ASTM E801-06(2011)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Controlling Quality of Radiological Examination of Electronic Devices
Standard Practice for Controlling Quality of Radiological Examination of Electronic Devices
ABSTRACT
This practice is intended to control the quality and repeatability of the radiological examination of electronic devices for internal discontinuities, extraneous material, missing components, crimped or broken wires, and defective solder joints in cavities, in the encapsulating materials, or the boards. However, this practice is not intended to control the acceptability or quality of the electronic devices imaged. The quality of the radiological examination shall be determined by image quality indicators (IQIs), which shall be manufactured from clear acrylic plastic with steel covers serving as shims, lead spheres, gold or tungsten wires, and lead numbers, and shall be permanently identified with the appropriate IQI number. The IQI shall simulate as closely as possible the device being examined. For example, the IQI shall have a radiographic density or grey level nearest to that of the device being examined. Two IQIs shall be used for each radiograph, with each IQI located at diagonally opposite corners of the film, and the radiographic image free of blemishes. To identify the image, in both radiography and radioscopy, a system of positive identification of the image shall be provided, which may include any or all of the following: the name of examining laboratory, the date, the part number, the serial number, the data code, the view, and whether original or subsequent exposure.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice relates to the radiological examination of electronic devices for internal discontinuities, extraneous material, missing components, crimped or broken wires, and defective solder joints in cavities, in the encapsulating materials, or the boards. Requirements expressed in this practice are intended to control the quality and repeatability of the radiological images and are not intended for controlling the acceptability or quality of the electronic devices imaged.
Note 1—Refer to the following publications for pertinent information on methodology and safety and protection: Guides E94 and E1000, and “General Safety Standard for Installation Using Non-Medical X Ray and Sealed Gamma Ray Sources, Energies Up to 10 MeV Equipment Design and Use,” Handbook No. 114.
1.2 If a nondestructive testing agency as described in Practice E543 is used to perform the examination, the testing agency should meet the requirements of Practice E543.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E801 −06 (Reapproved 2011)
Standard Practice for
Controlling Quality of Radiological Examination of
Electronic Devices
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E801; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope E1316 Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations
1.1 This practice relates to the radiological examination of
3. Terminology
electronic devices for internal discontinuities, extraneous
3.1 Definitions—Refer to Terminology E1316, Section D.
material, missing components, crimped or broken wires, and
defective solder joints in cavities, in the encapsulating
4. Direction of Radiation
materials, or the boards. Requirements expressed in this
4.1 When not otherwise specified, the direction of the
practice are intended to control the quality and repeatability of
the radiological images and are not intended for controlling the central beam of radiation shall be as perpendicular (65%)as
possible to the surface of the film or detector.
acceptability or quality of the electronic devices imaged.
NOTE 1—Refer to the following publications for pertinent information
5. Image Quality Indicators (IQI’s)
on methodology and safety and protection: Guides E94 and E1000, and
“General Safety Standard for Installation Using Non-Medical X Ray and
5.1 The quality of all levels of radiological examination
Sealed Gamma Ray Sources, Energies Up to 10 MeV Equipment Design
shall be determined by IQI’s conforming to the following
and Use,” Handbook No. 114.
specifications:
1.2 If a nondestructive testing agency as described in
5.1.1 The IQI’s shall be fabricated of clear acrylic plastic
Practice E543 is used to perform the examination, the testing
withsteelcovers,leadspheres,goldortungstenwires,andlead
agency should meet the requirements of Practice E543.
numbers. The steel covers serve as shims.
5.1.1.1 The IQI’s shall conform to the requirements of
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Fig. 1.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5.1.1.2 The IQI’s shall be permanently identified with the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
appropriate IQI number as shown in Fig. 1. The number shall
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
be affixed by mounting a 0.125-in. (3.18-mm) tall lead number
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
on the flat bottom of a 0.250-in. (6.35-mm) diameter hole. The
2. Referenced Documents
identification number shall be located as shown in Fig. 1 and
shall be of sufficient contrast to be clearly discernible in the
2.1 ASTM Standards:
radiological image.
E94 Guide for Radiographic Examination
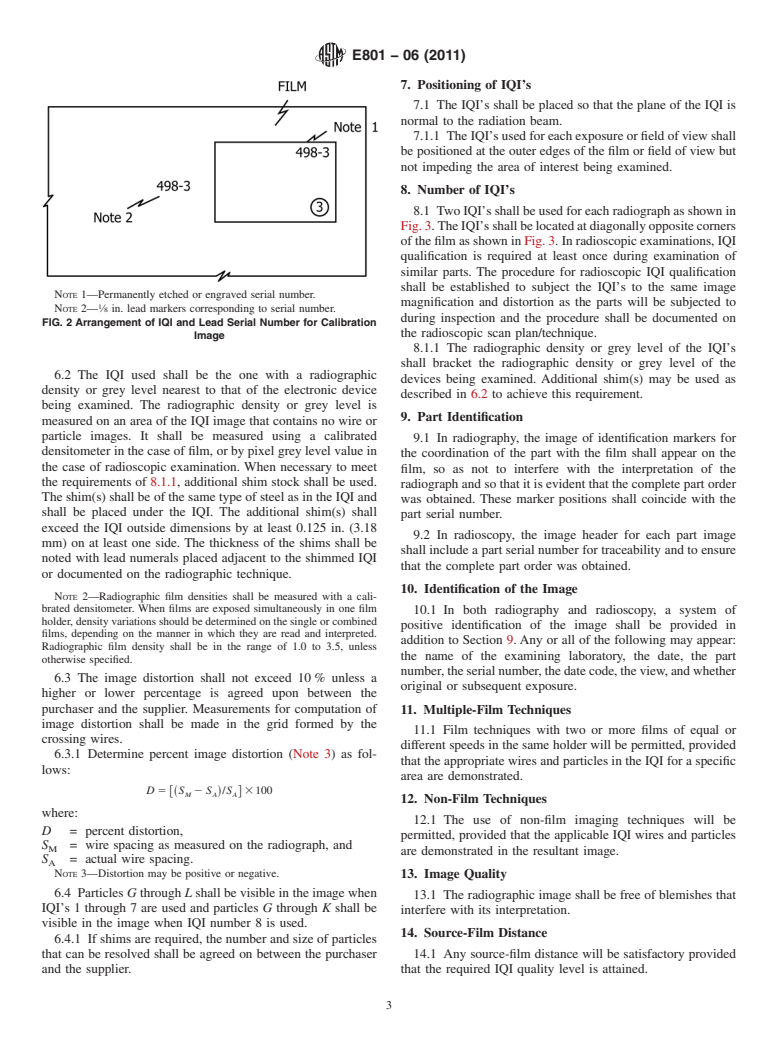
5.1.1.3 Each semiconductor IQI will have a serial number
E543 Specification for Agencies Performing Nondestructive
permanently etched or engraved on it. Each serial number will
Testing
be traceable to the calibration image supplied by the manufac-
E1000 Guide for Radioscopy
turer. The manufacturer shall radiograph the IQI with lead
E1255 Practice for Radioscopy
markers identifying the serial number. See Fig. 2.
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E07 on Nonde-
6. Application of the Image Quality Indicator (IQI)
structive Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.01 on
Radiology (X and Gamma) Method.
6.1 The application of the IQI’s shall be made in such a
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2011. Published March 2012. Originally
manner as to simulate as closely as possible the device being
approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as E801 - 06. DOI:
examined. To accomplish this objective, a set of eight IQI’s is
10.1520/E0801-06R11.
provided. These provide a range of cover thickness (of steel
Available from National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), 100
Bureau Dr., Stop 1070, Gaithersburg, MD 20899-1070, http://www.nist.gov.
shim stock) that is radiologically equivalent to the range of
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
devices from glass diodes or plastic-encapsulated circuits
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
(number one) to large power or hybrid circuit devices (number
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. eight). Wire size increases with shim stock thickness because
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
E801−06 (2011)
FIG. 1 Image Quality Indicator for Electron Devices
Dimensions, in. (mm)
a. 0.187 ( 4.750) f. 1.00 (25.40) k. 1.125 (28.575)
b. 0.375 ( 9.525) g. 0.375 ( 9.525) l. 1.313 (33.350)
c. 0.500 (12.700) h. 0.500 (12.700) m. 1.50 (38.10)
d. 0.625 (15.875) i. 0.625 (15.875) n. 0.125 ( 3.175)
e. 0.813 (20.650) j. 0.938 (23.825) p. 0.250 ( 6.350)
Particle Diameter, in. (mm)
G. 0.015(0.381) J. 0.006(0.152)
H. 0.010(0.254) K. 0.004(0.102)
I. 0.008(0.203) L. 0.002(0.051)
Shim and Wire Specifications
IQI Shim Wire Diameters, in. (mm)
Number Thickness, in. (mm) AB C D E F
1 0 0.002 0.001 0.0005 0.0005 0.001 0.002
0 (0.051) (0.025) (0.0127) (0.0127) (0.025) (0051)
2 0.002 0.002 0.001 0.0005 0.0005 0.001 0.002
(0.051) (0.051) (0.025) (0.0127) (0.0127) (0.025) (0.051)
3 0.005 0.002 0.001 0.0005 0.0005 0.001 0.002
(0.127) (0.051) (0.025) (0.0127) (0.0127) (0.025) (0.051)
4 0.007 0.002 0.001 0.0005 0.0005 0.001 0.002
0.178 (0.051) (0.025) (0.0127) (0.0127) (0.025) (0.051)
5 0.010 0.003 0.002 0.001 0.001 0.002 0.003
(0.254) (0.076) (0.051) (0.025) (0.025) (0.051) (0.076)
6 0.015 0.003 0.002 0.001 0.001 0.002 0.003
(0.381) (0.076) (0.051) (0.025) (0.025) (0.051) (0.076)
7 0.025 0.005 0.003 0.002 0.002 0.003 0.005
(0.635) (0.127) (0.076) (0.051) (0.051) (0.076) (0.127)
8 0.035 0.005 0.003 0.002 0.002 0.003 0.005
(0.889) (0.127) (0.076) (0.051) (0.051) (0.076) (0.127)
NOTE 1—Use additional layers of shim material as required.The layers shall be 1 by 1.625 in. (25.4 by 41.275 mm).The additional shim material shall
be identified by the placement of lead numbers which denote the thickness immediately adjacent to the IQI during exposure, or as an alternative,
documented on the radiographic technique.
NOTE 2—Tolerance is 60.001 in. (0.025 mm) where dimensions are 0.000 and 60.003 in. (0.076 mm) where dimensions are 0.00.
NOTE 3—Bond materials together with cyanoacrylic or equivalent fast-drying epoxy.
NOTE 4—Particle holes are 0.031 in. (0.787 mm) nominal diameter.
NOTE 5—Tolerance on particle diameter is + 0.0003 in. (0.0076 mm).
NOTE 6—Wire grooves are 0.007 in. (0.178 mm) depth with 90° inclusive angle.
NOTE 7—The number hole is 0.25 in. (0.635 mm) nominal diameter and 0.125 in. (0.318 mm) deep.
FIG. 1Image Quality Indicator for Electron Devices
higher power dev
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.