ASTM D2266-01(2008)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Wear Preventive Characteristics of Lubricating Grease (Four-Ball Method)
Standard Test Method for Wear Preventive Characteristics of Lubricating Grease (Four-Ball Method)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The four-ball wear-test method can be used to determine the relative wear-preventing properties of greases under the test conditions and if the test conditions are changed the relative ratings may be different. No correlation has been established between the four-ball wear test and field service. The test method cannot be used to differentiate between Extreme Pressure (EP) and Non-Extreme Pressure (Non-EP) Greases.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the wear preventive characteristics of greases in sliding steel-on-steel applications. It is not intended to predict wear characteristics with metal combinations other than steel-on-steel or to evaluate the extreme pressure characteristics of the grease.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard except where the test apparatus or consumable parts are only available in other units. In such cases, these will be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D2266 −01(Reapproved 2008)
Standard Test Method for
Wear Preventive Characteristics of Lubricating Grease
1
(Four-Ball Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2266; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope Data for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and
Lubricants
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the wear
3
2.2 ANSI Standard:
preventive characteristics of greases in sliding steel-on-steel
B3.12 for Metal Balls
applications. It is not intended to predict wear characteristics
withmetalcombinationsotherthansteel-on-steelortoevaluate
3. Terminology
the extreme pressure characteristics of the grease.
3.1 There are no terms in this test method that require new
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
or other than dictionary definitions.
standard except where the test apparatus or consumable parts
4. Summary of Test Method
are only available in other units. In such cases, these will be
regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for
1
4.1 Three ⁄2 in. (12.7-mm) diameter steel balls are clamped
information only.
together and covered with the lubricant to be evaluated. A
1
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
fourth ⁄2 in. diameter steel ball, referred to as the top ball, is
safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the pressed with a force of 40 kgf (392 N) into the cavity formed
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- by the three clamped balls for three-point contact. The tem-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- peratureofthelubricatinggreasespecimenisregulatedat75°C
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. (167°F) and then the top ball is rotated at 1200 rpm for 60 min.
Lubricants are compared by using the average size of the scar
2. Referenced Documents
diameters worn on the three lower clamped balls.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
NOTE 1—Because of differences in the construction of the various
D4172 Test Method for Wear Preventive Characteristics of
machines on which the four-ball test can be made, the manufacturer’s
Lubricating Fluid (Four-Ball Method) instructions should be consulted for proper machine setup and operation.
NOTE 2—Although the test can be run under other test parameters, the
D6300 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias
precision noted in Section 11 can vary when testing with other than test
parameters listed in Section 8.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
5. Significance and Use
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.G0.04 on Functional Tests - Tribology.
5.1 The four-ball wear-test method can be used to determine
Current edition approved May 1, 2008. Published September 2008. Originally
therelativewear-preventingpropertiesofgreasesunderthetest
approved in 1964. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D2266–01.
conditions and if the test conditions are changed the relative
This test method has been adopted for use by government agencies to replace
ratings may be different. No correlation has been established
Method 6514 of Federal Test Method Standard No. 791b. DOI: 10.1520/D2266-
01R08.
between the four-ball wear test and field service. The test
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
the ASTM website. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2266−01 (2008)
method cannot be used to differentiate between Extreme
4
Pressure (EP) and Non-Extreme Pressure (Non-EP) Greases.
6. Apparatus
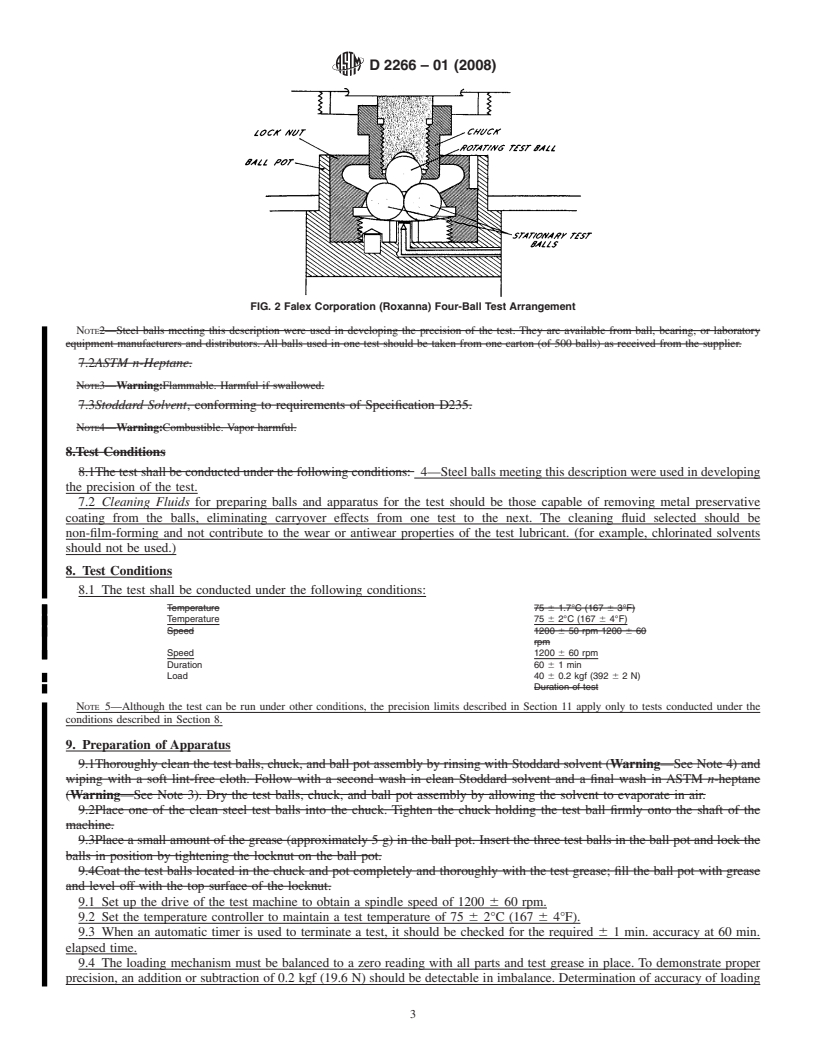
6.1 Four-Ball Wear-Tester and Accessories—See Fig. 1 and
5
Fig. 2.
NOTE 3—It is important to distinguish between the Four-Ball EPTester
and the Four-Ball Wear Tester. The Four-Ball EP Tester is designed for
testing under heavier loads and more severe conditions; it lacks the
sensitivity necessary for performing four-ball wear test.
6
6.2 Microscope, capable of measuring the diameters of the
scars produced on the three stationary balls to an accuracy of
0.01 mm. It is more efficient to measure the scars
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
An American National Standard
Designation:D2266–91 (Reapproved 1996) Designation: D 2266 – 01 (Reapproved 2008)
Standard Test Method for
Wear Preventive Characteristics of Lubricating Grease
1
(Four-Ball Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2266; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This test method standard has been adoptedapproved for use by government agencies to replace Method 6514 of the Department of
Federal Test Method Standard No. 791b. Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the wear preventive characteristics of greases in sliding steel-on-steel
applications. It is not intended to predict wear characteristics with metal combinations other than steel-on-steel or to evaluate the
extreme pressure characteristics of the grease.
1.2The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard except where the test apparatus or consumable parts are only
available in other units. In such cases, these will be regarded as standard.The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statement see 7.2, 7.3, and 9.1.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D235Specification for Mineral Spirits (Petroleum Spirits) (Hydrocarbon Dry Cleaning Solvent) 4172 Test Method for Wear
Preventive Characteristics of Lubricating Fluid (Four-Ball Method)
D 6300 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias Data for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and Lubricants
2.2 Other Document:
3
ANSI Specifications B3.12for Metal Balls ANSI Standard:
B3.12 for Metal Balls
3. Terminology
3.1 There are no terms in this standardtest method that require new or other than dictionary definitions.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1A steel ball is rotated under load against three stationary steel balls having grease-lubricated surfaces. The diameters of the
wear scars on the stationary balls are measured after completion of the test.
1
4.1 Three ⁄2 in. (12.7-mm) diameter steel balls are clamped together and covered with the lubricant to be evaluated. A fourth
1
⁄2 in. diameter steel ball, referred to as the top ball, is pressed with a force of 40 kgf (392 N) into the cavity formed by the three
clamped balls for three-point contact. The temperature of the lubricating grease specimen is regulated at 75°C (167°F) and then
the top ball is rotated at 1200 rpm for 60 min. Lubricants are compared by using the average size of the scar diameters worn on
the three lower clamped balls.
NOTE 1—Because of differences in the construction of the various machines on which the four-ball test can be made, the manufacturer’s instructions
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-2 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.G on
Lubricating Grease.
Current edition approved Sept. 15, 1991. Published November 1991. Originally published as D2266–64T. Last previous edition D2266–86.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.G0.04
on Functional Tests - Tribology.
Current edition approved May 1, 2008. Published September 2008. Originally approved in 1964. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D 2266–01.
This test method has been adopted for use by government agencies to replace Method 6514 of Federal Test Method Standard No. 791b.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 06.04.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 West 42nd Street, 13th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036,
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.