ASTM A395/A395M-99(2014)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Ferritic Ductile Iron Pressure-Retaining Castings for Use at Elevated Temperatures
Standard Specification for Ferritic Ductile Iron Pressure-Retaining Castings for Use at Elevated Temperatures
ABSTRACT
This specification covers standard requirements for ductile iron castings for pressure-retaining parts for use at elevated temperatures. Castings are classified by grades based on mechanical property requirements. These iron castings shall meet the specified values of tensile strength, yield strength, elongation and hardness. Chemical analysis shall be performed wherein the casting shall conform to the required chemical composition for carbon, silicon, and phosphorous. The material shall meet the required tensile properties, hardness, and microstructure. The iron casting shall undergo pressure test after machining. The thickness of any repaired section in relation to the size of the plug used shall be indicated. The minimum radius of repaired sections of cylinders or cones in relation to the size of plug used shall not exceed the prescribed limit. Other defective areas may also be repaired by plugging provided the minimum ligament between plugs in adjacent areas shall not be less than twice the distance from the nearest plug. Three Y-blocks shall be utilized as test coupons. The material shall undergo the following test methods: tension test, chemical analysis, yield strength test, and hardness test.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers ductile iron castings for pressure-retaining parts for use at elevated temperatures. Castings of all grades are suitable for use up to 450°F. For temperatures above 450°F and up to 650°F, only Grade 60–40–18 castings are suitable (Note 1).
1.2 Valves, flanges, pipe fittings, pumps, and other piping components are generally manufactured in advance and supplied from stock by the manufacturer, jobber, or dealer.
1.3 For supplemental casting requirements, Specification A834 may be utilized.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.Note 1—For service other than as specified in this section, reference should be made to Specification A536 for Ductile Iron Castings.2
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A395/A395M −99 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Specification for
Ferritic Ductile Iron Pressure-Retaining Castings for Use at
1
Elevated Temperatures
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA395/A395M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope A834 Specification for Common Requirements for Iron
Castings for General Industrial Use
1.1 This specification covers ductile iron castings for
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
pressure-retaining parts for use at elevated temperatures. Cast-
E10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials
ings of all grades are suitable for use up to 450°F. For
1
E186 Reference Radiographs for Heavy-Walled (2 to 4 ⁄2-in.
temperatures above 450°F and up to 650°F, only Grade
(50.8 to 114-mm)) Steel Castings
60–40–18 castings are suitable (Note 1).
1
E280 Reference Radiographs for Heavy-Walled (4 ⁄2 to 12-
1.2 Valves, flanges, pipe fittings, pumps, and other piping
in. (114 to 305-mm)) Steel Castings
components are generally manufactured in advance and sup-
E446 Reference Radiographs for Steel Castings Up to 2 in.
plied from stock by the manufacturer, jobber, or dealer.
(50.8 mm) in Thickness
1.3 For supplemental casting requirements, Specification E689 Reference Radiographs for Ductile Iron Castings
E1806 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determina-
A834 may be utilized.
tion of Chemical Composition
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
F1476 Specification for Performance of Gasketed Mechani-
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
cal Couplings for Use in Piping Applications
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
F1548 SpecificationforPerformanceofFittingsforUsewith
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
Gasketed Mechanical Couplings Used in Piping Applica-
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
tions
with the standard.
2.2 Manufacturer’sStandardizationSocietyoftheValveand
3
NOTE 1—For service other than as specified in this section, reference
Fittings Industry Standard:
2
should be made to Specification A536 for Ductile Iron Castings.
SP 25 Standard Marking Systems for Valves, Flanges, Pipe
Fittings, and Unions
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3. Classification
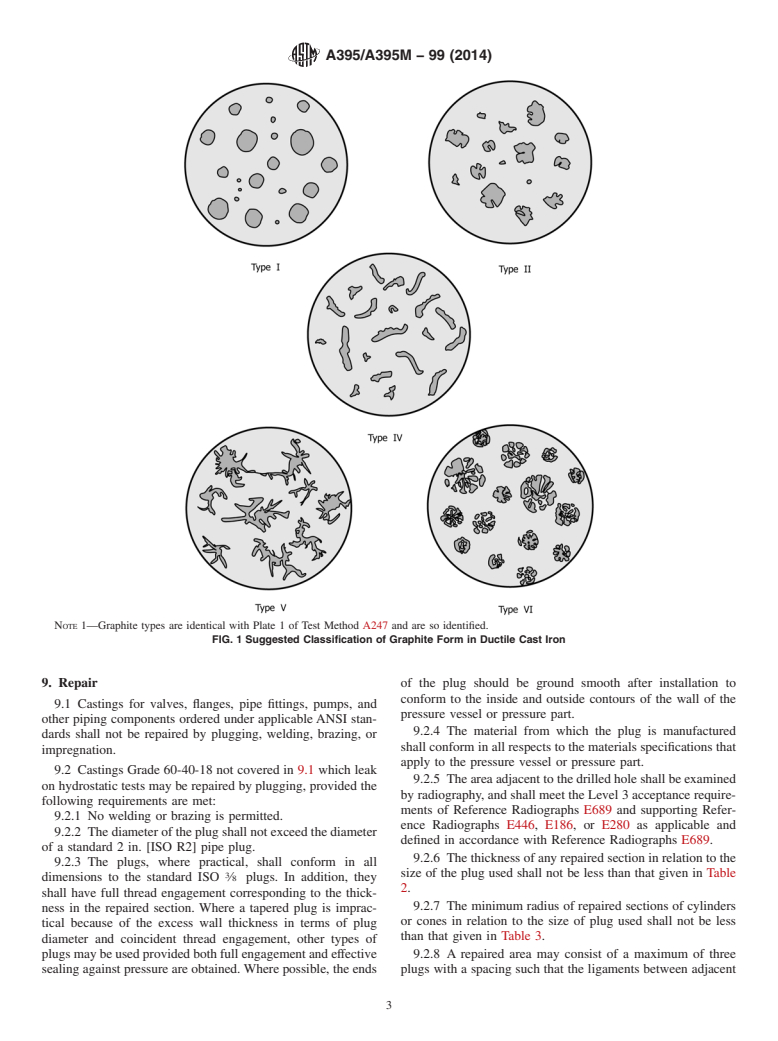
A247 Test Method for Evaluating the Microstructure of
3.1 Castings ordered to this specification are classified by
Graphite in Iron Castings
grades based on mechanical property requirements, as listed in
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
Table 1. See note following Table 1.
of Steel Products
A536 Specification for Ductile Iron Castings
4. Ordering Information
A732/A732M Specification for Castings, Investment, Car-
4.1 Orders for material under this specification shall include
bon and Low Alloy Steel for General Application, and
the following applicable information:
Cobalt Alloy for High Strength at Elevated Temperatures
4.1.1 Drawing, catalog number, or part identifications,
4.1.1.1 For grade 65-45-15, drawing indicating critical ar-
ea(s) of casting (see 7.2.2 and 7.3.2).
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A04 on Iron
4.1.2 Quantity (weight or number of pieces),
Castings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A04.02 on Malleable and
Ductile Iron Castings.
4.1.3 ASTM designation and year of issue,
Current edition approved April 1, 2014. Published April 2014. Originally
4.1.4 Grade (See Table 1), if a Grade is not specified, the
approved in 1955. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as A395/A395M – 99
manufacturer shall supply grade 60-40-18.
(2009). DOI: 10.1520/A0395_A0395M-99R14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on AvailablefromManufacturersStandardizationSocietyoftheValveandFittings
the ASTM website. Industry (MSS), 127 Park St., NE,Vienna,VA22180-4602, http://www.mss-hq.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A395/A395M − 99 (2014)
TABLE 1 Mechanical Property Requirements
7.1.1 The ductile iron as represented by the test specimens
Property Grade 60-40-18 Grade 65-45-15 shallconformtothemechanicalpropertyrequirementsinTable
Tensile Strength Minimum, psi [MPa] 60 000
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.