ASTM F2820-12(2021)e1
(Specification)Standard Specification for Polyetherketoneketone (PEKK) Polymers for Surgical Implant Applications
Standard Specification for Polyetherketoneketone (PEKK) Polymers for Surgical Implant Applications
ABSTRACT
This specification covers virgin polyetherketoneketone (PEKK) polymer resin as supplied by a vendor (for example, in pellets, powder, and fabricated forms). It provides requirements and associated test methods for these thermoplastics when they are to be used in the manufacture of intracorporeal devices such as surgical implants or components of surgical or dental devices. As with any material, some characteristics may be altered by the processing techniques (for example, molding, extrusion, machining, assembly, and sterilization) required for the production of a specific part or device. Therefore, properties of fabricated forms of these polymers should be evaluated using test methods which are appropriate to ensure safety and efficacy as agreed upon by the vendor, purchaser, and regulating bodies. This specification is designed to recommend physical, chemical, and biological test methods to establish a reasonable level of confidence concerning the performance of virgin PEKK polymers for use in medical implant devices. It lists the properties that should be considered in selecting material(s) in accordance with the specific end-use requirements. This specification also addresses classification, properties, sampling, and biocompatibility.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers virgin polyetherketoneketone (PEKK) polymer resin as supplied by a vendor (for example, in pellets, powder, and fabricated forms). It provides requirements and associated test methods for these thermoplastics when they are to be used in the manufacture of intracorporeal devices such as surgical implants or components of surgical or dental devices.
1.2 As with any material, some characteristics may be altered by the processing techniques (for example, molding, extrusion, machining, assembly, and sterilization) required for the production of a specific part or device. Therefore, properties of fabricated forms of these polymers should be evaluated using test methods which are appropriate to ensure safety and efficacy as agreed upon by the vendor, purchaser, and regulating bodies. With reduced crystallinity, certain polymers have been shown to be more susceptible to environmental stress cracking. Depending upon the implant application, the end user should characterize the material for environmental stress cracking resistance.
1.3 The properties included in this specification are those applicable for PEKK polymers only. Indicated properties are for fabricated forms. Fabricated forms and materials containing colorants, fillers, processing aids, or other additives, as well as polymer blends which contain PEKK, or reclaimed materials are not covered by this specification.
1.4 This specification is designed to recommend physical, chemical, and biological test methods to establish a reasonable level of confidence concerning the performance of virgin PEKK polymers for use in medical implant devices. The properties listed should be considered in selecting material(s) in accordance with the specific end-use requirements.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 When evaluating material in accordance with this specification, hazardous materials, operations, and equipment may be involved. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
´1
Designation:F2820 −12 (Reapproved 2021)
Standard Specification for
Polyetherketoneketone (PEKK) Polymers for Surgical
Implant Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2820; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
ε NOTE—Unreferenced documents were editorially removed from Section 2 in May 2021.
1. Scope 1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
1.1 This specification covers virgin polyetherketoneketone
standard.
(PEKK)polymerresinassuppliedbyavendor(forexample,in
1.6 When evaluating material in accordance with this
pellets, powder, and fabricated forms). It provides require-
specification, hazardous materials, operations, and equipment
ments and associated test methods for these thermoplastics
may be involved. This standard does not purport to address all
when they are to be used in the manufacture of intracorporeal
of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
devices such as surgical implants or components of surgical or
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
dental devices.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
1.2 As with any material, some characteristics may be
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
altered by the processing techniques (for example, molding,
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
extrusion, machining, assembly, and sterilization) required for
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
the production of a specific part or device. Therefore, proper-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
ties of fabricated forms of these polymers should be evaluated
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
using test methods which are appropriate to ensure safety and
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
efficacy as agreed upon by the vendor, purchaser, and regulat-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ing bodies. With reduced crystallinity, certain polymers have
2. Referenced Documents
been shown to be more susceptible to environmental stress
cracking.Dependingupontheimplantapplication,theenduser
2.1 ASTM Standards:
shouldcharacterizethematerialforenvironmentalstresscrack-
D256 Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum
ing resistance.
Impact Resistance of Plastics
D638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
1.3 The properties included in this specification are those
D695 Test Method for Compressive Properties of Rigid
applicable for PEKK polymers only. Indicated properties are
Plastics
forfabricatedforms.Fabricatedformsandmaterialscontaining
D790 Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced
colorants, fillers, processing aids, or other additives, as well as
and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materi-
polymer blends which contain PEKK, or reclaimed materials
als
are not covered by this specification.
D1505 Test Method for Density of Plastics by the Density-
1.4 This specification is designed to recommend physical,
Gradient Technique
chemical, and biological test methods to establish a reasonable
D1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics (Withdrawn 1998)
level of confidence concerning the performance of virgin
D3418 Test Method for Transition Temperatures and En-
PEKK polymers for use in medical implant devices. The
thalpies of Fusion and Crystallization of Polymers by
properties listed should be considered in selecting material(s)
Differential Scanning Calorimetry
in accordance with the specific end-use requirements.
D4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Materi-
als
1 2
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Subcommittee F04.11 on Polymeric Materials. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved May 15, 2021. Published May 2021. Originally the ASTM website.
approved in 2012. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as F2820 – 12. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/F2820-12R21E01. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
´1
F2820−12 (2021)
F748 PracticeforSelectingGenericBiologicalTestMethods these isomers defines the types of PEKK. The T/I ratio is
for Materials and Devices determined at synthesis and is currently of two types.
4.1.1 Type I PEKK—This EKK polymer is made with a T/I
2.2 ISO Standards:
ratio of 60/40. The resulting polymer system has a crystal
ISO 178 Plastics—Determination of Flexural Properties
kinetic behavior that makes processing in either amorphous or
ISO 180 Plastics—Determination of Izod Impact Strength
semi-crystalline forms practical.
ISO 527 Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties
4.1.2 Type II PEKK—This EKK polymer is made with a T/I
ISO604 Plastics—DeterminationofCompressiveProperties
ratio of 80/20. The resulting polymer system is used in a
ISO 1183 Plastics—Methods for Determining the Density of
semi-crystalline state.
Non-cellular Plastics—Part 2: Density Gradient Column
Method
4.2 Types of PEKK plastics, molding and extrusion grades
ISO 9001 Quality Systems Management
are described in Classification D4000.
ISO 10993 Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices, Parts
1–124
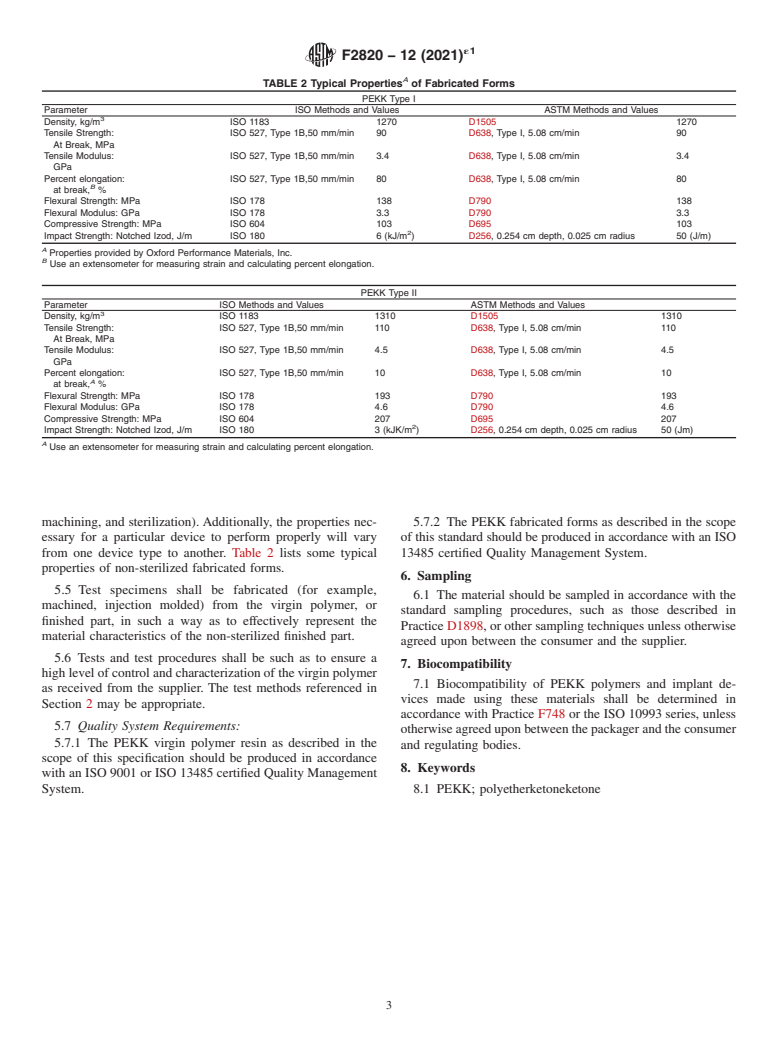
5. Properties
ISO 13485 Medical devices—Quality Management
5.1 The infrared spectrum of these materials is character-
Systems—Requirements for Regulatory Purposes
istic of their molecular repeating units. A representative spec-
2.3 Other Documents:
trum is listed in Appendix X3. The PEKK polymer shall yield
United States Pharmacopeia Vol XXI, or latest edition
an infrared spectrum, which exhibits major bands only at the
wavelengths listed for a standard reference spectrum of that
3. Terminology
material.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
5.1.1 The infrared spectrum, as used in this specification, is
3.1.1 fabricated forms, n—those items into which the virgin
to identify the material as polyetherketoneketone (PEKK) but
polymer resin may be converted. These include shapes and
does not necessarily indicate an acceptable degree of material
forms produced by means of machining, extruding, and com-
purity.
pression molding virgin polymer resin into a subsequent entity
5.1.2 The presence of additional bands in the sample’s
(for example, fibers, tubes, rods, slabs, sheets, film, or complex
infrared spectrum compared to that of the reference material
shaped parts and devices).
may indicate a different polyaryletherketone (PAEK) material
3.1.2 formulated compound, n—materials, parts, or devices
(for example, PEEK, PEKEKK, PEK) or impurities, or both.
fabricated from virgin polymer resin in such a way as to
5.2 Thephysicalandchemicalpropertyrequirementsforthe
contain intentional or unintentional adjuvant substances.
virginpolymerarelistedinTable1.Ifadditionalcharacteristics
3.1.3 virgin polymer, n—the initially delivered form of the
are necessary because of a specific application, the procedures
polymer as synthesized from its monomers prior to any
referenced in Section 2 are recommended, or as agreed upon
processing or fabrication into a medical device. The provided
between the vendor and the purchaser.
resinistypicallyintheformofpellets,granules,orpowderand
5.3 The viscosity requirements shall be agreed upon be-
is the material from which fibers, tubes, rods, slabs, sheets,
tween the vendor and the purchaser.
films, or specific parts and devices are fabricated.
5.4 The chemical, physical, and mechanical properties of
4. Classification
fabricated forms are related to the processes utilized in
producing the fabricated form (for example, molding,
4.1 The PEKK polymer in the scope of this specification is
a pure semi-crystalline copolymer consisting of phenylene
rings connected by ethe
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.