ASTM C779/C779M-05(2010)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Horizontal Concrete Surfaces
Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Horizontal Concrete Surfaces
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The three test methods provide simulated abrasion conditions, which can be used to evaluate the effects on abrasion resistance of concrete, concrete materials, and curing or finishing procedures. They may also be used for quality acceptance of products and surface exposed to wear. They are not intended to provide a quantitative measurement of length of service.
The equipment used by each of these procedures is portable and thus suitable for either laboratory or field testing. The three procedures determine the relative wear of concrete surfaces as follows:
Procedure A—The revolving-disk machine operates by sliding and scuffing of steel disks in conjunction with abrasive grit.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers three procedures for determining the relative abrasion resistance of horizontal concrete surfaces. The procedures differ in the type and degree of abrasive force they impart, and are intended for use in determining variations in surface properties of concrete affected by mixture proportions, finishing, and surface treatment. They are not intended to provide a quantitative measurement of the length of service that may be expected from a specific surface.
1.2 The values stated in SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the inch-pound units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of each other.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (WarningFresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause chemical burns to skin and tissue upon prolonged exposure.)
Note 1—Other procedures are available for measuring the abrasion resistance of concrete surfaces in addition to the three procedures contained in this test method. Consideration should be given to Test Methods C944 and C418. The test method most closely representing service conditions should be used.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C779/C779M − 05(Reapproved 2010)
Standard Test Method for
Abrasion Resistance of Horizontal Concrete Surfaces
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C779/C779M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope C670 Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements
for Test Methods for Construction Materials
1.1 This test method covers three procedures for determin-
C944 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete or
ing the relative abrasion resistance of horizontal concrete
Mortar Surfaces by the Rotating-Cutter Method
surfaces. The procedures differ in the type and degree of
abrasive force they impart, and are intended for use in
3. Significance and Use
determining variations in surface properties of concrete af-
3.1 The three test methods provide simulated abrasion
fected by mixture proportions, finishing, and surface treatment.
conditions, which can be used to evaluate the effects on
Theyarenotintendedtoprovideaquantitativemeasurementof
abrasion resistance of concrete, concrete materials, and curing
the length of service that may be expected from a specific
or finishing procedures. They may also be used for quality
surface.
acceptance of products and surface exposed to wear. They are
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
notintendedtoprovideaquantitativemeasurementoflengthof
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
service.
inch-pound units are shown in brackets. The values stated in
3.2 The equipment used by each of these procedures is
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
portable and thus suitable for either laboratory or field testing.
system shall be used independently of each other.
The three procedures determine the relative wear of concrete
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
surfaces as follows:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.2.1 Procedure A—The revolving-disk machine operates
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
by sliding and scuffing of steel disks in conjunction with
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
abrasive grit.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. (Warning—Fresh
3.2.2 Procedure B—The dressing-wheel machine operates
hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause
by impact and sliding friction of steel dressing wheels.
chemical burns to skin and tissue upon prolonged exposure.)
3.2.3 Procedure C—The ball-bearing machine operates by
NOTE 1—Other procedures are available for measuring the abrasion
high-contact stresses, impact, and sliding friction from steel
resistance of concrete surfaces in addition to the three procedures
balls.
contained in this test method. Consideration should be given to Test
Methods C944 and C418. The test method most closely representing
NOTE 2—Diagrams of three machines meeting these specifications are
service conditions should be used.
shown in Fig. 1, Fig. 2, and Fig. 3.
PROCEDURE A—REVOLVING DISKS
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4. Apparatus
C418 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete by
4.1 The function of the apparatus is dependent upon the
Sandblasting
abrasive action of the flat faces of three 60-mm (2 ⁄8-in.)
diameter, cold-rolled steel revolving disks, each attached to
motor-driven vertical shafts which also revolve about a vertical
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on
Concrete and Concrete Aggregatesand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
axis. The inside diameter of the resulting circular and abraded
C09.62 on Abrasion Testing.
track shall be approximately 150 mm (6 in.) and the outside
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2010. Published December 2010. Originally
approved in 1974. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as C779 – 05. DOI:
10.1520/C0779_C0779M-05(2010).
2 4
Section on Safety Precautions, Manual of Aggregate and Concrete Testing, The sole source of supply of these machines known to the committee at this
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol. 04.02. time isWhite Machine Co., 9591YorkAlpha Dr., North Royalton, OH 44133; Spirit
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Fabricating, Ltd., 9260 Valley View Rd., Macedonia, OH 44056. If you are aware
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Headquarters.Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
the ASTM website. responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
C779/C779M − 05 (2010)
FIG. 1 Revolving Disks Abrasion Test Machine
FIG. 2 Dressing Wheel Abrasion Test Machine
C779/C779M − 05 (2010)
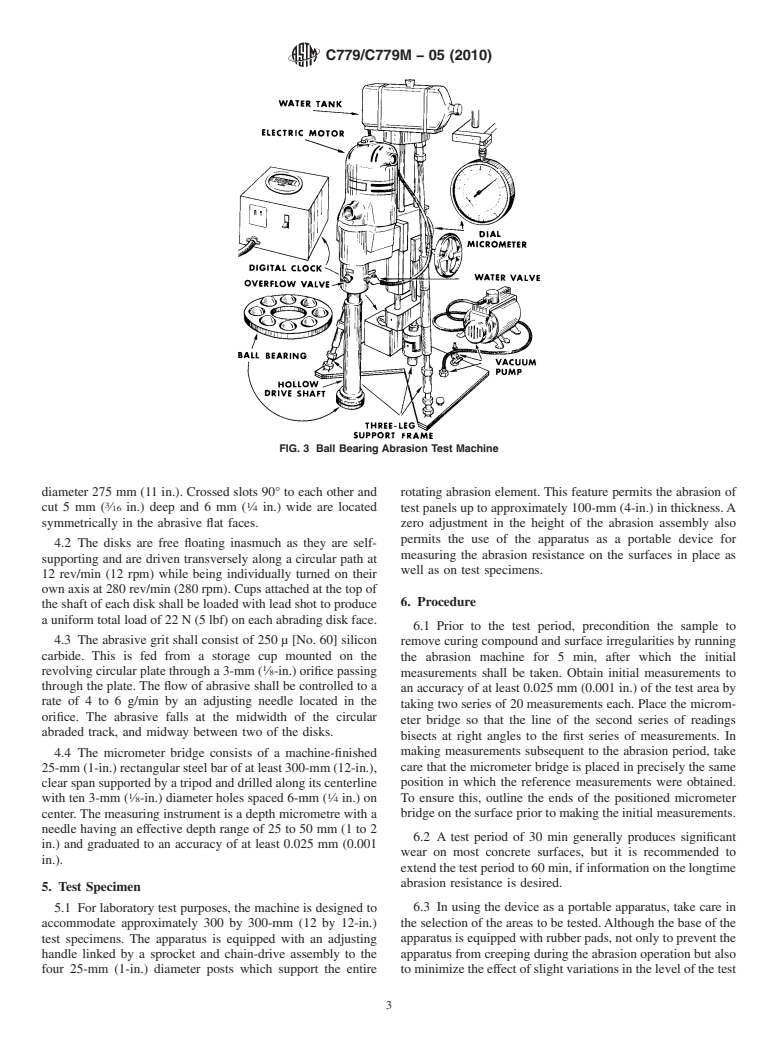
FIG. 3 Ball Bearing Abrasion Test Machine
diameter 275 mm (11 in.). Crossed slots 90° to each other and rotating abrasion element. This feature permits the abrasion of
3 1
cut5mm( ⁄16 in.) deep and 6 mm ( ⁄4 in.) wide are located
test panels up to approximately 100-mm (4-in.) in thickness.A
symmetrically in the abrasive flat faces.
zero adjustment in the height of the abrasion assembly also
permits the use of the apparatus as a portable device for
4.2 The disks are free floating inasmuch as they are self-
measuring the abrasion resistance on the surfaces in place as
supporting and are driven transversely along a circular path at
well as on test specimens.
12 rev/min (12 rpm) while being individually turned on their
own axis at 280 rev/min (280 rpm). Cups attached at the top of
6. Procedure
the shaft of each disk shall be loaded with lead shot to produce
a uniform total load of 22 N (5 lbf) on each abrading disk face.
6.1 Prior to the test period, precondition the sample to
4.3 The abrasive grit shall consist of 250 µ [No. 60] silicon
remove curing compound and surface irregularities by running
carbide. This is fed from a storage cup mounted on the
the abrasion machine for 5 min, after which the initial
revolving circular plate through a 3-mm ( ⁄8-in.) orifice passing
measurements shall be taken. Obtain initial measurements to
through the plate. The flow of abrasive shall be controlled to a
an accuracy of at least 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) of the test area by
rate of 4 to 6 g/min by an adjusting needle located in the
taking two series of 20 measurements each. Place the microm-
orifice. The abrasive falls at the midwidth of the circular
eter bridge so that the line of the second series of readings
abraded track, and midway between two of the disks.
bisects at right angles to the first series of measurements. In
making measurements subsequent to the abrasion period, take
4.4 The micrometer bridge consists of a machine-finished
care that the micrometer bridge is placed in precisely the same
25-mm (1-in.) rectangular steel bar of at least 300-mm (12-in.),
position in which the reference measurements were obtained.
clear span supported by a tripod and drilled along its centerline
1 1
To ensure this, outline the ends of the positioned micrometer
with ten 3-mm ( ⁄8-in.) diameter holes spaced 6-mm ( ⁄4 in.) on
center. The measuring instrument is a depth micrometre with a bridge on the surface prior to making the initial measurements.
needle having an effective depth range of 25 to 50 mm (1 to 2
6.2 A test period of 30 min generally produces significant
in.) and graduated to an accuracy of at least 0.025 mm (0.001
wear on most concrete surfaces, but it is recommended to
in.).
extend the test period to 60 min, if information on the longtime
abrasion resistance is desired.
5. Test Specimen
6.3 In using the device as a portable apparatus, take care in
5.1 For laboratory test purposes, the machine is designed to
the selection of the areas to be tested.Although the base of the
accommodate approximately 300 by 300-mm (12 by 12-in.)
test specimens. The apparatus is equipped with an adjusting apparatus is equipped with rubber pads, not only to prevent the
apparatus from creeping during the abrasion operation but also
handle linked by a sprocket and chain-drive assembly to the
four 25-mm (1-in.) diameter posts which support the entire to minimize the effect of slight variations in the level of the test
C779/C779M − 05 (2010)
areas. Select test areas with a minimum of variation in level so provided with 18 flattened points, each having dimensions of
as to eliminate the creeping effect. 3.0 by 2.0-mm (0.125 by 0.075 in.). The dressing wheels shall
be assembled on the shaft alternated with steel washers. The
6.4 Take measurements of depth wear with a micrometer
total width of seven dressing wheels and eight washers shall be
bridge as described in 4.4 to an accuracy of at least 0.025 mm
approximately 40 mm (1 ⁄2 in.). The dressing wheels must be
(0.001 in.). Prior to each set of measurements, clean the
loose enough to turn freely and independently.
specimen surface carefully by removing loose particles.
9.6 The measuring instrument shall be a dial micrometer,
6.5 Make three tests on surfaces representative of the
reading to an accuracy of at least 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) with a
concrete to be evaluated. When wear of the disks reduces the
range of at least 10 mm (0.4 in.). The contact end of the
depth of the slots to less than 1.5 mm ( ⁄16 in.), they shall be
micrometer spindle shall have a spherical surface of 9.5-mm
replaced.Newdiskfacesshallbesubjectedtoabreak-inperiod
( ⁄8-in.) diameter. A jig located on the underside of the spider
of at least 15 min.
holdsthemicrometremagneticallyintheapproximatecenterof
7. Interpretation of Results
the path of the dressing wheels.
7.1 The comparison of measurements of average depth of
10. Test Specimen
wear of representative surfaces at 30 and 60-min exposure to
10.1 Place a sample approximately 300 by 300 by 100-mm
abrasion will indicate the relative abrasion resistance of these
(12 by 12 by 4-in.) thick into the machine and lock it in place
surfaces.
with vises provided. Do not remove the sample until the test is
8. Report
completed. Test three identical samples.
8.1 Report the depth of wear of each surface tested as well
11. Procedure
as the average obtained on replicate surfaces.
11.1 Position the abrasion apparatus over surface to be
8.2 Record mixture proportions (including cement content
tested. Rubber pads on the bottom of machine will hold the
and water-cement ratio), specific gravities, grading of fine and
machine in place. Turn the screw crank until the full weight of
coarse aggregates, Los Angeles abrasion test results, type and
each dressing-wheel shaft is resting on the concrete surface.
amount of material added to freshly placed concrete surface,
Lower the spider as far as possible without exerting any
typeandextentoftroweling,curingdetails,andageofconcrete
pressure from the spider itself onto these three shafts. Allow a
when tested.
spacing of 15 mm (0.5 in.) for vertical travel of the dressing
PROCEDURE B—DRESSING WHEELS
wheels. Lock the screw crank to prevent any change in vertical
movement of the spider during testing.
9. Apparatus
11.2 Take an initial measurement to the nearest 0.025 mm
9.1 The function of the apparatus is dependent upon the
(0.001 in.) on the test area with the dial micrometer in place
abrasive action of three sets of steel dressing wheels riding in
while revolving the spider two revolutions by hand. Record
a circular path over a horizontal concrete surface. The dressing
this initial reading as a reference reading and then remove the
wheels in each of the three sets of wheels turn freely on a
micrometer. Start the machine and let it run for 30 min, brush
horizontal axle at the bottom of a free-floating, weighted,
offtheloosematerial,insertthedialmicrometer,andrecordthe
vertical steel shaft.
average reading again. If the readings are not reasonably
9.2 Each of the three sets of seven dressing wheels are
uniform, record several readings taken around the circumfer-
spaced so that each set cuts approximately a 40-mm (1 ⁄2-in.)
ence of the abraded surface from which the average reading
wide path. The machine produces a circular abrasion path of
may be computed. The difference between the reference
1 1
about 140-mm (5 ⁄2-in.) inside diameter and 220-mm (8 ⁄2-in.)
reading and the 30-min reading is indicative of the depth of
outside diameter.
wear.
9.3 The apparatus shall consist of a motor-driven spider
11.3 Make three tests on surfaces representative of the
arrangementturningat56rev/min(56rpm).Themotorshallbe
concrete to be evaluated. After every third test, install new
mounted on a horizontal plate supported by four screw jacks
dressing wheels.
allowing the motor to be raised and lowered. The spider shall
11.4 A test period of 30 min generally produces significant
be hung from the vertical motor shaft. The three vertical shafts
wear on most concrete surfaces, but it is recommended to
shall be mounted in the spider arrangement so that they rotate
extend the period to 60 min, if simulation of more severe
with the spider and are free to move up and down in
abrasion is desired. Take depth-of-wear readings at 15-min
independent thrust-bearing sockets.
intervals to the nearest 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) to obtain a time
9.4 The three shafts shall be fitted with a yoke inside, upon
versus wear curve.
which a series of seven dressing wheels are placed on a
horizontal axle. The mass of each complete dressing wheel 12. Interpretation of Results
assembly as it bears on the concrete surface shall be 7.5 kg
12.1 The comparison of measurements of average depth of
(16.5 lb).
wear of representative surfaces at 30 and 60-min exposure to
9.5 The dressing wheels shall have an outside diameter of abrasion will indicate the relative abrasion resistance of these
3 1
60 mm (2 ⁄8 in.) and a thickness of 3 mm ( ⁄8 in.) and shall be surfaces.
C779/C779M − 05 (2010)
12.2 A comparison of curves will indicate whether the 14.8 The machine base shall be provided with a vacuum
resistance to abrasion is primarily at the surface or at a greater hold-down device having three support points.
depth.
15. Test Specimen
13. Report
15.1 When tests are run on concrete specimens rather than
13.1 Plot the time versus dept
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.