ASTM D1319-02a
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types in Liquid Petroleum Products by Fluorescent Indicator Adsorption
Standard Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types in Liquid Petroleum Products by Fluorescent Indicator Adsorption
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of hydrocarbon types over the concentration ranges from 5 to 99 volume % aromatics, 0.3 to 55 volume % olefins, and 1 to 95 volume % saturates in petroleum fractions that distill below 315°C. This test method may apply to concentrations outside these ranges, but the precision has not been determined. Samples containing dark-colored components that interfere in reading the chromatographic bands cannot be analyzed.
Note 1—The scope of this test method today is NOT to depentanize to reflect current practice. Results obtained from the analysis of samples containing significant levels of C5 and lighter hydrocarbons might be less accurate. The potential bias is not certain and may not be consistent. Prior versions of Test Method D 1319 have specified depentanization when samples contain any of the following: C3 or lighter hydrocarbons, more than 5 % C4 hydrocarbons, or more than 10 % C4 and C5 hydrocarbons. The results of this are still unclear and certainly controversial. In such a case, depentanization was done according to Test Method D 2001 followed by subsequent analysis of the depentanized sample by Test Method D 1319. A correction to the depentanized sample results was then required to place them on an as-received basis by using such method as Test Method D 2427 which determined the amounts of C5 minus hydrocarbons in the undepentanized sample.
1.2 This test method is intended for use with full boiling range products. Cooperative data have established that the precision statement does not apply to narrow boiling petroleum fractions near the 315°C limit. Such samples are not eluted properly, and results are erratic.
1.3 The applicability of this test method to products derived from fossil fuels other than petroleum, such as coal, shale, or tar sands, has not been determined, and the precision statement may or may not apply to such products.
1.4 The precision statement for this test method has been determined with unleaded fuels that do not contain oxygenated blending components. It may or may not apply to automotive gasolines containing lead antiknock mixtures or oxygenated gasoline blending components, or both.
1.5 The oxygenated blending components, methanol, ethanol, methyl-tert-butylether (MTBE), methyl- tert-amylmethyl (TAME), and ethyl-tert-butylether (ETBE), do not interfere with the determination of hydrocarbon types at concentrations normally found in commercial blends. These oxygenated components are not detected since they elute with the alcohol desorbent. Other oxygenated compounds shall be individually verified. When samples containing oxygenated blending components are analyzed, correct the results to a total-sample basis.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
Note 2—For the determination of olefins below 0.3 volume %, other test methods are available, such as Test Method D 2710.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 7, 8.1, and 10.5.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: D 1319 – 02a
Designation: 156/97
Standard Test Method for
Hydrocarbon Types in Liquid Petroleum Products by
1
Fluorescent Indicator Adsorption
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1319; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This test method has been approved by the sponsoring committees and accepted by the cooperating societies in accordance with
established procedures.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope * tar sands, has not been determined, and the precision statement
may or may not apply to such products.
1.1 This test method covers the determination of hydrocar-
1.4 The precision statement for this test method has been
bon types over the concentration ranges from 5 to 99 volume %
determined with unleaded fuels that do not contain oxygenated
aromatics, 0.3 to 55 volume % olefins, and 1 to 95 volume %
blending components. It may or may not apply to automotive
saturates in petroleum fractions that distill below 315°C. This
gasolines containing lead antiknock mixtures or oxygenated
test method may apply to concentrations outside these ranges,
gasoline blending components, or both.
but the precision has not been determined. Samples containing
1.5 The oxygenated blending components, methanol, etha-
dark-colored components that interfere in reading the chro-
nol, methyl-tert-butylether (MTBE), tert-amylmethylether
matographic bands cannot be analyzed.
(TAME), and ethyl-tert-butylether (ETBE), do not interfere
NOTE 1—The scope of this test method today is NOT to depentanize to
with the determination of hydrocarbon types at concentrations
reflect current practice. Results obtained from the analysis of samples
normally found in commercial blends. These oxygenated
containing significant levels of C and lighter hydrocarbons might be less
5
components are not detected since they elute with the alcohol
accurate. The potential bias is not certain and may not be consistent. Prior
desorbent. Other oxygenated compounds shall be individually
versions of Test Method D 1319 have specified depentanization when
verified. When samples containing oxygenated blending com-
samples contain any of the following: C or lighter hydrocarbons, more
3
than 5 % C hydrocarbons, or more than 10 % C and C hydrocarbons.
ponents are analyzed, correct the results to a total-sample basis.
4 4 5
The results of this are still unclear and certainly controversial. In such a
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
case, depentanization was done according to Test Method D 2001 fol-
standard.
lowed by subsequent analysis of the depentanized sample by Test Method
D 1319. A correction to the depentanized sample results was then required NOTE 2—For the determination of olefins below 0.3 volume %, other
to place them on an as-received basis by using such method as Test test methods are available, such as Test Method D 2710.
Method D 2427 which determined the amounts of C minus hydrocarbons
5
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
in the undepentanized sample.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.2 This test method is intended for use with full boiling
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
range products. Cooperative data have established that the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
precision statement does not apply to narrow boiling petroleum
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
fractions near the 315°C limit. Such samples are not eluted
statements, see Section 7, 8.1, and 10.5.
properly, and results are erratic.
1.3 The applicability of this test method to products derived 2. Referenced Documents
from fossil fuels other than petroleum, such as coal, shale, or
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products at
2
Atmospheric Pressure
2
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on D 1655 Specification for Aviation Turbine Fuels
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D 2001 Test Method for Depentanization of Gasoline and
D02.04 on Hydrocarbon Analysis.
2
Naphthas
In the IP, this test method is under the jurisdiction of the Standardization
Committee.
Current edition approved April 10, 2002. Published July 2002. Originally
published as D 1319–54T. Last previous edition D 1319–02.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © AS
...







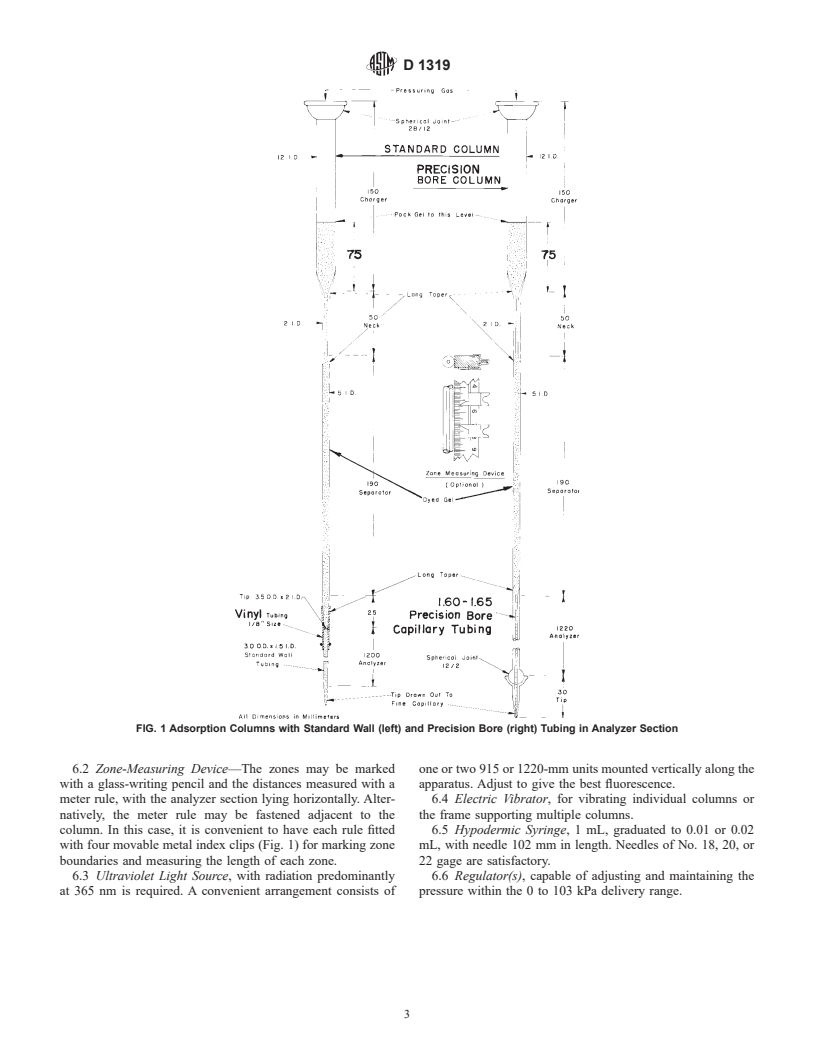
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.