ASTM D2094-00e1
(Practice)Standard Practice for Preparation of Bar and Rod Specimens for Adhesion Tests
Standard Practice for Preparation of Bar and Rod Specimens for Adhesion Tests
SCOPE
1.1 This practice describes bar- and rod-type butt-joined adhesion test specimens and procedures for preparing and bonding them. The specimens are intended to be used with various adherend materials in like or unlike combinations for determining the strength properties of adhesives in accordance with Test Method D2095.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are considered to be the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
e1
Designation: D 2094 – 00
Standard Practice for
1
Preparation of Bar and Rod Specimens for Adhesion Tests
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2094; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
e NOTE—Adjunct references were corrected editorially in April 2006.
1. Scope 4. Significance and Use
1.1 This practice describes bar- and rod-type butt-joined 4.1 The procedures outlined in this practice are designed to
adhesion test specimens and procedures for preparing and standardize the test specimens, surface preparations, combina-
bonding them. The specimens are intended to be used with tions of materials, and adhesive selection. Because of the
various adherend materials in like or unlike combinations for flexibility in the procedure, it is important to have some idea of
determining the strength properties of adhesives in accordance the kind of properties that will be observed during testing.
with Test Method D 2095.
5. Test Specimens
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
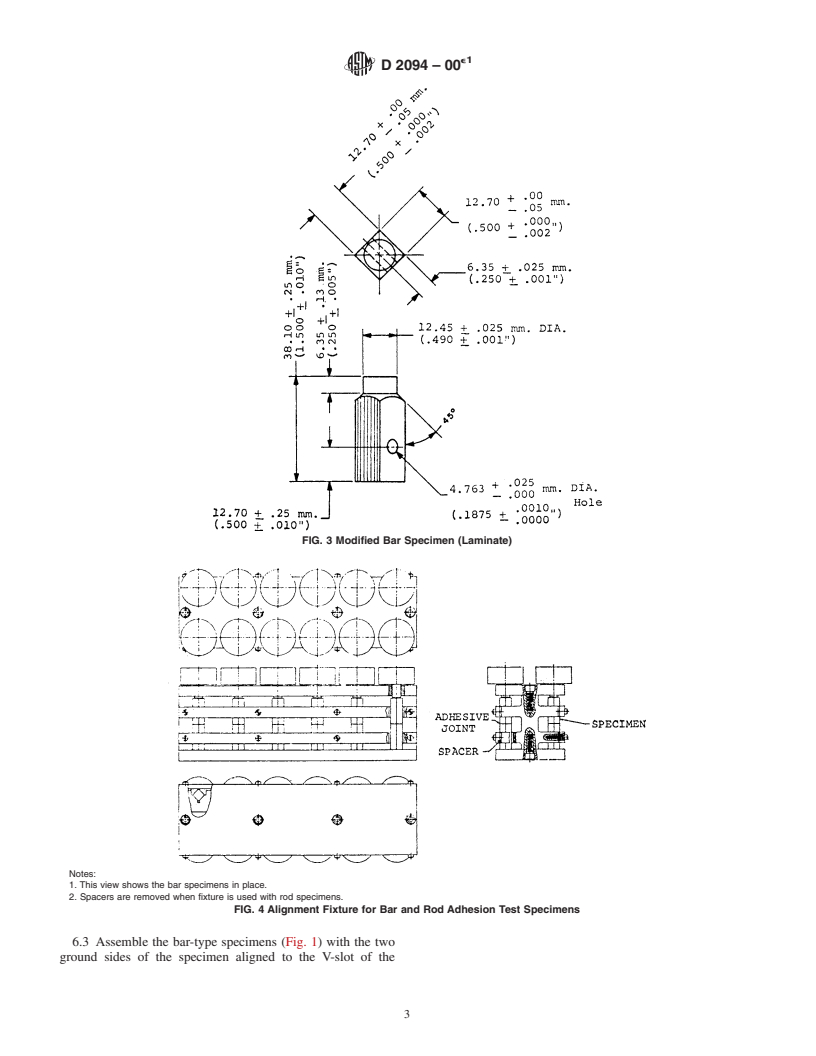
5.1 Geometry—Test specimens conform to the forms and
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- dimensions shown in Fig. 1, Fig. 2,or Fig. 3. Only the bar
specimen (Fig. 1) shall be used for cleavage strength tests.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Only the rod specimen (Fig. 2) or the modified bar specimen
(Fig. 3) shall be used for tests in torsional shear.Amodification
1.3 The values stated in SI units are considered to be the
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only. of the specimen is permissible in tensile tests with dissimilar
adherends, particularly if one of the adherend materials is
2. Referenced Documents
difficulttomachine(forexample,glass)orifthestrengthofthe
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: adherend is such that failure under stress occurs at the drilled
D 907 Terminology of Adhesives hole. This modification consists of a sheet of the material
3 1 1
D 2093 PracticeforPreparationofSurfacesofPlasticsPrior approximately 19 mm ( ⁄4 in.) square and 1 ⁄2to6mm( ⁄16 to
1
to Adhesive Bonding ⁄4 in.) thick inserted and bonded between the ends of the bar or
D 2095 Test Method for Tensile Strength of Adhesives by rod specimens. For comparison purposes, specimen geometry
Means of Bar and Rod Specimens shall be the same unless the effect of insert dimensions is under
D 2651 Guide for Preparation of Metal Surfaces for Adhe- study.
sive Bonding 5.2 Machining of Adherends:
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts: 5.2.1 Use metal adherends machined from bar or rod stock
3
Alignment Fixture Drawings with the surface to be bonded finished to 1 µm.
5.2.2 Machine plastic from laminated flat panels using a
3. Terminology
diamond charged wheel for rough machining and a carbide-
3.1 Definitions—Many terms in this practice are defined in
tipped tool for finish machining. Do all machining dry using
Terminology D 907. care not to damage surfaces by overheating or contamination
with lubricants. Machine laminar materials so that the axis of
the specimen will lie in the plane of the lamina, and so that the
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D14 on Adhesives
plane of the lamina coincides with one side of the specimen
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D14.80 on Metal Bonding
with the hole perpendicular to the plane of the lamina. Finish
Adhesives.
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 2000. Published December 2000. Originally
plastic to 80 µm or better unless studying surface finish.
published as D 2094 – 62 T. Last previous edition D 2094 – 91.
5.2.3 Nonreinforced plastics (either thermoplastic or ther-
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
mosetting) molded in a 127 by 12.7 by 12.7-mm (5 by 0.5 by
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on 0.5-in.) bar mold, machined to a 38.1 mm (1.5 in.) length and
the ASTM website.
a hole drilled as shown in Fig. 1. Specimens machined from
3
Detailed working drawings of the fixtures shown in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5 and their
extruded, cast, or molded plastic rod or sheet are also accept-
parts are available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No.
able.
ADJD2094. Original adjunct produced in 1966.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ------
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.