ASTM C16-03
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Load Testing Refractory Shapes at High Temperatures
Standard Test Method for Load Testing Refractory Shapes at High Temperatures
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the resistance to deformation or shear of refractory shapes when subjected to a specified compressive load at a specified temperature for a specified time.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C 16 – 03
Standard Test Method for
1
Load Testing Refractory Shapes at High Temperatures
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationC16;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope to the loading direction. Occasionally, shear fracture can occur.
Since the test provides easily measurable changes in dimen-
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the resis-
sions, prescribed limits can be established, and the test method
tance to deformation or shear of refractory shapes when
has been long used to determine refractory quality. The test
subjected to a specified compressive load at a specified
method has often been used in the establishment of written
temperature for a specified time.
specifications between producers and consumers.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3.2 This test method is not applicable for refractory mate-
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
rials that are unstable in an oxidizing atmosphere unless means
information only.
are provided to protect the specimens.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
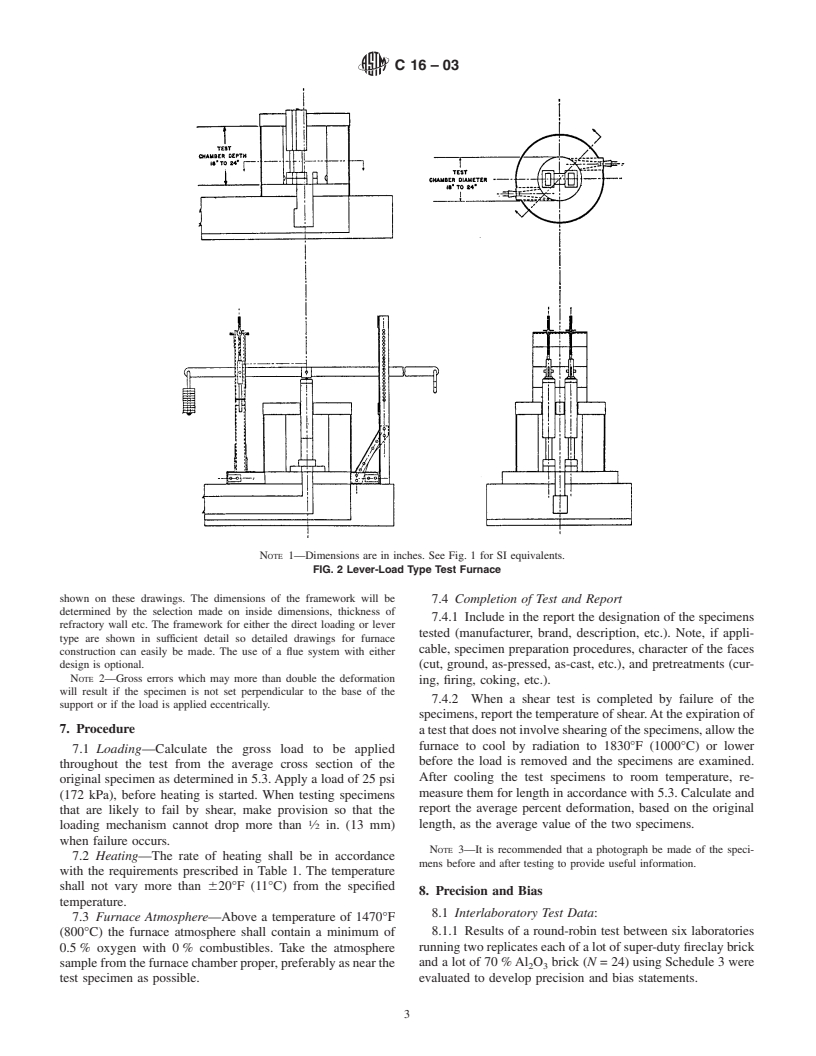
4. Apparatus
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 The apparatus shall consist essentially of a furnace and
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
a loading device. It may be constructed in accordance with Fig.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3
1 or Fig. 2 or their equivalent.
2. Referenced Documents 4.1.1 The furnace shall be so constructed that the tempera-
2
ture is substantially uniform in all parts of the furnace. The
2.1 ASTM Standards:
temperature as measured at any point on the surface of the test
C 862 Practice for Preparing Refractory Concrete Speci-
specimens shall not differ by more than 10°F (5.5°C) during
mens by Casting
the holding period of the test or, on test to failure, above
E 220 Method for Calibration of Thermocouples by Com-
2370°F (1300°C). To accomplish this, it may be necessary to
parison Techniques
install and adjust baffles within the furnace.Aminimum of two
3. Significance and Use burners shall be used. If difficulty is encountered in following
the low-temperature portion of the schedule (particularly for
3.1 The ability of a refractory shapes to withstand pre-
silica brick), a dual-burner system is recommended, one to
scribed loads at elevated temperatures is a measure of the
supply heat for low temperatures and another for the higher
high-temperature service potential of the material. By defini-
temperatures.
tion, refractory shapes must resist change due to high tempera-
4.2 The temperature shall be measured either with cali-
ture; and the ability to withstand deformation or shape change
, ,
4 5 6
brated platinum - platinum - rhodium thermocouples, each
when subjected to significant loading at elevated temperatures
encased in a protection tube with the junction not more than 1
isclearlydemonstratedwhenrefractoryshapesaresubjectedto
in. (25 mm) from the center of the side or edge of each
this test method.The test method is normally run at sufficiently
4,5,6
specimen or with a calibrated pyrometer.Arecording form
high temperature to allow some liquids to form within the test
of temperature indicator is recommended. If the optical pyrom-
brick or to cause weakening of the bonding system. The result
eter is used, observations shall be made by sighting on the face
is usually a decrease in sample dimension parallel to the
applied load and increase in sample dimensions perpendicular
3
Blueprints of detailed drawings of the furnaces shown in Figs. 1 and 2 are
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C08 on available from ASTM International. Request ADJC0016.
4
Refractories and is the direct responsibility of Subcommiteee C08.01on Strength. Method E 220 specifies calibration procedures for thermocouples.
5
Current edition approved Nov 1, 2003. Published November 2003. Originally The National Institutes of Standards andTechnology, Gaithersburg, MD 20899,
approved in 1917. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as C 16 – 02. will, for a fee, furnish calibrations for radiation-type pyrometers and for thermo-
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or couples.
6
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM All temperatures specified in this test conform to the International Practical
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Temperature Scale of 1968 (
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.