ASTM E3076-18e1
(Practice)Standard Practice for Determination of the Slope in the Linear Region of a Test Record
Standard Practice for Determination of the Slope in the Linear Region of a Test Record
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 It is often necessary to determine the slope of a linear region within a test record, and for standardization purposes, it is desirable to have a method for determining the slope that is not subjective. There are numerous ASTM standard test methods where the test procedure or analysis requires that slope be determined, but the procedures for doing so are not well defined. Ideally, if multiple laboratories analyze the same data for determination of slope, they should produce the same result. The objective of this standard practice is to eliminate the linear-fit as a source of variability in test results.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice presents an automated, objective linear-fitting method for determining the slope of the linear portion of a test record. The method assumes that there is a linear region early in the test record where the value of the y variable increases roughly in proportion to the x variable and the slope of the record decreases after the linear region. The practice determines the best linear fit to the data based on the least normalized residual and provides metrics for evaluating the quality of the test record and the quality of the resultant fit.
1.2 Data quality metrics are applied that evaluate the level of noise and the digital resolution of the data to determine if the test record is adequate for a linear regression analysis. Fit quality metrics use analysis of residuals in the vicinity of the fit range to determine if the test record is adequately linear and the fit range is sufficiently large.
1.3 For test records that meet the data and fit quality metrics, the practice determines a repeatable slope without the need for operator input that is independent of operator judgment. For test records that fail one or more of the quality metrics, it is recommended that the analyst evaluate the fit to determine if it is acceptable.
1.4 This practice represents a general purpose approach that is applicable for any test standard or method in which a linear fit is desired. It is intended that this practice can be called upon by standard test methods when slope must be determined.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
´1
Designation: E3076 − 18
Standard Practice for
Determination of the Slope in the Linear Region of a Test
1
Record
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E3076; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Footnote 3 was editorially corrected in May 2023.
1. Scope Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.1 This practice presents an automated, objective linear-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
fitting method for determining the slope of the linear portion of
a test record. The method assumes that there is a linear region
2. Referenced Documents
early in the test record where the value of the y variable
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
increases roughly in proportion to the x variable and the slope
E1942 Guide for Evaluating Data Acquisition Systems Used
of the record decreases after the linear region. The practice
in Cyclic Fatigue and Fracture Mechanics Testing
determines the best linear fit to the data based on the least
E2443 Guide for Verifying Computer-Generated Test Re-
normalized residual and provides metrics for evaluating the
sults Through The Use Of Standard Data Sets
quality of the test record and the quality of the resultant fit.
3
2.2 ASTM Data Set:
1.2 Data quality metrics are applied that evaluate the level
E3076-DS1(2018) File 01 Benchmark Data Set to Evaluate
of noise and the digital resolution of the data to determine if the
Computer Implementation of the Algorithm in Standard
test record is adequate for a linear regression analysis. Fit
E3076.
quality metrics use analysis of residuals in the vicinity of the fit
3. Terminology
range to determine if the test record is adequately linear and the
fit range is sufficiently large.
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 digital resolution, n—the precision of stored informa-
1.3 For test records that meet the data and fit quality metrics,
the practice determines a repeatable slope without the need for tion resulting from a discrete digital representation of analog
operator input that is independent of operator judgment. For data.
test records that fail one or more of the quality metrics, it is
3.1.2 linear region, n—a region of the test record where the
recommended that the analyst evaluate the fit to determine if it
underlying physics indicate that the dependent variable would
is acceptable.
increase in proportion to the independent variable if there were
no noise in the test record.
1.4 This practice represents a general purpose approach that
is applicable for any test standard or method in which a linear
3.1.3 normalized, n—data with global minima of 0 and
fit is desired. It is intended that this practice can be called upon
global maxima of 1 in x and y.
by standard test methods when slope must be determined.
3.1.4 residual, n—the difference between the linear fit and
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
the original test record y-values at a given x-value.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.5 test record, n—the basic raw data from a data set
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter- 4. Summary of Practice
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.1 This practice is intended for the analysis of test records
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
where the y variable increases roughly in proportion to the x
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
variable over a region early in the test record.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E08 on Fatigue and contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Fracture and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E08.03 on Advanced Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Apparatus and Techniques. the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2018. Published April 2019. DOI: 10.1520/ This data set is available for download from ASTM at
E3076–18E01 https://www.astm.org/get-involved/technical-committees/adhoc-e08.html
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Pa
...








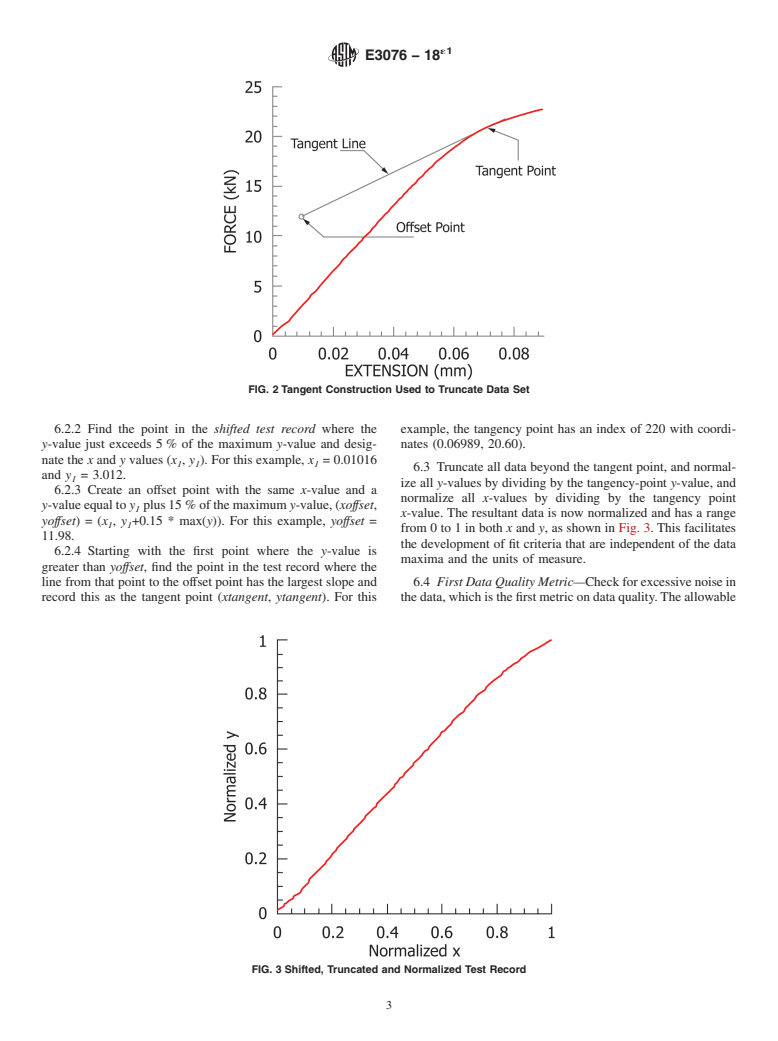
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.