ASTM D6024/D6024M-16
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Ball Drop on Controlled Low Strength Material (CLSM) to Determine Suitability for Load Application
Standard Test Method for Ball Drop on Controlled Low Strength Material (CLSM) to Determine Suitability for Load Application
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is used primarily as a field test to determine the readiness of the CLSM to accept loads prior to adding a temporary or permanent wearing surface.
5.2 This test method is not meant to predict the load bearing strength of a CLSM mixture.
5.3 This test is one of a series of quality control tests that can be performed on CLSM during construction to monitor compliance with specification requirements. The other tests that can be used during construction control are Test Methods D4832, D6023, and D6103.
Note 1: The quality of the result produced by this standard is dependent on the competence of the personnel performing it, and the suitability of the equipment and facilities used. Agencies that meet the criteria of Practice D3740 are generally considered capable of competent and objective testing/sampling/inspection/and the like. Users of this standard are cautioned that compliance with Practice D3740 does not in itself assure reliable results. Reliable results depend on many factors; Practice D3740 provides a means of evaluating some of those factors.
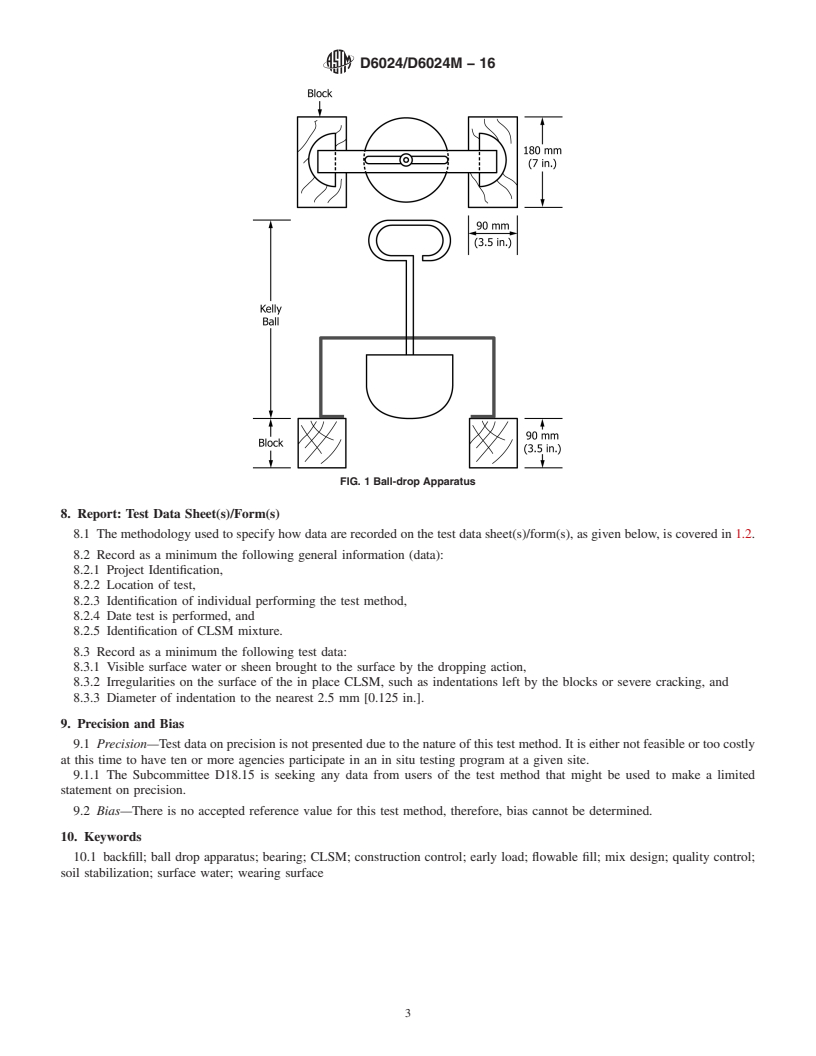
SCOPE
1.1 This test method explains the determination of the ability of Controlled Low Strength Material (CLSM) to withstand loading by repeatedly dropping a metal weight onto the in-place material.
1.2 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the guidelines for significant digits and rounding established in Practice D6026.
1.2.1 The procedures used to specify how data are collected/recorded and calculated in the standard are regarded as the industry standard. In addition, they are representative of the significant digits that generally should be retained. The procedures used do not consider material variation, purpose for obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any considerations for the user’s objectives; and it is common practice to increase or reduce significant digits of reported data to be commensurate with these considerations. It is beyond the scope of these test methods to consider significant digits used in analysis methods for engineering data.
1.3 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units presented in brackets are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 CLSM is also known as flowable fill, controlled density fill, soil-cement slurry, soil-cement grout, unshrinkable fill, “K-Krete,” and other similar names.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (Warning—Fresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause chemical burns to skin and tissue upon prolonged exposure.2)
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D6024/D6024M − 16
Standard Test Method for
Ball Drop on Controlled Low Strength Material (CLSM) to
1
Determine Suitability for Load Application
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6024/D6024M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause
2
chemical burns to skin and tissue upon prolonged exposure. )
1.1 This test method explains the determination of the
ability of Controlled Low Strength Material (CLSM) to with-
2. Referenced Documents
stand loading by repeatedly dropping a metal weight onto the 3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
in-place material.
C125 Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Ag-
gregates
1.2 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the
D653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
guidelines for significant digits and rounding established in
Fluids
Practice D6026.
D3740 Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies
1.2.1 Theproceduresusedtospecifyhowdataarecollected/
Engaged in Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock as
recorded and calculated in the standard are regarded as the
Used in Engineering Design and Construction
industry standard. In addition, they are representative of the
D4832 Test Method for Preparation and Testing of Con-
significant digits that generally should be retained. The proce-
trolled Low Strength Material (CLSM) Test Cylinders
dures used do not consider material variation, purpose for
D6023 Test Method for Density (Unit Weight), Yield, Ce-
obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any consider-
ment Content, and Air Content (Gravimetric) of Con-
ations for the user’s objectives; and it is common practice to
trolled Low-Strength Material (CLSM)
increase or reduce significant digits of reported data to be
D6026 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Geotechnical
commensuratewiththeseconsiderations.Itisbeyondthescope
Data
of these test methods to consider significant digits used in
D6103 Test Method for Flow Consistency of Controlled
4
analysis methods for engineering data.
Low Strength Material (CLSM) (Withdrawn 2013)
1.3 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-
3. Terminology
pound units presented in brackets are to be regarded separately
3.1 Definitions:
as standard. The values stated in each system shall be used
3.1.1 For definitions of common technical terms in this test
independently of the other. Combining values from the two
method, refer to Terminology standards C125 and D653.
systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
3.1.2 Controlled Low Strength Material (CLSM), n—a mix-
1.4 CLSM is also known as flowable fill, controlled density
ture of soil, aggregates (sand, gravel, or both), cementitious
fill, soil-cement slurry, soil-cement grout, unshrinkable fill, materials, water, and sometimes admixtures, that hardens into
“K-Krete,” and other similar names. a material with a higher strength than the soil, but less than
8400 kPa [1200 psi].
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.2.1 Discussion—Used as a replacement for compacted
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
backfill, CLSM can be placed as a slurry, a mortar, or a
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
compacted material and typically has strengths of 350 to 700
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
kPa [50 to 100 psi] for most applications.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. (Warning—Fresh
2
Section on Safety Precautions, Manual of Aggregate and Concrete Testing,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol. 04.02.
1 3
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD18onSoiland For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.15 on Stabilization With contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Admixtures. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2016. Published January 2017. Originally the ASTM website.
4
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D6024 – 07. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/D6024_D6024M-16. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Cons
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6024/D6024M − 15 D6024/D6024M − 16
Standard Test Method for
Ball Drop on Controlled Low Strength Material (CLSM) to
1
Determine Suitability for Load Application
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6024/D6024M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method explains the determination of the ability of Controlled Low Strength Material (CLSM) to withstand loading
by repeatedly dropping a metal weight onto the in-place material.
1.2 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the guidelines for significant digits and rounding established in Practice
D6026.
1.2.1 The procedures used to specify how data are collected/recorded and calculated in the standard are regarded as the industry
standard. In addition, they are representative of the significant digits that generally should be retained. The procedures used do not
consider material variation, purpose for obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any considerations for the user’s objectives;
and it is common practice to increase or reduce significant digits of reported data to be commensurate with these considerations.
It is beyond the scope of these test methods to consider significant digits used in analysis methods for engineering data.
1.3 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units presented in brackets are to be regarded separately as
standard. The values stated in each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may
result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 CLSM is also known as flowable fill, controlled density fill, soil-cement slurry, soil-cement grout, unshrinkable fill,
“K-Krete,” and other similar names.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. (Warning—Fresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause chemical burns to skin and
2
tissue upon prolonged exposure. )
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C125 Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Aggregates
D653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained Fluids
D3740 Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies Engaged in Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock as Used in
Engineering Design and Construction
D4832 Test Method for Preparation and Testing of Controlled Low Strength Material (CLSM) Test Cylinders
D6023 Test Method for Density (Unit Weight), Yield, Cement Content, and Air Content (Gravimetric) of Controlled
Low-Strength Material (CLSM)
D6026 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Geotechnical Data
4
D6103 Test Method for Flow Consistency of Controlled Low Strength Material (CLSM) (Withdrawn 2013)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of common technical terms in this test method, refer to Terminology standards C125 and D653.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:Definitions:
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D18 on Soil and Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.15 on Stabilization With
Admixtures.
Current edition approved July 1, 2015Dec. 1, 2016. Published July 2015January 2017. Originally approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 20072015 as
D6024 – 07. DOI: 10.1520/D6024_D6024M-15.10.1520/D6024_D6024M-16.
2
Section on Safety Precautions, Manual of Aggregate and Concrete Testing, Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol. 04.02.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6024/D6024M − 16
3.1.1 For definitions of common technical terms in this test method, refer to Terminology standards C125 and D65
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.