ASTM A47/A47M-99(2009)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Ferritic Malleable Iron Castings
Standard Specification for Ferritic Malleable Iron Castings
ABSTRACT
This specification covers ferritic malleable castings for general engineering usage. The castings are classified as Grade 32510. The chemical composition of the iron shall be such as to produce the structural and mechanical properties required by this specification. Tension test may be machined from the standard cast bar to the required dimensions. The microstructure of the malleable iron shall consist of temper carbon nodules distributed through ferritic matrix and shall be free of excessive pearlite, massive carbides, and primary graphite. All castings, on visual examination, shall be sound and free of obvious shrinkage and porosity. The castings shall conform to the dimensions given by this specification.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers ferritic malleable castings for general engineering usage at temperatures from normal ambient to approximately 400°C (750°F).
1.2 No precise quantitative relationship can be stated between the properties of the iron in various locations of the same casting and those of a test specimen cast from the same iron (see Appendix X1).
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A47/A47M −99(Reapproved 2009)
Standard Specification for
1
Ferritic Malleable Iron Castings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A47/A47M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
4
1. Scope 2.2 Military Standard:
2 MIL-STD-129Marking for Shipment and Storage
1.1 This specification covers ferritic malleable castings for
4
2.3 Federal Standard:
general engineering usage at temperatures from normal ambi-
Fed. Std. No. 123Marking for Domestic Shipment (Civilian
ent to approximately 400°C (750°F).
Agencies)
1.2 No precise quantitative relationship can be stated be-
tweenthepropertiesoftheironinvariouslocationsofthesame 3. Terminology
casting and those of a test specimen cast from the same iron
3.1 Definitions—Definitions for many terms common to
(see Appendix X1).
iron are found in Terminology A644.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
4. Classification
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
4.1 Castings ordered and produced under this specification
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining are classified under the following grades based on tests on
separately cast test bars. Separately cast test bars shall be
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
with the standard. poured from the same lot of iron as the castings they represent
andshallbeheattreatedwiththosecastingsexceptasprovided
2. Referenced Documents
in 7.2.3.
3 4.1.1 Grade 32510 [Grade 22010]:
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.1.1.1 The first three digits of the grade designation indi-
A153/A153MSpecification for Zinc Coating (Hot-Dip) on
cate the minimum yield strength (×100 psi [MPa]) and the last
Iron and Steel Hardware
two digits indicate the minimum elongation (% in 2 in. [50
A247Test Method for Evaluating the Microstructure of
mm]).
Graphite in Iron Castings
A644Terminology Relating to Iron Castings
5. Ordering Information
E8Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
5.1 The purchase order for castings ordered under this
E10Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
specification shall state the specification designation, the year
E18Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Ma-
in which the specification was issued, and the grade of
terials
malleable iron to be supplied. Any option or special additions
E140Hardness Conversion Tables for Metals Relationship
to the basic requirements of this specification shall be clearly
Among Brinell Hardness, Vickers Hardness, Rockwell
and fully stipulated.
Hardness, Superficial Hardness, Knoop Hardness, and
Scleroscope Hardness
6. Chemical Composition
6.1 Thechemicalcompositionoftheironshallbesuchasto
produce the structural and mechanical properties required by
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A04 on Iron
this specification.
Castings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A04.02 on Malleable and
Ductile Iron Castings.
7. Mechanical Properties
Current edition approved May 1, 2009. Published August 2009. Originally
approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as A47/A47M–99
7.1 Factors influencing the properties of castings and their
(2004). DOI: 10.1520/A0047_A0047M-99R09.
2
relationship to those of test specimens and separate test
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specifi-
cation SA-47 in Section II of that code.
castings are discussed in Appendix X1.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
the ASTM website. Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A47/A47M−99 (2009)
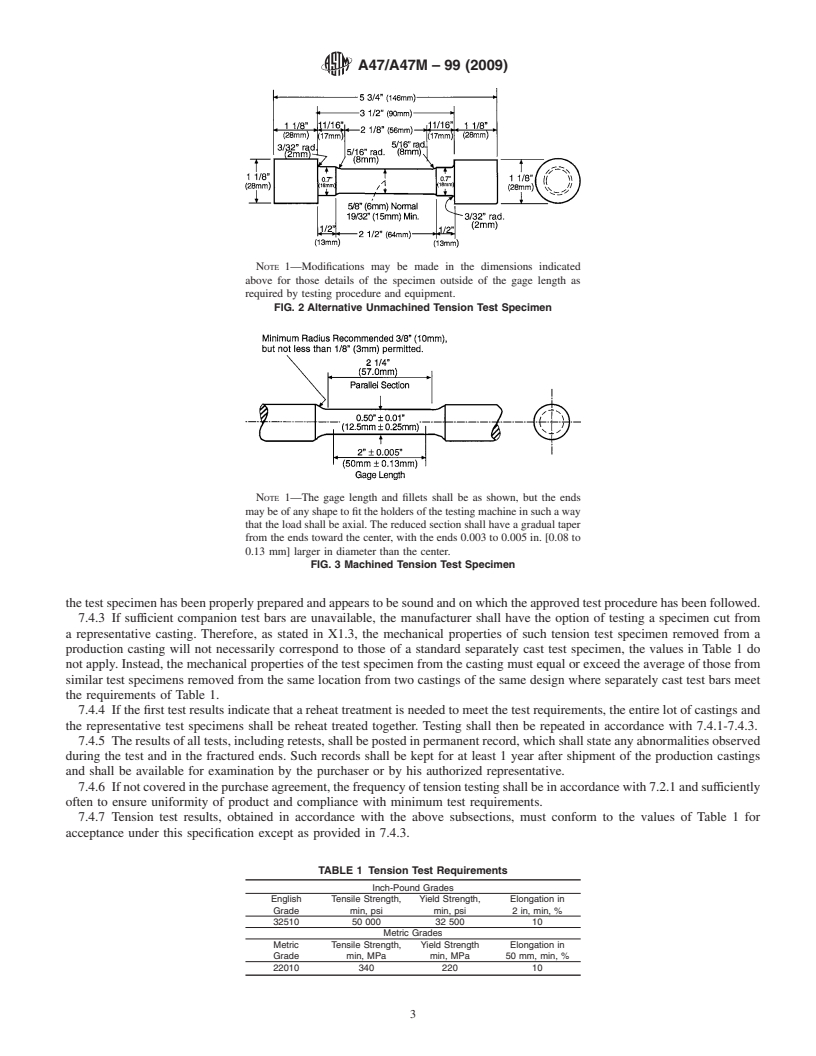
7.2 Tension Test Specimens:
7.2.1 The tension test specimens shall be cast to the form
and dimensions shown in Fig. 1 or Fig. 2, in the same kind of
molding material used for the production castings. At least
three such specimens shall be cast from a representative ladle
of iron either from each batch-melted heat or, in continuous
melting, from each 4-h pour period during which the purchas-
er’s castings were poured, or as otherwise agreed upon
between manufact
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:A 47/A 47M–99 (Reapproved 2004) Designation: A47/A47M – 99
(Reapproved 2009)
Standard Specification for
1
Ferritic Malleable Iron Castings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A47/A47M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
2
1.1 This specification covers ferritic malleable castings for general engineering usage at temperatures from normal ambient to
approximately 400°C (750°F).
1.2 No precise quantitative relationship can be stated between the properties of the iron in various locations of the same casting
and those of a test specimen cast from the same iron (see Appendix X1).
1.3 The values stated in either inch-poundSI units or SIinch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the
text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system aremay not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system
shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the
specification. standard.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A153153/A153M Specification for Zinc Coating (Hot-Dip) on Iron and Steel Hardware
A247 Test Method for Evaluating the Microstructure of Graphite in Iron Castings
A644 Terminology Relating to Iron Castings
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness and Rockwell Superficial Hardness of Metallic MaterialsTest Methods for Rockwell
Hardness of Metallic Materials
E140 Hardness Conversion Tables for Metals Relationship Among Brinell Hardness, Vickers Hardness, Rockwell Hardness,
Superficial Hardness, Knoop Hardness, and Scleroscope Hardness
4
2.2 Military Standard:
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
4
2.3 Federal Standard:
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Domestic Shipment (Civilian Agencies)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions for many terms common to iron are found in Terminology A 644.A644.
4. Classification
4.1 Castingsorderedandproducedunderthisspecificationareclassifiedunderthefollowinggradesbasedontestsonseparately
cast test bars. Separately cast test bars shall be poured from the same lot of iron as the castings they represent and shall be heat
treated with those castings except as provided in 7.2.3.
4.1.1 Grade 32510 [Grade 22010]:
4.1.1.1 The first three digits of the grade designation indicate the minimum yield strength (3100 psi [MPa]) and the last two
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM CommitteeA04 on Iron Castings and is the direct responsibility of SubcommitteeA04.02 on Malleable and Ductile
Iron Castings.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2004. Published October 2004. Originally approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as A 47/A 47M–99.
Current edition approved May 1, 2009. Published August 2009. Originally approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as A47/A47M – 99 (2004). DOI:
10.1520/A0047_A0047M-99R09.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specification SA-47 in Section II of that code.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4, Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A47/A47M – 99 (2009)
digits indicate the minimum elongation (% in 2 in. [50 mm]).
5. Ordering Information
5.1 The purchase order for castings ordered under this specification shall state the specification designation, the year in which
the specification was issued, and the grade of malleable iron to be supplied. Any option or special additions to the basic
requirements of this specification shall be clearly and fully stipulated.
6. Chemical Composition
6.1 The chemical composition of the iron shall be such as to produce the structural and mechanical properties required by
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.