ASTM B769-07
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Shear Testing of Aluminum Alloys
Standard Test Method for Shear Testing of Aluminum Alloys
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The intent of this method is to provide a means of measuring the ultimate shear strength of aluminum-alloy wrought and cast products. Data obtained by this method are used to calculate minimum properties that can be utilized in the design of structural members such as found in aircraft. It is recognized that loading conditions developed by this method, and by most others, are not ideal in that they do not strictly satisfy the definition of pure shear. However, rarely do pure shear conditions exist in structures.
Note 2—This method is not interchangeable with that described in Test Method B 565. Shear strengths obtained by Test Method B 565 are about 10 % lower than those developed by this test method.
The presence of a lubricant on the surface of the specimen and fixture may result in shear strengths up to 3 % lower than those determined in the absence of lubrication (see 8.1 and Test Method B 565).
SCOPE
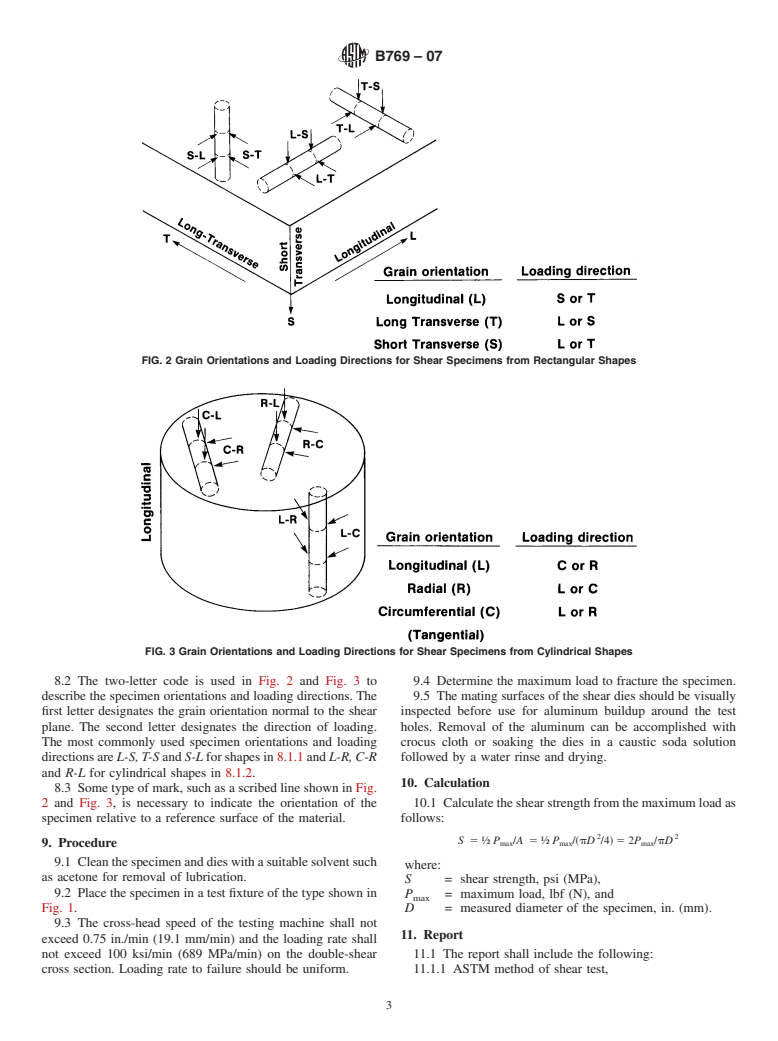
1.1 This test method covers double-shear testing of wrought and cast aluminum products to determine shear ultimate strengths. Note 1
The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:B769–07
Standard Test Method for
1
Shear Testing of Aluminum Alloys
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B769; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 4. Summary of Test Method
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversdouble-sheartestingofwrought 4.1 This test method consists of subjecting a machined
and cast aluminum products to determine shear ultimate cylindrical test specimen to double-shear loading in a test
strengths. fixture using a tension (or compression) testing machine to
determine the shear stress required to fracture the specimen,
NOTE 1—Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegardedasthe
that is, the shear strength.
standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information
only.
5. Significance and Use
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
5.1 The intent of this method is to provide a means of
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
measuring the ultimate shear strength of aluminum-alloy
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
wrought and cast products. Data obtained by this method are
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
usedtocalculateminimumpropertiesthatcanbeutilizedinthe
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
design of structural members such as found in aircraft. It is
recognized that loading conditions developed by this method,
2. Referenced Documents
and by most others, are not ideal in that they do not strictly
2.1 The following documents of the issue in effect on the
satisfy the definition of pure shear. However, rarely do pure
dateofmaterialpurchase,unlessotherwisenotedformapartof
shear conditions exist in structures.
this specification to the extent referenced herein:
2
2.2 ASTM Standards: NOTE 2—ThismethodisnotinterchangeablewiththatdescribedinTest
Method B565. Shear strengths obtained by Test Method B565 are about
B565 Test Method for Shear Testing of Aluminum and
10% lower than those developed by this test method.
Aluminum-AlloyRivetsandCold-HeadingWireandRods
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines 5.2 The presence of a lubricant on the surface of the
E6 TerminologyRelatingtoMethodsofMechanicalTesting specimen and fixture may result in shear strengths up to 3%
lower than those determined in the absence of lubrication (see
3. Terminology
8.1 and Test Method B565).
3.1 The definitions of terms relating to shear testing in
6. Apparatus
Terminology E6 are applicable to the terms used in this test
method. 6.1 Testing Machines—The testing machines shall conform
to the requirements of Practices E4. The loads used to
determine the shear strength shall be within the loading range
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B07 on Light of the testing machine as defined in Practices E4.
Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B07.05 on
6.2 Loading Device:
Testing.
6.2.1 The loading device shall be a double-shear test fixture
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2007.PublishedJuly2007.Originallyapproved
of the type shown in Fig. 1. The fixture shall be made of tool
in1987.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2006asB769–06.DOI:10.1520/B0769-
07.
steel having a Rockwell hardness from 60 to 62 HRC. A
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
suitable alternative is to use a lower-strength steel for the main
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
frame of the fixture and have only the steel inserts hardened
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. from 60 to 62 HRC.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B769–07
FIG. 1 Three Views of an Amsler Shear Tool
6.2.2 The shearing edges of the holes shall have a radius of 7. Test Specimens
no more than 0.0005 in. (0.013 mm). The mating surfaces of
7.1 The minimum length of the cylindrical specimens shall
the center and outside dies shall have a finish of 16 µin. (0.4
be equal to the combined lengths of the three dies in accor-
µm) R orless.Thereshallbesufficientclearancesbetweenthe
a
dance with 6.2.3.
die interfaces to ensure that no binding occurs; clearance
3
7.2 The minimum specimen size shall be ⁄16 in. (4.76 mm)
should not exceed 0.002 in. (0.051 mm). Consequently, the
in diameter. The 0.375-in. (9.52-mm) diameter specimen is a
rigidity of the test
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.