imaging systems are available. Emphasis is placed on the use of nuclear reactor neutron sources.
1.3 Interpretation and Acceptance Standards—Interpretation and acceptance standards are not covered by this guide. Designation of accept-reject standards is recognized to be within the cognizance of product specifications.
1.4 Safety Practices—General practices for personnel protection against neutron and associated radiation peculiar to the neutron radiologic process are discussed in Section 18. Jurisdictional nuclear regulations will also apply.
1.5 Other Aspects of the Neutron Radiographic Process—For many important aspects of neutron radiography such as technique, files, viewing of radiographs, storage of radiographs, film processing, and record keeping, refer to Guide E94, which covers these aspects for X-ray radiography. (See Section 2.)
1.6 The values stated in either SI or inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E748 − 19
Standard Guide for
1
Thermal Neutron Radiography of Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E748; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* radiographs, film processing, and record keeping, refer to
Guide E94, which covers these aspects for X-ray radiography.
1.1 Purpose—Practicestobeemployedfortheradiographic
(See Section 2.)
examination of materials and components with thermal neu-
trons are outlined herein. They are intended as a guide for the 1.6 The values stated in either SI or inch-pound units are to
production of neutron radiographs that possess consistent be regarded as the standard.
qualitycharacteristics,aswellasaidingtheusertoconsiderthe
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
applicabilityofthermalneutronradiology.Statementsconcern-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ing preferred practice are provided without a discussion of the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
technical background for the preference. The necessary tech-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
2
nical background can be found in Refs (1-16).
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accor-
1.2 Limitations—Acceptancestandardshavenotbeenestab-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
lished for any material or production process (see Section 5 on
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Basis of Application). Adherence to the guide will, however,
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
produce reproducible results. Neutron radiography, whether
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
performed by means of a reactor, an accelerator, subcritical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
assembly,orradioactivesource,willbeconsistentinsensitivity
and resolution only if the consistency of all details of the
2. Referenced Documents
technique, such as neutron source, collimation, geometry, film,
3
etc., are maintained. This guide is limited to the use of
2.1 ASTM Standards:
photographicorradiographicfilmincombinationwithconver-
E94Guide for Radiographic Examination Using Industrial
sion screens for image recording; other imaging systems are
Radiographic Film
available. Emphasis is placed on the use of nuclear reactor
E543Specification forAgencies Performing Nondestructive
neutron sources.
Testing
E545Test Method for Determining Image Quality in Direct
1.3 Interpretation and Acceptance Standards—
Thermal Neutron Radiographic Examination
Interpretationandacceptancestandardsarenotcoveredbythis
E803TestMethodforDeterminingthe L/DRatioofNeutron
guide. Designation of accept-reject standards is recognized to
Radiography Beams
be within the cognizance of product specifications.
E1316Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations
1.4 Safety Practices—General practices for personnel pro-
4
2.2 ASNT Standard:
tection against neutron and associated radiation peculiar to the
Recommended Practice SNT-TC-1Afor Personnel Qualifi-
neutron radiologic process are discussed in Section 18. Juris-
cation and Certification
dictional nuclear regulations will also apply.
5
2.3 ANSI Standard:
1.5 Other Aspects of the Neutron Radiographic Process—
ANSI/ASNT-CP-189Standard for Qualification and Certifi-
For many important aspects of neutron radiography such as
cation of Nondestructive Testing Personnel
technique, files, viewing of radiographs, storage of
1 3
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee E07 on Nondestruc- For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
tive Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.05 on Radiology contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
(Neutron) Method. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved May 1, 2019. Published June 2019. Originally the ASTM website.
4
approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as E748–16. DOI: AvailablefromAmericanSocietyforNondestructiveTesting(ASNT),P.O.Box
10.1520/E0748-19. 28518, 1711 Arlingate Ln., Columbus, OH 43228-0518, http://www.asnt.org.
2 5
Theboldfacenumbersinparenthesesrefertothelistofreferencesattheendof Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
this standard. 4th
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E748 − 16 E748 − 19
Standard Guide for
1
Thermal Neutron Radiography of Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E748; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 Purpose—Practices to be employed for the radiographic examination of materials and components with thermal neutrons
are outlined herein. They are intended as a guide for the production of neutron radiographs that possess consistent quality
characteristics, as well as aiding the user to consider the applicability of thermal neutron radiology. Statements concerning
preferred practice are provided without a discussion of the technical background for the preference. The necessary technical
2
background can be found in Refs (1-16).
1.2 Limitations—Acceptance standards have not been established for any material or production process (see Section 5 on Basis
of Application). Adherence to the guide will, however, produce reproducible results. Neutron radiography, whether performed by
means of a reactor, an accelerator, subcritical assembly, or radioactive source, will be consistent in sensitivity and resolution only
if the consistency of all details of the technique, such as neutron source, collimation, geometry, film, etc., are maintained. This
guide is limited to the use of photographic or radiographic film in combination with conversion screens for image recording; other
imaging systems are available. Emphasis is placed on the use of nuclear reactor neutron sources.
1.3 Interpretation and Acceptance Standards—Interpretation and acceptance standards are not covered by this guide.
Designation of accept-reject standards is recognized to be within the cognizance of product specifications.
1.4 Safety Practices—General practices for personnel protection against neutron and associated radiation peculiar to the neutron
radiologic process are discussed in Section 1718. Jurisdictional nuclear regulations will also apply.
1.5 Other Aspects of the Neutron Radiographic Process—For many important aspects of neutron radiography such as technique,
files, viewing of radiographs, storage of radiographs, film processing, and record keeping, refer to Guide E94, which covers these
aspects for x-rayX-ray radiography. (See Section 2.)
1.6 The values stated in either SI or inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E94 Guide for Radiographic Examination Using Industrial Radiographic Film
E543 Specification for Agencies Performing Nondestructive Testing
E545 Test Method for Determining Image Quality in Direct Thermal Neutron Radiographic Examination
E803 Test Method for Determining the L/D Ratio of Neutron Radiography Beams
E1316 Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations
1
These practices areThis guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E07 on Nondestructive Testing and areis the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.05
on Radiology (Neutron) Method.
Current edition approved Feb. 15, 2016May 1, 2019. Published February 2016June 2019. Originally approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 20082016 as
E748 – 02E748 – 16.(2008). DOI: 10.1520/E0748-16.10.1520/E0748-19.
2
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of these practices.this standard.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C7
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.