ASTM D4651-14
(Specification)Standard Specification for Isobutane Thermophysical Property Tables
Standard Specification for Isobutane Thermophysical Property Tables
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the isobutane thermophysical property tables which are used in the calculation of the pressure-volume-temperature (PVT), thermodynamic, and transport properties of isobutane for process design and operations. Tables are provided for gaseous and liquid isobutane at temperatures between 135 and 600K at pressures to 35 MPa. These tables apply directly only to pure gaseous and liquid isobutane. However, it is expected that mathematical models and tables shall be useful for the thermophysical properties of mixtures containing isobutane, such as natural gas. These thermophysical property tables are: Thermophysical Properties of Coexisting Gaseous and Liquid Isobutane, in SI units and Thermophysical Properties of Isobutane, along isobars, in SI units.
SCOPE
1.1 The thermophysical property tables for isobutane are for use in the calculation of the pressure-volume-temperature (PVT), thermodynamic, and transport properties of isobutane for process design and operations. Two tables provide properties at the conditions of liquid-vapor equilibrium (saturation properties), one for liquid and one for vapor, at temperatures between 120 K and the critical point, 407.81 K. A third table provides properties at selected T, p points for the equilibrium phase at temperatures between 120 K and 570 K at pressures to 20 MPa. The tables were developed using the National Institute of Standards and Technology Standard Reference Database product REFPROP, version 9.1.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D4651 −14
Standard Specification for
1
Isobutane Thermophysical Property Tables
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4651; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2.1 Thermophysical Properties of Isobutane Liquid at
Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium, in SI units. See Table 1.
1.1 The thermophysical property tables for isobutane are for
3.2.2 Thermophysical Properties of Isobutane Vapor at
use in the calculation of the pressure-volume-temperature
Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium, in SI units. See Table 2.
(PVT), thermodynamic, and transport properties of isobutane
3.2.3 Thermophysical Properties of Isobutane Along
for process design and operations. Two tables provide proper-
Isobars, in SI units. See Table 3.
ties at the conditions of liquid-vapor equilibrium (saturation
3.3 The symbols are:
properties), one for liquid and one for vapor, at temperatures
between 120 K and the critical point, 407.81 K. A third table T, temperature (K)
-1
ρ, molar density (mol·L )
provides properties at selected T, p points for the equilibrium
-1
phase at temperatures between 120 K and 570 K at pressures to H, molar enthalpy (J·mol )
-1 -1
S, molar entropy (J·K ·mol )
20MPa.ThetablesweredevelopedusingtheNationalInstitute
-1 -1
of Standards and Technology Standard Reference Database C , constant volume molar heat capacity (J·K ·mol )
v
-1 -1
C , constant pressure molar heat capacity (J·K ·mol )
product REFPROP, version 9.1.
p
-1
c, speed of sound (m·s )
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
η, viscosity (µPa·s)
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
-1 -1
λ, thermal conductivity (mW·m ·K )
standard.
3.4 The tabulated thermophysical properties are:
-1
2. Applicability
ρ, molar density (mol·L )
-1
H, molar enthalpy (J·mol )
2.1 These tables apply directly only to pure isobutane. They
-1 -1
S, molar entropy (J·K ·mol )
may also be used in mathematical models and tables for the
-1 -1
C , constant volume molar heat capacity (J·K ·mol )
v
thermophysical properties of mixtures containing isobutane.
-1 -1
C , constant pressure molar heat capacity (J·K ·mol )
p
-1
c, speed of sound (m·s )
3. Tables
η, viscosity (µPa·s)
3.1 These tables were produced by equations from a com-
-1 -1
λ, thermal conductivity (mW·m ·K )
puter package, “NIST Standard Reference Database 23; Ref-
erence Fluid Thermodynamic and Transport Properties Data-
4. Additional Information
2
base (REFPROP): Version 9.1.” A wide selection of units (SI
4.1 Reference state properties are required to calculate the
units, engineering units, chemical units) and additional prop-
thermodynamic properties enthalpy and entropy from an equa-
erties are available with this program.
tion of state formulation. The reference state properties used
3.2 These thermophysical property tables are:
are those specified by the International Institute of Refrigera-
tion (IIR): enthalpy,H = 200 J/g, and entropy,S = 1 J/(g·K), for
the saturated liquid at 273.15K (0°C).
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on
4.2 The molar mass of isobutane is 58.122 g/mol.
Gaseous Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.08 on
Thermophysical Properties.
5. Keywords
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2014.PublishedJuly2014.Originallyapproved
in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as D4651 – 08. DOI: 10.1520/
5.1 isobutane; isobutane gas tables; natural gas; thermody-
D4651-14.
2 namic properties of isobutane; transport properties of isobu-
Available from Standard Reference Data, National Institute of Standards and
Technology (NIST), 100 Bureau Drive, Stop 3460, Gaithersburg, MD 20899. tane; 2-methylpropane
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4651−14
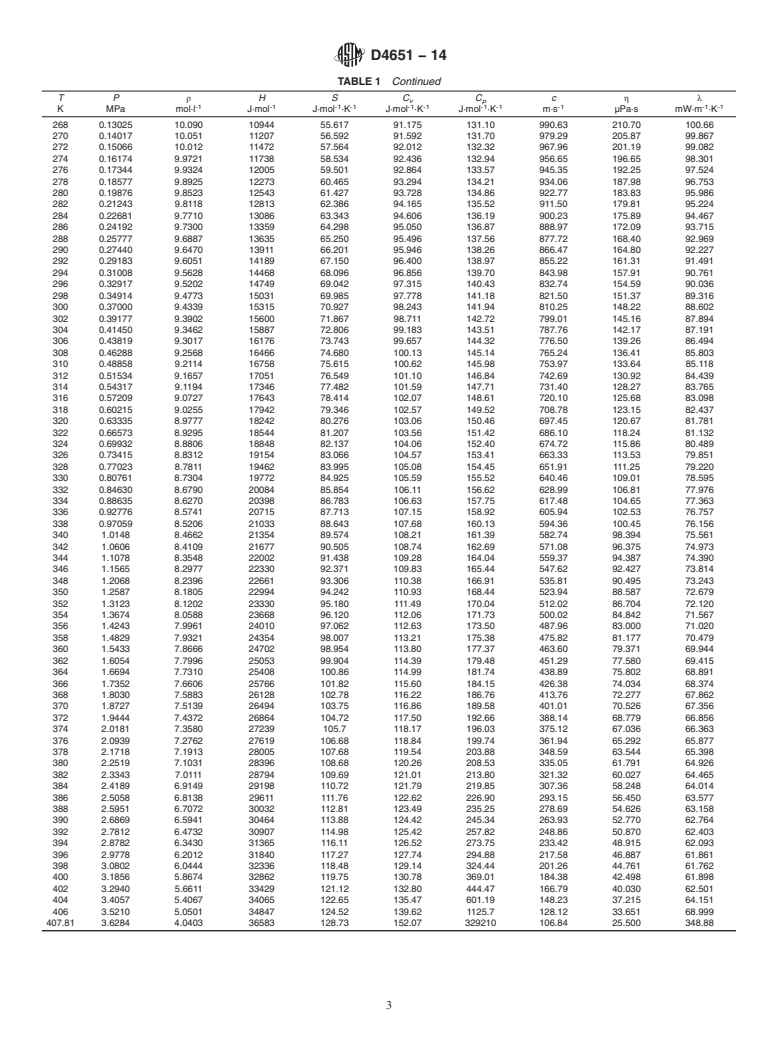
TABLE 1 Thermophysical Properties of Isobutane Liquid at Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium
TP ρ HS C C c ηλ
v p
-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
K MPa mol·l J·mol J·mol ·K J·mol ·K J·mol ·K m·s µPa·s mW·m ·K
120 1.0633E-07 12.636 -5912.6 -34.216 69.001 99.308 1945.4 6055.8 156.73
122 1.6734E-07 12.603 -5713.6 -32.571 69.251 99.681 1928.5 5441.0 156.30
124 2.5915E-07 12.571 -5513.9 -30.948 69.501 100.06 1911.9 4910.8 155.85
126 3.9524E-07 12.538 -5313.4 -29.344 69.752 100.43 1895.5 4450.9 155.38
128 5.9407E-07 12.506 -5112.1 -27.759 70.004 100.81 1879.3 4049.9 154.89
130 8.8064E-07 12.473 -4910.1 -26.193 70.255 101.18 1863.4 3698.4 154.39
132 1.2883E-06 12.441 -4707.4 -24.646 70.505 101.56 1847.7 3389.0 153.86
134 1.86
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4651 − 08 D4651 − 14
Standard Specification for
1
Isobutane Thermophysical Property Tables
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4651; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 The thermophysical property tables for isobutane are for use in the calculation of the pressure-volume-temperature (PVT),
thermodynamic, and transport properties of isobutane for process design and operations. Tables are provided for gaseous and liquid
isobutane at temperatures between 120 and 570 K at pressures to 20 MPa. One table provides properties at the conditions of
liquid-vapor equilibrium (saturation properties). The other Two tables provide properties at the conditions of liquid-vapor
equilibrium (saturation properties), one for liquid and one for vapor, at temperatures between 120 K and the critical point, 407.81
K. A third table provides properties at selected T,p points for the equilibrium phase at those conditions. temperatures between 120
K and 570 K at pressures to 20 MPa. The tables were developed byusing the National Institute of Standards and Technology from
a Standard Reference Database product REFPROP, version 8.0.9.1.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
2. Applicability
2.1 These tables apply directly only to pure gaseous isobutane. However, it is expected that they may find substantial
useisobutane. They may also be used in mathematical models and tables for the thermophysical properties of mixtures containing
isobutane.
3. Tables
3.1 These tables were produced by equations from a computer package, “NIST Standard Reference Database 23; Reference
2
Fluid Thermodynamic and Transport Properties Database (REFPROP): Version 9.1.” A wide selection of units (SI units,
engineering units, chemical units) and additional properties are available with this program.
3.2 These thermophysical property tables are:
3.2.1 Thermophysical Properties of Coexisting Gaseous and Liquid Isobutane, Isobutane Liquid at Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium,
in SI units. See Table 1.
3.2.2 Thermophysical Properties of Isobutane Along Isobars, Vapor at Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium, in SI units. See Table 2.
3.2.3 Thermophysical Properties of Isobutane Along Isobars, in SI units. See Table 3.
3.3 The tabulated thermophysical properties symbols are:
T, temperature (K)
-1
ρ, molar density (mol·l(mol·L )
-1
H, molar enthalpy (J·mol )
-1 -1
S, molar entropy (J·K ·mol )
-1 -1
C , constant volume molar heat capacity (J·K ·mol )
v
-1 -1
C , constant pressure molar heat capacity (J·K ·mol )
p
-1
c, speed of sound (m·s )
η, viscosity (μPa·s)
-1 -1
λ, thermal conductivity (mW·m ·K )
3.4 The tabulated thermophysical properties are:
-1
ρ, molar density (mol·L )
-1
H, molar enthalpy (J·mol )
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.08 on Thermophysical
Properties.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2008June 1, 2014. Published January 2009July 2014. Originally approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 20032008 as
D4651 – 93 (2003).D4651 – 08. DOI: 10.1520/D4651-08.10.1520/D4651-14.
2
Available from Standard Reference Data, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), 100 Bureau Drive, Stop 3460, Gaithersburg, MD 20899.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4651 − 14
TABLE 1 Thermophysical Properties of Isobutane Liquid at Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium
T P ρ H S C C c η λ
v p
-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
K MPa mol·l J·mol J·mol ·K J·mol ·K J·mol ·K m·s μPa·s mW·m ·K
120 1.0633E-07 12.636 -5912.6 -34.216 69.001 99.308 1945.4 6055.8 156.73
122 1.6734E-07 12.603 -5713.6 -32.571 69.251 99.681 1928.5 5441.0 156.30
124 2.5915E-07 12.571 -5513.9 -30.948 69.501 100.06 1911.9 4910.8 155.85
126 3.9524E-07 12.538 -5313.4 -29.344 69.752 100.43 1895.5 4450.9 155.38
128 5.9407E-07 12.506 -5112.1 -27.759 70.004 100.81 1879.3 4049.9 154.89
130 8.8064E-07 12.473 -4910.1 -26.193 70.255 101.18 1863.4 3698.4 154.39
132 1.2883E-06 12.441 -4707.4 -24.646 70.505 101.56 1847.7 3389.0 153.86
134 1.8611E-06 12.408 -4503.9 -23.116 70
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.