ASTM E2008-17(2021)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Volatility Rate by Thermogravimetry
Standard Test Methods for Volatility Rate by Thermogravimetry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Volatility of a material is not an equilibrium thermodynamic property but is a characteristic of a material related to a thermodynamic property that is vapor pressure. It is influenced by such factors as surface area, temperature, particle size, and purge gas flow rate; that is, it is diffusion controlled.
5.2 The extent of containment achieved for specimens in these test methods by means of a pinhole opening between 0.33 mm to 0.38 mm allows for measurement circumstances that are relatively insensitive to experimental variables other than temperature. Decreasing the extent of containment by use of pinholes larger than 0.38 mm will increase the magnitude of the observed rate of mass loss but will also reduce the measurement precision by increasing the sensitivity to variations in other experimental variables.
5.3 Results obtained by these test methods are not strictly equivalent to those experienced in processing or handling conditions but may be used to rank materials for their volatility in such circumstances. Therefore, the volatility rates determined by these test methods should be considered as index values only.
5.4 The volatility rate may be used to estimate such quantifiable values as drying interval or the extent of volatile release from a process.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover procedures for assessing the volatility of solids and liquids at given temperatures using thermogravimetry under prescribed experimental conditions. Results of these test methods are obtained as volatility rates expressed as mass per unit time. Rates ≥5 μg/min are achievable with these test methods.
1.2 Temperatures typical for these test methods are within the range from 25 °C to 500 °C. This temperature range may differ depending upon the instrumentation used.
1.3 These test methods are intended to provide a value for the volatility rate of a sample using a thermogravimetric analysis measurement on a single representative specimen. It is the responsibility of the user of these test methods to determine the need for and the number of repetitive measurements on fresh specimens necessary to satisfy end use requirements.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E2008 − 17 (Reapproved 2021)
Standard Test Methods for
1
Volatility Rate by Thermogravimetry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2008; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 These test methods cover procedures for assessing the 2.1 ASTM Standards:
volatility of solids and liquids at given temperatures using E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
thermogravimetry under prescribed experimental conditions. ASTM Test Methods
Results of these test methods are obtained as volatility rates E473 Terminology Relating to Thermal Analysis and Rhe-
expressed as mass per unit time. Rates ≥5 µg/min are achiev- ology
able with these test methods. E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.2 Temperatures typical for these test methods are within
E1142 Terminology Relating to Thermophysical Properties
the range from 25 °C to 500 °C. This temperature range may
E1582 Test Method for Temperature Calibration of Thermo-
differ depending upon the instrumentation used.
gravimetric Analyzers
1.3 These test methods are intended to provide a value for
E1860 Test Method for Elapsed Time Calibration of Ther-
the volatility rate of a sample using a thermogravimetric
mal Analyzers
analysismeasurementonasinglerepresentativespecimen.Itis
E2040 Test Method for Mass Scale Calibration of Thermo-
theresponsibilityoftheuserofthesetestmethodstodetermine
gravimetric Analyzers
the need for and the number of repetitive measurements on
fresh specimens necessary to satisfy end use requirements.
3. Terminology
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1 Definitions:
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.1.1 The following terms are applicable to these test
standard.
methods and can be found in Terminologies E473 and E1142:
3.1.1.1 thermogravimetric analysis (TGA),
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.1.2 thermogravimetry (TG), and
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.1.3 volatility.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.2.1 volatility rate—the rate of conversion of a solid or
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
liquid substance into the vapor state at a given temperature;
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
mass per unit time.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4. Summary of Test Method
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.1 Asolid or liquid specimen is confined in an appropriate
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
container with a pinhole opening between 0.33 mm and 0.38
mm. The confined specimen is heated within a thermogravi-
metricanalyzereithertoatemperatureandheldconstantatthat
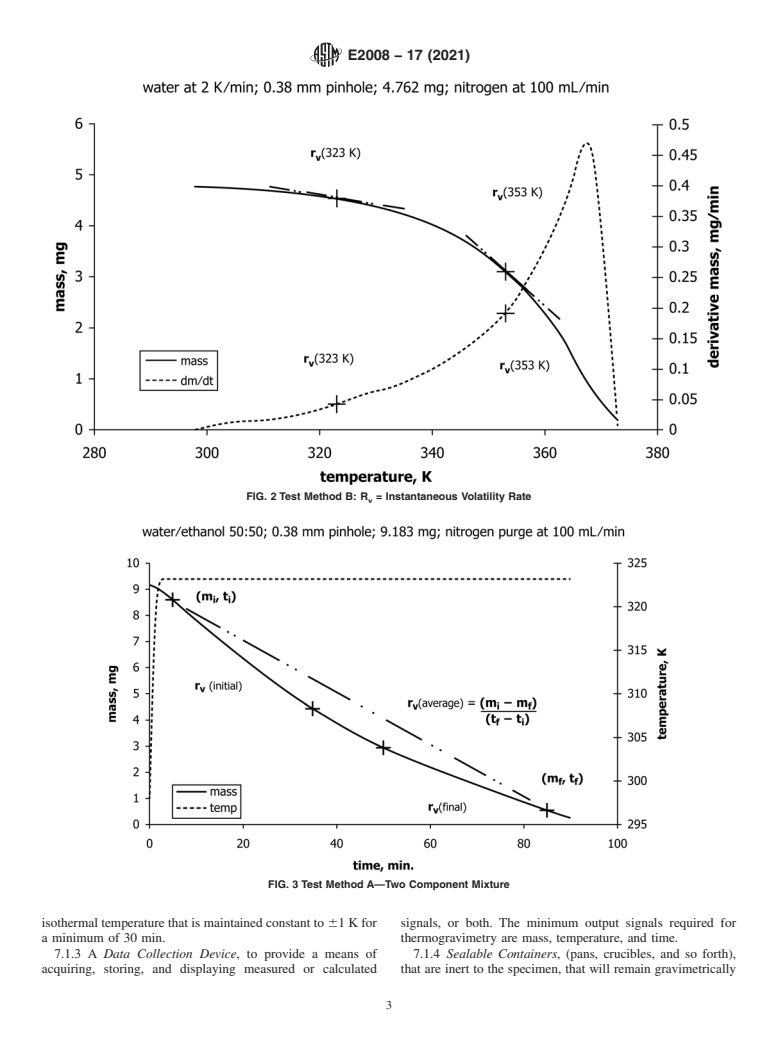
temperature for a fixed interval of time (Test MethodA, Fig. 1)
or at a slow constant heating rate between temperature limits
(TestMethodB,Fig.2).Themassofthespecimenismeasured
continuously and it or its rate of change is displayed as a
function of time or temperature. The volatility rate at any
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E37 on
ThermalMeasurementsandarethedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeE37.01on
2
Calorimetry and Mass Loss. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
CurrenteditionapprovedJuly1,2021.PublishedJuly2021.Originallyapproved contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as E2008 – 17. DOI: 10.1520/ Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
E2008-17R21. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2008 − 17 (2021)
FIG. 1 Test Method A: R = Average Volatility Rate
v
temperature is reported either as the average rate of mass loss 6. Interferences
per unit time from Test Method A or as the instantaneous rate
6.1 Specimens that consist of a mixture of two or more
of mass loss (first derivative)
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.