ASTM D2457-03
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Specular Gloss of Plastic Films and Solid Plastics
Standard Test Method for Specular Gloss of Plastic Films and Solid Plastics
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Specular gloss is used primarily as a measure of the shiny appearance of films and surfaces. Precise comparisons of gloss values are meaningful only when they refer to the same measurement procedure and same general type of material. In particular, gloss values for transparent films should not be compared with those for opaque films, and vice versa. Gloss is a complex attribute of a surface which cannot be completely measured by any single number.
Specular gloss usually varies with surface smoothness and flatness. It is sometimes used for comparative measurements of these surface properties.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes procedures for the measurement of gloss of plastic films and solid plastics, both opaque and transparent. It contains four separate gloss angles (Note 1):
1.1.1 60-deg, recommended for intermediate-gloss films,
1.1.2 20-deg, recommended for high-gloss films,
1.1.3 45-deg, recommended for intermediate and low-gloss films, and
1.1.4 75-deg, recommended for plastic siding and soffit.
Note 1—The 75-deg, 60-deg, and 20-deg apparatus and method of measurement duplicate those in Test Method D 523; those for the 45 procedure are similarly taken from Test Method C 346.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 2—There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D2457–03
Standard Test Method for
1
Specular Gloss of Plastic Films and Solid Plastics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2457; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method describes procedures for the measure- 3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
ment of gloss of plastic films and solid plastics, both opaque method, see Terminology E 284.
and transparent. It contains four separate gloss angles (Note 1):
4. Significance and Use
1.1.1 60-deg, recommended for intermediate-gloss films,
1.1.2 20-deg, recommended for high-gloss films, 4.1 Specular gloss is used primarily as a measure of the
shiny appearance of films and surfaces. Precise comparisons of
1.1.3 45-deg, recommended for intermediate and low-gloss
films, and gloss values are meaningful only when they refer to the same
measurement procedure and same general type of material. In
1.1.4 75-deg, recommended for plastic siding and soffit.
particular, gloss values for transparent films should not be
NOTE 1—The 75-deg, 60-deg, and 20-deg apparatus and method of
compared with those for opaque films, and vice versa. Gloss is
measurement duplicate those in Test Method D 523; those for the 45°
a complex attribute of a surface which cannot be completely
procedure are similarly taken from Test Method C 346.
measured by any single number.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.2 Specular gloss usually varies with surface smoothness
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
and flatness. It is sometimes used for comparative measure-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ments of these surface properties.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
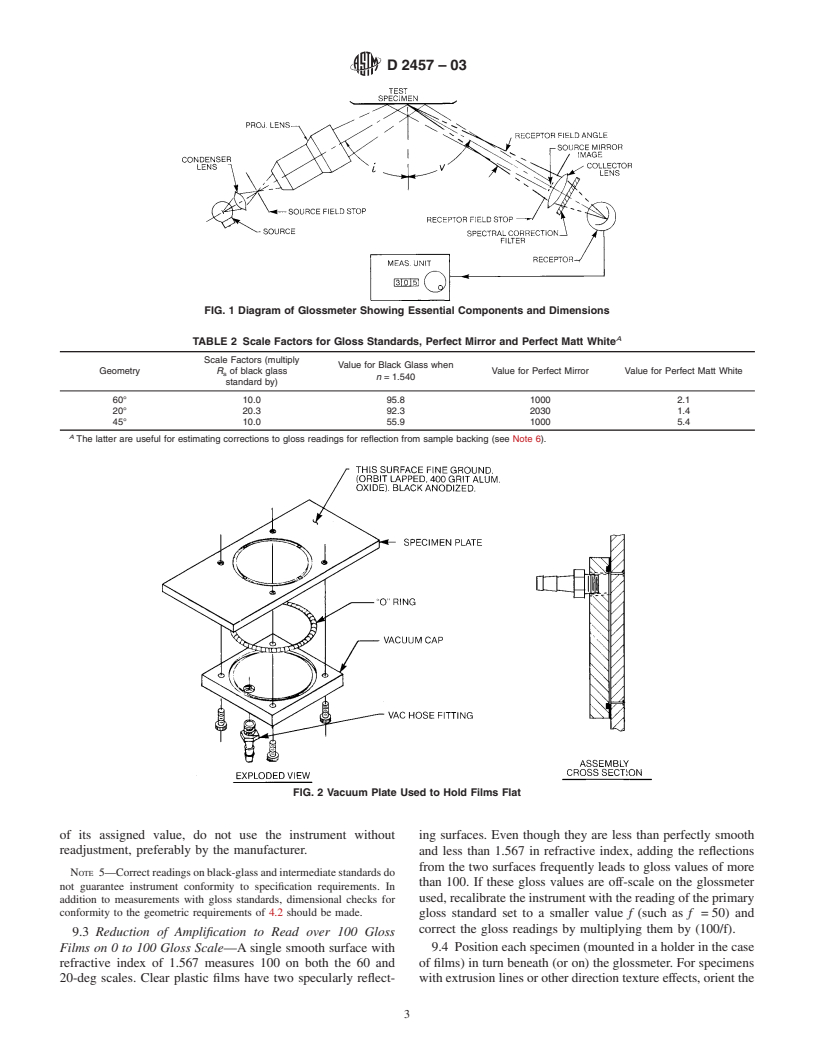
5. Apparatus
NOTE 2—There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard. 5.1 Instrumental Components—Each apparatus (Note 3)
shall consist of an incandescent light source furnishing an
2. Referenced Documents
incident beam, means for locating the surface of the specimen,
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
and a receptor located to receive the required pyramid of rays
C 346 Test Method for 45° Specular Gloss of Ceramic
reflected by the specimen. The receptor shall be a photosensi-
Materials
tive device responding to visible radiation.
D 523 Test Method for Specular Gloss
NOTE 3—The 75-, 60-, and 20-deg procedures require apparatus iden-
E 284 Terminology of Appearance
tical to that specified in Test Method D 523. The 45° procedure requires
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
apparatus like that specified in Test Method C 346.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
5.2 Geometric Conditions—The axis of the incident beam
E 1347 Test Method for Color and Color-Difference Mea-
shall be at one of the specified angles from the perpendicular to
surement by Tristimulus (Filter) Colorimetry
the specimen surface. The axis of the receptor shall be at the
E 1349 Test Method for Reflectance Factor and Color by
mirror reflection of the axis of the incident beam. With a flat
Spectrophotometry Using Bidirectional Geometry
piece of polished black glass or other front-surface mirror in
specimen position, an image of the source shall be formed at
the center of the receptor field stop (receptor window). The
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
length of the illuminated area of the specimen shall be equal to
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.40 on Optical Properties.
not more than one third of the distance from the center of this
Current edition approved Aug. 10, 2003. Published October 2003. Originally
approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 1997 as D 2457 – 97.
area to the receptor field stop. The angular dimensions and
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
tolerances of the geometry of the source and receptor shall be
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
as indicated in Table 1. The angular dimensions of the receptor
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. field stop are measured from the center of the test surface. The
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 -------
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.