ASTM F721-81(1998)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Gage Piping Assemblies
Standard Specification for Gage Piping Assemblies
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers details of gage piping assemblies for pressure gages with optional provisions for additional gages, pressure switches, transmitters, etc., for use with steam, steam drains, feed water, condensate, fresh water, salt water, compressed air, fuel oil, and lubricating oil systems.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: F 721 – 81 (Reapproved 1998)
Standard Specification for
Gage Piping Assemblies
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 721; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope B 453 Specification for Copper-Zinc-Lead Alloy (Leaded-
Brass) Rod
1.1 This specification covers details of gage piping assem-
B 466/B 466M Specification for Seamless Copper-Nickel
blies for pressure gages with optional provisions for additional
Pipe and Tube
gages, pressure switches, transmitters, and so forth, for use
2.2 American National Standard Institute Standards:
with steam, steam drains, feed water, condensate, fresh water,
B16.11 Forged Steel Fittings, Socket Weld, and Threaded
salt water, compressed air, fuel oil, and lubricating oil systems.
B16.15 Cast Bronze Threaded Fittings
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
2.3 Federal Specifications:
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
QQ-S-637 Steel Bar, Carbon, Cold Finished (Standard
information only.
Quality, Free Machining)
2. Referenced Documents
QQ-S-763 Steel Bars, Wire, Shapes, and Forgings,
Corrosion-Resisting
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A 105/A105M Specification for Carbon Steel Forgings for
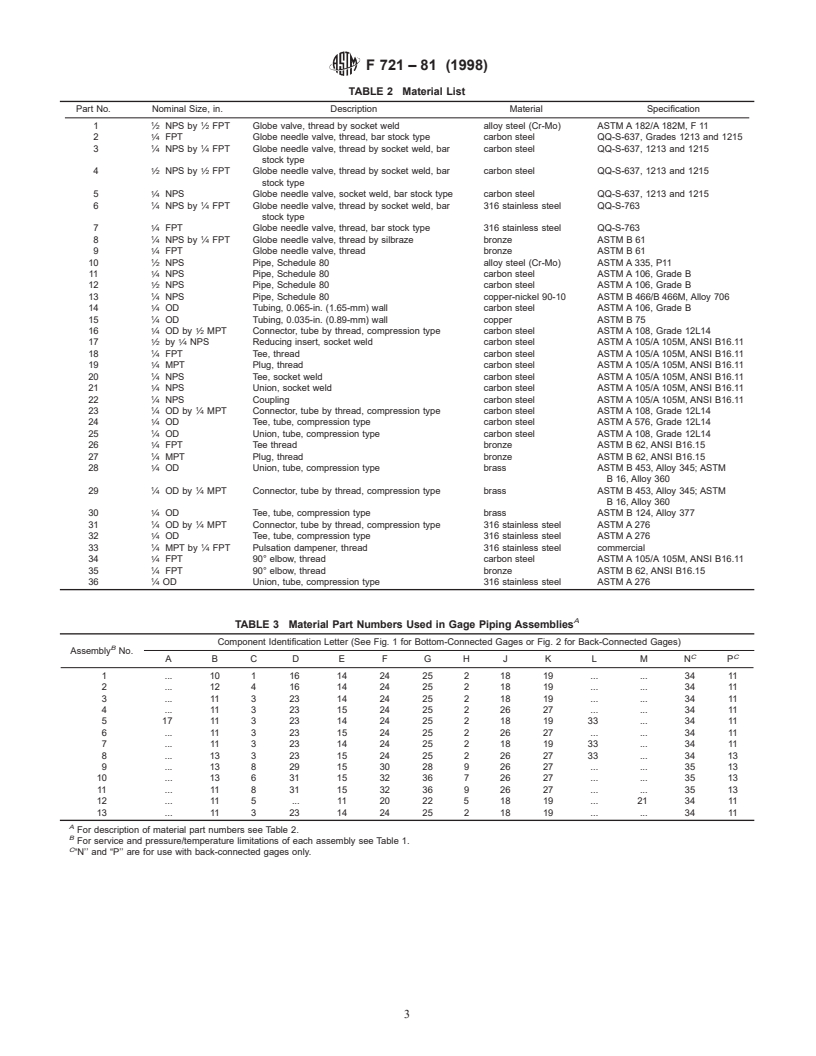
3. List of Assemblies
Piping Applications
3.1 This specification incorporates 13 gage piping assem-
A 106 Specification for Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe for
blies as described in Table 1.
High-Temperature Service
A 108 Specification for Steel Bars, Carbon, Cold Finished,
4. General Requirements and Guidelines
Standard Quality
4.1 Fig. 1 shows a typical piping assembly for bottom-
A 182/A182M Specification for Forged or Rolled Alloy-
connected gages and Fig. 2 a typical piping assembly for
Steel Pipe Flanges, Forged Fittings, and Valves and Parts
2 back-connected gages.
for High-Temperature Service
4 4.2 A siphon shall be used as shown in all gage applications
A 276 Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes
for steam systems to maintain a protective water seal between
A 335/A335M Specification for Seamless Ferritic Alloy-
2 the gage and the steam supply.
Steel Pipe for High-Temperature Service
4.3 Each assembly includes a test connection beyond the
A 576 Specification for Steel Bars, Carbon, Hot-Wrought,
3 gage valve which consists of a tee with a ⁄4-in. NPT threaded
Special Quality
plug in the branch. The plug is removable for the purpose of
B 16 Specification for Free-Cutting Brass Rod, Bar, and
5 installing a test gage for calibration. As an alternative, a gage
Shapes for Use in Screw Machines
5 valve that incorporates a built-in test connection integral with
B 61 Specification for Steam or Valve Bronze Castings
the valve may be substituted for the gage valve and test tee.
B 62 Specification for Composition Bronze or Ounce Metal
5 4.4 Root connections should be kept to a minimum by
Castings
connecting other instruments at the tee between the root and
B 75 Specification for Seamless Copper Tube
gage valves. There is no limit to the number of dead-end-type
B 124 Specification for Copper and Copper Alloy Forging
instruments that can be served from a single root connection.
Rod, Bar, and Shapes
However, each instrument should have its own shutoff valve
and, if desired, a test tee may be fitted at each instrument.
1 4.5 Two shutoff valves are generally used in each assembly,
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships
and Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.11 on a root valve and a gage cutout valve. The gage valve may be
Machinery and Piping Systems.
Current edition approved April 24, 1981. Published July 1981.
2 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.01. Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.05. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
4 7
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03 Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.01. Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F 721 – 81 (1998)
A,B
TABLE 1 Gage Piping Assemblies
Assembly Maximum Pressure, Maximum Temperature,
Service
No. psi (kPa) °F (°C)
1 Superheated steam 1125 (7757) 960 (516)
2 High-pressure desuperheated steam and high-pressure extractions 1100 (7584) 580 (304)
3 Low-pressure extractions, gland seal, auxiliary exhaust, and 150-psig (1034-MPa) 900 (6205) 563 (295)
steam
4 Low-pressure steam 125 (861) 353 (178)
5 Boiler feed discharge 1500 (10 342) 450 (232)
6 Feed suction and condensate 165 (1138) 300 (149)
7 Compressed air above 165 psi (1.14 MPa) 900 (6205) 563 (295)
8 Compressed air 165 (1138) 300 (149)
9 Fresh and potable water 200 (1379) 150 (66)
10 Main and auxiliary salt water circulating, salt water service, and wet firemain 200 (1379) 150 (66)
11 Dry firemain and deck washdown 200 (1379) 150 (66)
12 Fuel oil and lube oil 900 (6205) 250 (121)
13 Diesel oil 900 (6205) 563 (295)
A
For typical piping assemblies see Fig. 1 and Fig. 2.
B
For materials required see Table 2 and Table 3.
NOTE 1—For material identification see Table 3.
NOTE 2—Use siphon for Assemblies 1 through 4.
NOTE 3—For pulsation dampener requirements see 4.6 and Table 3.
NOTE 4—Piping through the root valve is normally detailed on the
piping arrangement drawings but is shown here as an aid in establishing
NOTE 1—For material identification see Table 3.
material requirements.
NOTE 2—Use siphon for Assemblies 1 through 4.
FIG. 1 Typical Piping Assembly for Bottom-Connected Gages
NOTE 3—For pulsation dampener requirements see 4.6 and Table 3.
NOTE 4—Piping through the root valve is normally detailed on the
piping arrangement drawings but is shown here as an aid in establishing
material requirements.
eliminated and a single shutoff valve may serve as both a root
FIG. 2 Typical Piping Assembly for Back-Connected Gages
and gage valve prov
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.