ASTM F1469-99(2004)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Conducting a Repeatability and Reproducibility Study on Test Equipment for Nondestructive Testing
Standard Guide for Conducting a Repeatability and Reproducibility Study on Test Equipment for Nondestructive Testing
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This guide is recommended for the purpose of evaluating test equipment that may be utilized in statistical process control, testing laboratories, and for in-process control of manufacturing operations.
Ask the question: What effect does the operator have on the measurement process? If possible, the operators who normally use the test equipment should be included in the study. If operator calibration of the equipment is likely to be a significant cause of variation, then the operator should recalibrate the equipment prior to each group of readings.
The test equipment should provide direct readings in which the smallest digit is no larger than one tenth of the tolerance of the characteristic being evaluated.
It is recommended that a test equipment repeatability and reproducibility study be a mandatory part of all test equipment purchases and that acceptance criteria be 10 % for certification and statistical process control (SPC) use.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide describes the steps required to conduct a complete repeatability and reproducibility (RR) study on nondestructive test equipment. This guide is a manual (use of calculator) method. Other methods may utilize the application of computer driven software.
1.2 This guide can be used to evaluate all test equipment that provides variable measuring data.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F1469–99(Reapproved 2004)
Standard Guide for
Conducting a Repeatability and Reproducibility Study on
Test Equipment for Nondestructive Testing
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1469; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope equipment purchases and that acceptance criteria be <10 % for
certification and statistical process control (SPC) use.
1.1 This guide describes the steps required to conduct a
complete repeatability and reproducibility (RR) study on
4. Equipment Certification
nondestructive test equipment. This guide is a manual (use of
4.1 Test equipment shall be certified through use of certified
calculator) method. Other methods may utilize the application
standards as accurate to the manufacturer’s/user’s calibration
of computer driven software.
systems with certified standards before a repeatability and
1.2 This guide can be used to evaluate all test equipment
reproducibility study is performed.
that provides variable measuring data.
4.2 Certifications must be traceable to the National Institute
2. Terminology of Standards and Technology (NIST), or recognized equiva-
lent, and shall be current to the test equipment’s calibration
2.1 Definitions:
schedule.
2.1.1 repeatability—variation in the values of measure-
ments obtained when one operator uses the same gage for
5. Procedure
measuring identical characteristics of the same parts.
5.1 Although the number of operators, trials, and parts may
2.1.2 reproducibility—variation in the average of measure-
be varied, the following guidelines represent the optimum
ments made by different operators using the same parts.
conditions for conducting a study using the forms in Figs. 1
3. Significance and Use and 2.
5.2 Select three operators and identify them as Operators A,
3.1 This guide is recommended for the purpose of evaluat-
B, and C.
ing test equipment that may be utilized in statistical process
5.3 Calibrate the test equipment with a certified standard.
control, testing laboratories, and for in-process control of
5.4 Select ten parts for measurements and number them
manufacturing operations.
from 1 to 10, such that the numbers, if possible, are not visible
3.2 Ask the question: What effect does the operator have on
to the operator. Place a mark on each part to indicate the
the measurement process? If possible, the operators who
precise position at which the part shall be measured. This
normally use the test equipment should be included in the
eliminates the variation within the part from the study results
study. If operator calibration of the equipment is likely to be a
so that only the gage’s performance and operator variation
significant cause of variation, then the operator should recali-
influences the study outcome.
brate the equipment prior to each group of readings.
5.5 Allow Operator A to inspect all ten parts in a sequential
3.3 The test equipment should provide direct readings in
order by measuring each part at the designated location. Enter
which the smallest digit is no larger than one tenth of the
the results in the 1st trial column for Operator A of the
tolerance of the characteristic being evaluated.
Repeatability and Reproducibility Data Sheet (Fig. 1). Part
3.4 It is recommended that a test equipment repeatability
identification and associated data entry shall be performed by
and reproducibility study be a mandatory part of all test
an observer.
5.6 Repeat 5.5 with Operators B and C and enter the results
in the corresponding 1st trial column for each operator.
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F16 on Fasteners and
isthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeF16.93onQualityAssuranceProvisions
5.7 Repeat 5.5 and 5.6 using a random selection of the ten
for Fasteners.
parts. Enter data in the 2nd trial column for each operator. If
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2004. Published November 2004. Originally
three trials are needed, repeat the cycle and enter data in the
approved in 1993. Last previous e
...







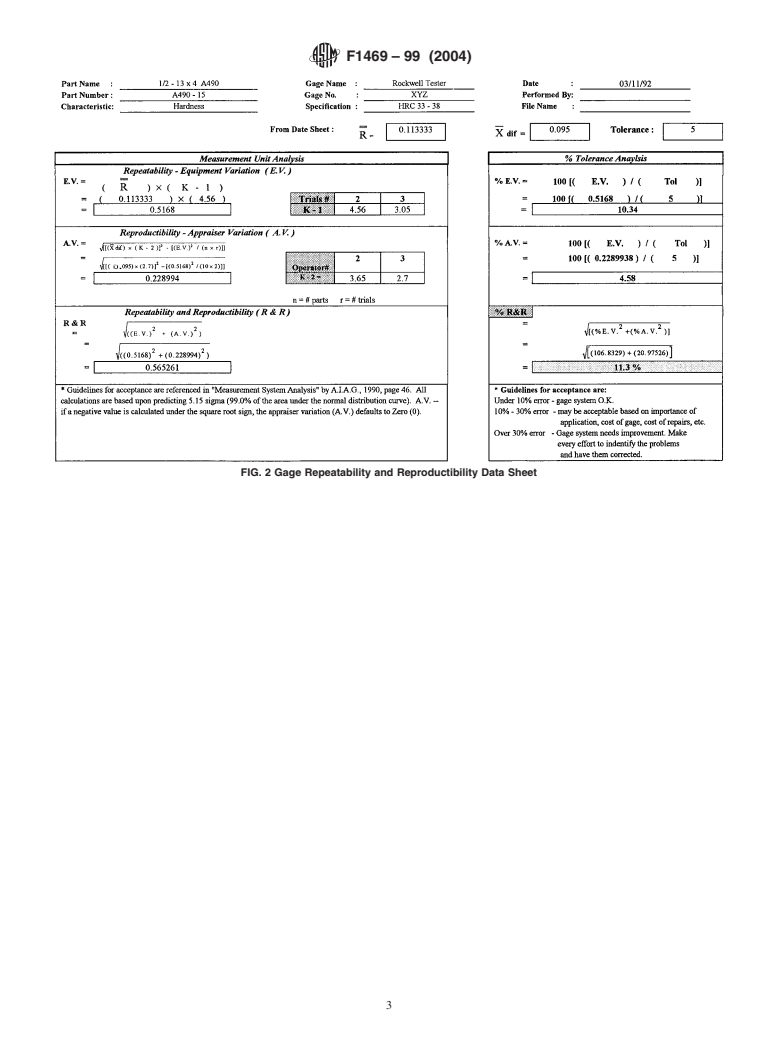
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.