ASTM D1981-11(2020)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring Color After Heating of Tall Oil Fatty Acids
Standard Test Method for Measuring Color After Heating of Tall Oil Fatty Acids
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 The color of a tall oil fatty acid is readily affected by heat and oxidization. Variations in degree of heat, time of heat, and exposure to atmosphere during heating have a marked effect on the color obtained; therefore, conformity to the equipment and procedure outlined in this test method is essential to accuracy and precision.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the Gardner color of tall oil fatty acids after heating in an atmosphere of nitrogen at 205°C for one or two hours, depending on whether its iodine value is over or under 15, respectively. The specimen may be heated using either an aluminum heating block or an oil bath. This method is applicable to all tall oil fatty acids. Applicability of this method to other types of fatty acids has not been determined.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
´1
Designation: D1981 − 11 (Reapproved 2020)
Standard Test Method for
Measuring Color After Heating of Tall Oil Fatty Acids
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1981; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
ε NOTE—Editorial changes were made in subsections 7.3 and 8.3 in September 2020.
1. Scope 3. Significance and Use
1.1 ThistestmethodcoversthemeasurementoftheGardner 3.1 The color of a tall oil fatty acid is readily affected by
color of tall oil fatty acids after heating in an atmosphere of heat and oxidization. Variations in degree of heat, time of heat,
nitrogen at 205°C for one or two hours, depending on whether and exposure to atmosphere during heating have a marked
its iodine value is over or under 15, respectively.The specimen effect on the color obtained; therefore, conformity to the
maybeheatedusingeitheranaluminumheatingblockoranoil equipment and procedure outlined in this test method is
bath. This method is applicable to all tall oil fatty acids. essential to accuracy and precision.
Applicability of this method to other types of fatty acids has
4. Heating Apparatus—Method A, Aluminum Block
not been determined.
4.1 Forced Draft Oven, maintained at 205 6 2°C.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
4.2 Aluminum Heating Block (see Fig. 1). Wrap the outer
only.
surface with an appropriate insulating material.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
5. Heating Apparatus—Method B, Oil Bath
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5.1 Oil Bath—A5-L steel beaker equipped with a mechani-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
cal stirrer and containing any light-colored alkali-refined oil
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
such as hydrogenated cottonseed oil.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
5.2 Heat Source—An electric immersion heater with suit-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
able thermostatic control may be used. The heater shall be of
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
sufficient capacity so that when placing several tubes in the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
bath, the bath temperature does not drop by more than 5°C
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
below the minimum bath temperature and the recovery time to
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
reach 205°C does not exceed 5 min.
2. Referenced Documents
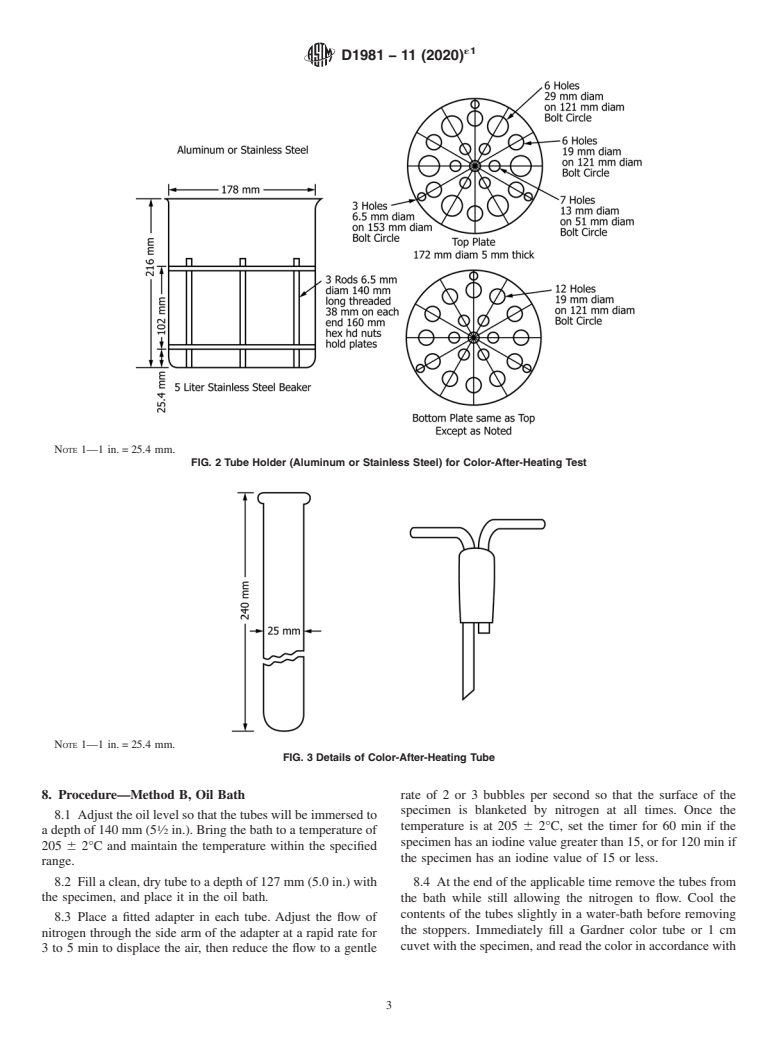
5.3 Test Tube Holder (see Fig. 2).
2.1 ASTM Standards:
6. Materials
D1544 Test Method for Color of Transparent Liquids (Gard-
ner Color Scale)
6.1 Thermometer Measuring Device—A thermometer con-
D6166 Test Method for Color of Pine Chemicals and Re-
forming to the requirements of Specification E1 or an elec-
lated Products (Instrumental Determination of Gardner
tronic temperature measuring device, such as a resistance
Color)
thermometer or thermocouple. The device must exhibit the
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
same temperature response as the thermometers specified in
Specification E1.
1 1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint 6.2 Tubes, 25 mm (1 in.) in diameter, 240 mm (9 ⁄2 in.) in
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
length with ground-glass joints (see Fig. 3) and adapter.
Subcommittee D01.34 on Pine Chemicals and Hydrocarbon Resins.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2020. Published September 2020. Originally 6.3 Timer, capable of registering up to 135 min.
approved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D1981 – 11 (2015).
6.4 Nitrogen, a source of nitrogen capable of being regu-
DOI: 10.1520/D1981-11R20E01.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or lated to a pressure of 7 to 14 kPa (1 to 2 psi).
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
6.5 BubbleCounterforNitrogen—As a liquid, use a portion
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. of tall oil fatty acid, instead of water or mercury.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.