ASTM D2245-90(2005)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Identification of Oils and Oil Acids in Solvent-Reducible Paints
Standard Test Method for Identification of Oils and Oil Acids in Solvent-Reducible Paints
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method provides a procedure to identify the fatty acids present in the vehicle of a paint.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the identification of oils and oil acids in vehicles that have been separated from solvent-reducible paints. The test method is based on a gas chromatographic technique (of the methyl esters) applicable to products containing both saturated and unsaturated, animal and vegetable, unpolymerized or partially polymerized fatty acids having 8 to 20 carbon atoms.
1.2 This test method is not applicable to products containing fatty acids that have been polymerized or oxidized to such an extent that no characteristic monomeric fatty acids remain.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2245 – 90 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Test Method for
Identification of Oils and Oil Acids in Solvent-Reducible
Paints
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2245; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope D2800 Test Method for Preparation of Methyl Esters From
Oils for Determination of Fatty Acid Composition by
1.1 This test method covers the identification of oils and oil
Gas-Liquid Chromatography
acids in vehicles that have been separated from solvent-
reducible paints. The test method is based on a gas chromato-
3. Summary of Test Method
graphic technique (of the methyl esters) applicable to products
3.1 This test method is based upon the differential migration
containing both saturated and unsaturated, animal and veg-
and partitioning of constituent fatty acids in the form of
etable, unpolymerized or partially polymerized fatty acids
vaporized methyl esters between a flowing gas phase and a
having 8 to 20 carbon atoms.
supported liquid phase in a gas chromatographic column. The
1.2 Thistestmethodisnotapplicabletoproductscontaining
test method is based on isothermal operation of the gas
fatty acids that have been polymerized or oxidized to such an
chromatograph and a hot wire, thermal conductivity detector.
extent that no characteristic monomeric fatty acids remain.
3.2 The test method consists in the separation of the vehicle
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
from the paint by centrifugation, extraction of fatty acids from
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
the vehicle after saponification, conversion of fatty acids and a
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
measured addition of margaric acid (internal standard) into
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
methyl esters, preparation of the gas chromatogram, and
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
interpretation of the chromatogram. The amount of each
2. Referenced Documents monomeric fatty acid ester is calculated, totaled, subtracted
from100 %toyieldpolymerizedfattyacids,reportedasis,and
2.1 ASTM Standards:
interpreted by comparison with standards as being from
D1398 Test Method for FattyAcid Content ofAlkyd Resins
specific oils or oil acids.
and Alkyd Resin Solutions
D1983 Test Method for Fatty Acid Composition by Gas-
4. Significance and Use
Liquid Chromatography of Methyl Esters
4.1 This test method provides a procedure to identify the
D2372 Practice for Separation of Vehicle From Solvent-
fatty acids present in the vehicle of a paint.
Reducible Paints
5. Apparatus
5.1 Centrifuge, high-speed, capable of developing in excess
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
of 10 000 g.
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.21 on Chemical Analysis of Paints and Paint Materials.
5.2 Separatory Funnels, with PTFE-fluorocarbon stop-
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2005. Published February 2005. Originally
cocks.
approved in 1964. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as D2245 – 90 (1999).
5.3 Gas Chromatograph and Accessories, suitable for
DOI: 10.1520/D2245-90R05.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or analysis of fatty acids as methyl esters (see Test Method
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
D1983).
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
6. Reagent
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
on www.astm.org. 6.1 Hydroquinone.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D2245 – 90 (2005)
7. Calibration and Standardization 8.5 Compare the chromatogram or fatty acid composition,
or both, with the chromatograms or fatty acid compositions, or
7.1 Establish optimum operating conditions on the gas
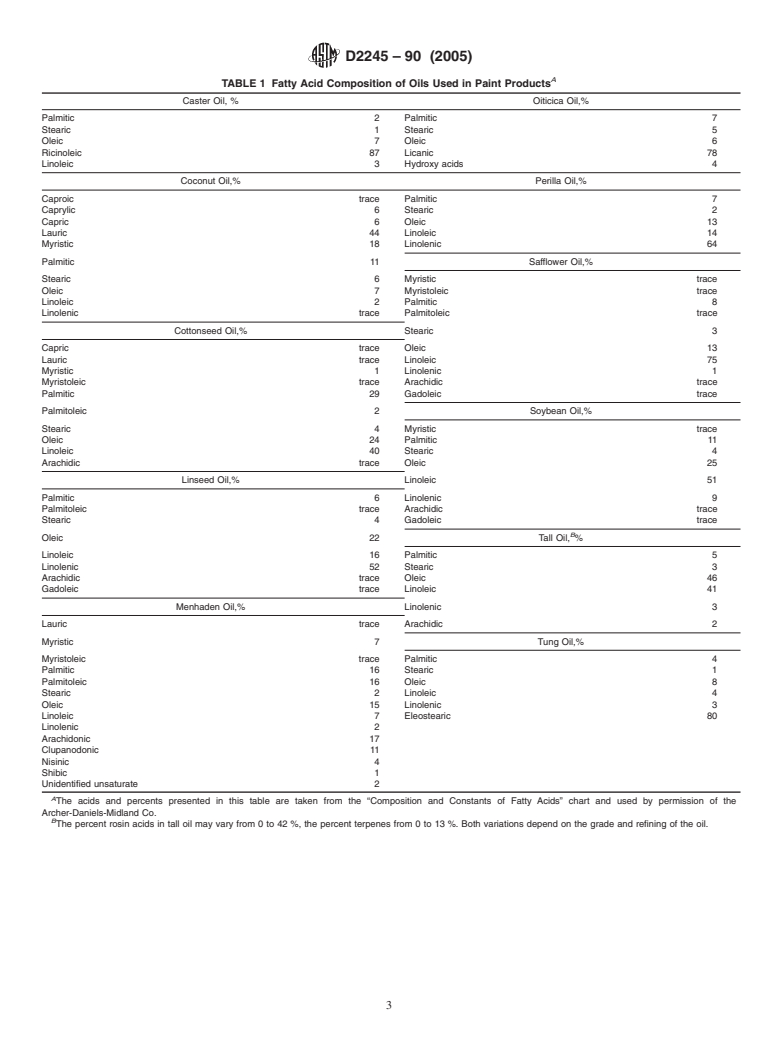
both, of suspected known materials (See Table 1, for typical
chromatograph with known samples of methyl esters as de-
fatty acid compositions of oils used in paint products). Con-
scribed in Test Method D1983.
sider the content of specific fatty acids characteristic of specific
7.2 Prepare working standards by running known paints or
oils. Consider the total saturates versus unsaturates and poly-
vehicles through the procedure described in Section 8. Include
mer content in relation to what the original starting oil or oil
particularly compositions with chemical or structural modifi-
acids might have been.
cations that might be expected to alter the fatty acid distribu-
tion or the apparent polymer content of the starting raw
9. Report
materials.
9.1 Report the type of oil or oil acid when the fatty acid
8. Procedure
distribution approximates a specific known distribution or
combination, when the limit of the possibilities is known and
8.1 Separate the vehicle from the paint by direct high-speed
when the polymer content can be explained. (SeeAppendix X1
centrifuging (see Practice D2372).
for some of the considerations in interpreting the analysis
8.2 Extract the fatty acids from the separated vehicle after
results).
saponification and removal of the dicarboxylate salts and
unsaponifiable matter in accordance with Test Method D1398,
9.2 Even when the identification is positive, it is recom-
but substitute separatory funnels with PTFE-fluorocarbon stop- mendedthattheactualpercentdistributionsofmonomericfatty
cocks when available. In cases involving unsaturated fatty
acids and the polymer content be reported. In very complex
acids, add a crystal or diethyl ether solution of hydroquinone
systems where the possible combinations are too numerous to
(equivalent to less than 0.05 weight % of the fatty acids to the
allow an immediate identification, the percent breakdown
fatty acid fractions obtained in the Procedure Section, Method
figures should be recorded. Considered with other data that
B, of Test Method D1398. Swirl the flask containing the fatty
might subsequently be obtained, the fatty acid and polymer
acids, some ether solvent, and the hydroquinone until the
distribution can be important.
hydroquinone is well dispersed; evaporate off the remaining
ether carefully under vacuum as described in Test Method
10. Precision
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.