ASTM D2512-95(2002)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Compatibility of Materials with Liquid Oxygen (Impact Sensitivity Threshold and Pass-Fail Techniques)
Standard Test Method for Compatibility of Materials with Liquid Oxygen (Impact Sensitivity Threshold and Pass-Fail Techniques)
SCOPE
1.1 This method 2,3,4 covers the determination of compatibility and relative sensitivity of materials with liquid oxygen under impact energy using the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA)-type impact tester. Materials that are impact-sensitive with liquid oxygen are generally also sensitive to reaction by other forms of energy in the presence of oxygen.
1.2 This standard should be used to measure and describe the properties of materials, products, or assemblies in response to heat and flame under controlled laboratory conditions and should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or fire risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However, results of this test may be used as elements of a fire risk assessment which takes into account all of the factors which are pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard of a particular end use.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D2512–95 (Reapproved 2002)
Standard Test Method for
Compatibility of Materials with Liquid Oxygen (Impact
Sensitivity Threshold and Pass-Fail Techniques)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2512; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2.2 Military Standards:
, ,
2 3 4 MIL-D-16791G Detergent, General Purpose (Liquid, Non-
1.1 Thismethod coversthedeterminationofcompatibil-
ionic)
ity and relative sensitivity of materials with liquid oxygen
MIL-P-27401C Propellant Pressurizing Agent, Nitrogen
under impact energy using the Army Ballistic Missile Agency
MIL-PRF-25508F Propellant, Oxygen
(ABMA)-typeimpacttester.Materialsthatareimpact-sensitive
MIL-T-27602B Trichloroethylene, Oxygen Propellant
with liquid oxygen are generally also sensitive to reaction by
Compatible
other forms of energy in the presence of oxygen.
MIL-C-81302D Cleaning Compound, Solvent, Trichlorotri-
1.2 This standard should be used to measure and describe
fluorocarbon
the properties of materials, products, or assemblies in response
to heat and flame under controlled laboratory conditions and
3. Summary of Test Method
should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or
3.1 A sample of the test material is placed in a specimen
fire risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire
cup, precooled and covered with liquid oxygen, and placed in
conditions. However, results of this test may be used as
the cup holder located in the anvil region assembly of the
elements of a fire risk assessment which takes into account all
impact tester. A precooled striker pin is then centered in the
of the factors which are pertinent to an assessment of the fire
cup. The plummet is dropped from selected heights onto the
hazard of a particular end use.
pin, which transmits the energy to the test specimen. Observa-
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
tion for any reaction is made and the liquid oxygen impact
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
sensitivityofthetestmaterialisnoted.Droptestsarecontinued
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
using a fresh specimen cup and striker pin for each drop, until
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
the threshold valve is achieved. A series of drop tests are
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
conducted at an energy level of 98 J (72 ft·lbf) or as specified
2. Referenced Documents for the pass-fail tests.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4. Significance and Use
C 145 Specification for Solid Load-Bearing Concrete Ma-
5 4.1 When this test method is used to measure the threshold
sonry Units
6 impact sensitivity of a material, a relative sensitivity assess-
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
ment is obtained which permits the ranking of materials.
4.2 This test method may also be used for acceptance-
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G04 on testing materials for use in liquid oxygen systems. Twenty
Compatibility and Sensitivity of Materials in Oxygen EnrichedAtmospheres and is
separate samples of the material submerged in liquid oxygen
the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G04.01 on Test Methods.
are subjected to 98 J (72 ft·lbf) or as specified. Impact energy
Current edition approved Feb. 15, 1995. Published April 1995. Originally
e1
delivered through a 12.7-mm ( ⁄2-in.) diameter contact. More
published as D 2512 – 66. Last previous edition D 2512 – 82 (1994) .
“NASA Handbook 8060. 1B, Ambient LOX Mechanical Impact Screening
than one indication of sensitivity is cause for immediate
Test,” September 1981, pp. 4-53 through 4-71. “Oxygen Systems.” George C.
rejection. A single explosion, flash, or other indication of
Marshall Space Flight Center, National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
Specification MSFC 106B. September 1981.
“Lubrication and Related Research and Test Method Development forAviation
Propulsion Systems.” Technical Report No. 59-726. Wright Air Development AvailablefromStandardizationDocumentsOrderDesk,Bldg.4SectionD,700
Division, January 1960. Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, Attn: NPODS.
4 8
“General Safety Precautions for Missile Liquid Propellants.” Cancelled in 1983. Previously available from Standardization Documents
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.05. Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01. Attn: NPODS.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D2512–95 (2002)
sensitivity during the initial series of 20 tests requires that an
additional 40 samples be tested without incident to ensure
acceptability of the material.
4.3 The threshold values are determined by this test method
at ambient pressure. The sensitivity of materials to mechanical
impact is known to increase with increasing pressure. Since
mostliquidoxygensystemsoperateatpressuresaboveambient
condition, some consideration should be given to increased
sensitivity and reactivity of materials at higher pressure when
selecting materials for use in pressurized system.
5. Apparatus
5.1 ABMA-Type Impact Tester (Fig. 1), for determining the
sensitivity of materials to liquid oxygen with impact energy.
Fig. 2 shows the schematic diagram of the typical power
supply. The tester consists of the following parts:
5.1.1 Three Guide Tracks, capable of maintaining accurate
vertical alignment under repeated shock conditions.
5.1.2 Plummet, with a weight of 9.072 6 0.023 kg (20 6
0.05 lbs).
5.1.3 Safety Catch, operated by a solenoid, and designed to
FIG. 2 Schematic Diagram of Power Supply
hold the plummet near the base of the magnet. It is used to
support the plummet in the event of a power failure.
5.1.4 Electromagnet, for supporting or releasing the plum-
5.1.5 Base—The base of the tester is composed of the
met.Theelectromagnetisdesignedtohold9.072kg(20lbs)of
following: a rigid 0.61- by 0.61- by 0.61-m (2- by 2- by 2-ft)
weight with a minimum amount of electrical energy.
(min)reinforcedconcreteblock(concreteconformingtoSpeci-
fication C 145), a 3.2-mm ( ⁄8-in.) stainless steel sheet, and a
25-mm (1-in.) thick stainless steel base plate. Four stainless
Detailed drawings for the ABMA-Type Impact Tester and Anvil Region
steel foundation bolts protruding from the concrete block are
Assembly are available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct
used to fasten the plate and sheet to the smooth surface of the
ADJD2512.
concrete block with stainless steel nuts.
NOTE 1—Where not otherwise indicated, stainless steel shall be of the
AISI 300 series.
5.1.6 Anvil Plate (Fig. 3), made from a 51-mm (2-in.) thick
FIG. 1 ABMA-Type Impact Tester FIG. 3 Anvil Region Assembly
D2512–95 (2002)
Type 440B heat-treated steel plate, (56 to 58 HRC) that is such as stainless steel Dewar flasks, liquid oxygen protective
centered and rests on the base plate. It in turn centers the gloves, lintless laboratory coat, eye protection equipment, and
specimen cup holder. liquid oxygen storage containers. Special handling equipment
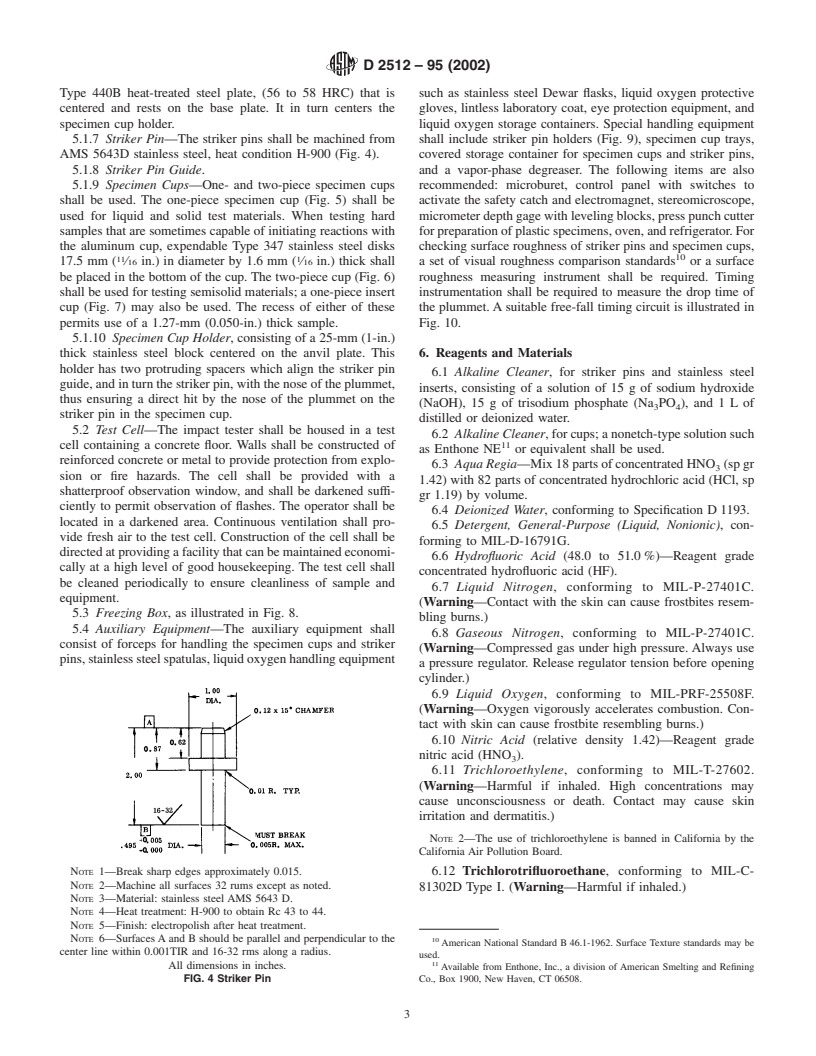
5.1.7 Striker Pin—The striker pins shall be machined from shall include striker pin holders (Fig. 9), specimen cup trays,
AMS 5643D stainless steel, heat condition H-900 (Fig. 4). covered storage container for specimen cups and striker pins,
5.1.8 Striker Pin Guide. and a vapor-phase degreaser. The following items are also
5.1.9 Specimen Cups—One- and two-piece specimen cups recommended: microburet, control panel with switches to
shall be used. The one-piece specimen cup (Fig. 5) shall be activate the safety catch and electromagnet, stereomicroscope,
used for liquid and solid test materials. When testing hard micrometerdepthgagewithlevelingblocks,presspunchcutter
samples that are sometimes capable of initiating reactions with forpreparationofplasticspecimens,oven,andrefrigerator.For
the aluminum cup, expendable Type 347 stainless steel disks checking surface roughness of striker pins and specimen cups,
11 1
17.5 mm ( ⁄16 in.) in diameter by 1.6 mm ( ⁄16 in.) thick shall a set of visual roughness comparison standards or a surface
be placed in the bottom of the cup. The two-piece cup (Fig. 6) roughness measuring instrument shall be required. Timing
shall be used for testing semisolid materials; a one-piece insert instrumentation shall be required to measure the drop time of
cup (Fig. 7) may also be used. The recess of either of these the plummet. A suitable free-fall timing circuit is illustrated in
permits use of a 1.27-mm (0.050-in.) thick sample. Fig. 10.
5.1.10 Specimen Cup Holder, consisting of a 25-mm (1-in.)
thick stainless steel block centered on the anvil plate. This 6. Reagents and Materials
holder has two protruding spacers which align the striker pin
6.1 Alkaline Cleaner, for striker pins and stainless steel
guide, and in turn the striker pin, with the nose of the plummet,
inserts, consisting of a solution of 15 g of sodium hydroxide
thus ensuring a direct hit by the nose of the plummet on the
(NaOH), 15 g of trisodium phosphate (Na PO ), and 1 L of
3 4
striker pin in the specimen cup.
distilled or deionized water.
5.2 Test Cell—The impact tester shall be housed in a test
6.2 Alkaline Cleaner, for cups; a nonetch-type solution such
cell containing a concrete floor. Walls shall be constructed of 11
as Enthone NE or equivalent shall be used.
reinforced concrete or metal to provide protection from explo-
6.3 Aqua Regia—Mix 18 parts of concentrated HNO (sp gr
sion or fire hazards. The cell shall be provided with a
1.42) with 82 parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl, sp
shatterproof observation window, and shall be darkened suffi-
gr 1.19) by volume.
ciently to permit observation of flashes. The operator shall be
6.4 Deionized Water, conforming to Specification D 1193.
located in a darkened area. Continuous ventilation shall pro-
6.5 Detergent, General-Purpose (Liquid, Nonionic), con-
vide fresh air to the test cell. Construction of the cell shall be
forming to MIL-D-16791G.
directedatprovidingafacilitythatcanbemaintainedeconomi-
6.6 Hydrofluoric Acid (48.0 to 51.0 %)—Reagent grade
cally at a high level of good housekeeping. The test cell shall
concentrated hydrofluoric acid (HF).
be cleaned periodically to ensure cleanliness of sample and
6.7 Liquid Nitrogen, conforming to MIL-P-27401C.
equipment.
(Warning—Contact with the skin can cause frostbites resem-
5.3 Freezing Box, as illustrated in Fig. 8.
bling burns.)
5.4 Auxiliary Equipment—The auxiliary equipment shall
6.8 Gaseous Nitrogen, conforming to MIL-P-27401C.
consist of forceps for handling the specimen cups and striker
(Warning—Compressed gas under high pressure. Always use
pins,stainlesssteelspatulas,liquidoxygenhandlingequipment
a pressure regulator. Release regulator tension before opening
cylinder.)
6.9 Liquid Oxygen, conforming to MIL-PRF-25508F.
(Warning—Oxygen vigorously accelerates combustion. Con-
tact with skin can cause frostbite resembling burns.)
6.10 Nitric Acid (relative density 1.42)—Reagent grade
nitric acid (HNO ).
6.11 Trichloroethylene, conforming to MIL-T-27602.
(Warning—Harmful if inhaled. High concentrations may
cause unconsciousness or death. Contact may cause skin
irritation and dermatitis.)
NOTE 2—The use of trichloroethylene is banned in California by the
California Air Pollution Board.
NOTE 1—Break sharp edges approximately 0.015. 6.12 Trichlorotrifluoroethane, conforming to MIL-C-
NOTE 2—Machine all surfaces 32 rums except as noted.
81302D Type I. (Warning—Harmful if inhaled.)
NOTE 3—Material: stainless steel AMS 5643 D.
NOTE 4—Heat treatment: H-900 to obtain Rc 43 to 44.
NOTE 5—Finish: electropolish after heat treatment.
NOTE 6—Surfaces A and B should be parallel and perpendicular to the 10
American National Standard B 46.1-1962. Surface Texture standards may be
center line within 0.001TIR and 16-32 rms along a radius.
used.
All dimensions in inches.
Available from Enthone, Inc., a division of American Smelting and Refining
FIG. 4 Striker Pin Co., Box 1900, New Haven, CT 06508.
D2512–95 (2002)
NOTE 1—Break sharp edges 0.015.
NOTE 2—The cup is formed by deep drawing.
NOTE 3—The thickness and parallelness of the cup bottom shall be controllled to 0.0610 to 0.0630 by coining.
NOTE 4—Materal: aluminum alloy QQ-A-318 (5052) temper H32.
All dimensions in inches.
FIG. 5 One-Piece Specimen Cup
7. Safety Precautions take steps to make sure that no oxygen remains absorbed in
clothing before smoking or approaching any source of ignition.
7.1 The hazards involved with liquid oxygen are very
7.5 The threshold limit value, that is, the time-weighed
serious. Contact with the skin can cause frostbites resembling
average concentration of trichloroethylene believed safe for
burns. Contact with hydrocarbons or other fuels causes an
continuous exposure during a normal 8-h workday, has been
explosion hazard, as such mixtures are usually shock, impact,
established by the American Conference of Governmental
and vibration-sensitive.
Industrial Hygienists at 100 ppm. Operations using trichloro-
7.2 The first-aid procedure for liquid oxygen contact is to
ethylene should always be conducted in a well-ventilated area.
flush the affected area with water. This treatment should be
The comparable figure for trichlorotrifluorethane is 1000 ppm,
followed by medical attention. A safety shower must be
and normal ventilation is usually adequate. When a ventilation
available in the immediate area.
system is used, an effort should be made to have the natural air
7.3 The following safety rules must be observed: personnel
currentsinthevicinityassistratherthanopposethemechanical
working with liquid oxygen must be familiar with its nature
ventilation. For cleaning by vapor degreasing, the vapor level
and characteristics. Approved goggles or face shields, protec-
shall be controlled by heat input and cooling coils, which
tive clothing, gloves, and boots must be worn during handling
establish a vapor “ceiling.” Such vapor degreasing units should
or transfer. Such operations shall be performed by not less than
always be installed in a location that is free from draft
two persons as a group. Extreme caution shall be exercised in
conditionsandshouldbeventilatedbyhorizontalslotexhau
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.